Questions
... triangles by lines drawn from the vertices through a common interior point. The areas of four of these triangles are as indicated. Find the area of triangle ABC. ...
... triangles by lines drawn from the vertices through a common interior point. The areas of four of these triangles are as indicated. Find the area of triangle ABC. ...
THE SIZE OF PRIME
... For most prime bases the above conditions assure that a large percentage of generalized Cullen numbers have small prime factors. For example, for b = 31, these conditions cause 94 out of the first 100 numbers to have small factors. The first value of N for which C31 N does not have a factor less ...
... For most prime bases the above conditions assure that a large percentage of generalized Cullen numbers have small prime factors. For example, for b = 31, these conditions cause 94 out of the first 100 numbers to have small factors. The first value of N for which C31 N does not have a factor less ...
Calculating with Significant Figures
... 2. Round up if the digit to be removed is 5 or greater. Rounding to two significant figures, 1.36 becomes 1.4 and 3.15 becomes 3.2. ...
... 2. Round up if the digit to be removed is 5 or greater. Rounding to two significant figures, 1.36 becomes 1.4 and 3.15 becomes 3.2. ...
PDF
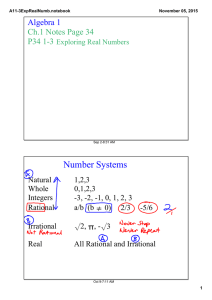
... (when the number is reduced to lowest terms) is odd. This is because if the exponent is a fraction with an even denominator (such as ½), the exponent indicates an even root. An even root of a negative number does not give a real result. If we restrict the domains of x, m, and n to the real numbers, ...
... (when the number is reduced to lowest terms) is odd. This is because if the exponent is a fraction with an even denominator (such as ½), the exponent indicates an even root. An even root of a negative number does not give a real result. If we restrict the domains of x, m, and n to the real numbers, ...