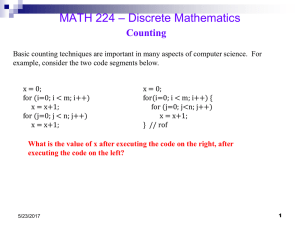
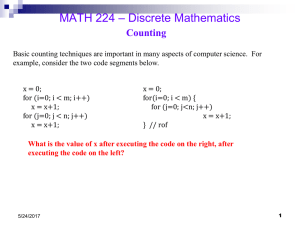
Permutations+Combina..
... Combinations count the number of ways of choosing r objects from a set of n objects r-choose n, where order doesn’t count. So C(n, r) = P(n, r)/r!. Here we divide by the number of ways of ordering r objects. ...
... Combinations count the number of ways of choosing r objects from a set of n objects r-choose n, where order doesn’t count. So C(n, r) = P(n, r)/r!. Here we divide by the number of ways of ordering r objects. ...
I_can_maths_sheet_y2_expected
... Count forward in steps of 2, 3, 10 and 5 from any number up to 100. Count backward in steps of 2, 3, 10 and 5 from any number near to 100. Order at least three numbers both increasing and decreasing from 0 up to 100 using <, > and = Partition numbers (tens, ones) and use this to solve missing number ...
... Count forward in steps of 2, 3, 10 and 5 from any number up to 100. Count backward in steps of 2, 3, 10 and 5 from any number near to 100. Order at least three numbers both increasing and decreasing from 0 up to 100 using <, > and = Partition numbers (tens, ones) and use this to solve missing number ...
UNIT 1: DIVISIBILITY. INTEGERS NUMBERS. REVIEW 2ºESO
... 3. Write a number with 4 digits, divisible by both of the followings numbers: a. ...
... 3. Write a number with 4 digits, divisible by both of the followings numbers: a. ...