Multiplying Decimals
... the sum of the number of decimal places in the factors (numbers being multiplied). Numbers ...
... the sum of the number of decimal places in the factors (numbers being multiplied). Numbers ...
Math 7 - TeacherWeb
... 5 L = _____?____ kL Start at Over and move to the left as kL are larger than L. (Think of O as original unit) We moved 3 places. 5 L = .005 kL CAUTION: Remember all whole numbers have a decimal point ...
... 5 L = _____?____ kL Start at Over and move to the left as kL are larger than L. (Think of O as original unit) We moved 3 places. 5 L = .005 kL CAUTION: Remember all whole numbers have a decimal point ...
(aligned with the 2014 National Curriculum)
... Recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 times tables (up to the 12th multiple) Find all factor pairs of a given number; find all common factors for a pair of numbers Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts e.g. 7 x 8 = 56; 7 x ...
... Recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 times tables (up to the 12th multiple) Find all factor pairs of a given number; find all common factors for a pair of numbers Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts e.g. 7 x 8 = 56; 7 x ...
Lesson 2, Section 1
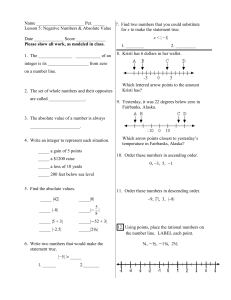
... 1. Multiply or Divide the absolute values. 2. If the two numbers have the ‘same’ sign, the answer is positive. 3. If the two numbers have ‘different’ signs, the answer is negative. 4. If there are more than two numbers, count the number of negatives. If odd, the answer is negative; if even, the answ ...
... 1. Multiply or Divide the absolute values. 2. If the two numbers have the ‘same’ sign, the answer is positive. 3. If the two numbers have ‘different’ signs, the answer is negative. 4. If there are more than two numbers, count the number of negatives. If odd, the answer is negative; if even, the answ ...
Writing
... Students multiply by powers of 10, link division by powers of 10 to multiplication by decimals and use these in estimation. They know that the position of the digit zero affects the size of numbers, such as 00.070 = 0.07. They explain dividing by a number between one and zero, such as dividing by 0. ...
... Students multiply by powers of 10, link division by powers of 10 to multiplication by decimals and use these in estimation. They know that the position of the digit zero affects the size of numbers, such as 00.070 = 0.07. They explain dividing by a number between one and zero, such as dividing by 0. ...
NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS
... •Count on from a given number (other than 1) within the known sequence to 100. •Count up to 20 objects with 1-1 correspondence. •Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group with quantities up to 20. •Compare two n ...
... •Count on from a given number (other than 1) within the known sequence to 100. •Count up to 20 objects with 1-1 correspondence. •Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group with quantities up to 20. •Compare two n ...
Introduction to Whole Numbers and Integers
... Numbers can be used for many different purposes. The cost of a house is a number that mathematics can be performed on to obtain some new amount. For example: Vendor wants a quick sale, was $500 000, now ...
... Numbers can be used for many different purposes. The cost of a house is a number that mathematics can be performed on to obtain some new amount. For example: Vendor wants a quick sale, was $500 000, now ...