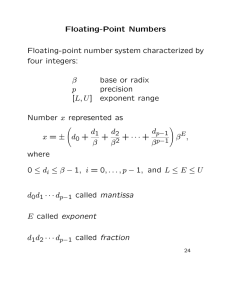
Floating-Point Numbers
... • NaN, which stands for “not a number,” results from undefined or indeterminate operations such as 0/0, 0 ∗ Inf, or Inf/Inf Inf and NaN implemented in IEEE arithmetic through special reserved values of exponent ...
... • NaN, which stands for “not a number,” results from undefined or indeterminate operations such as 0/0, 0 ∗ Inf, or Inf/Inf Inf and NaN implemented in IEEE arithmetic through special reserved values of exponent ...
Real numbers, chaos, and the principle of a bounded density
... For instance, consider N iterations s0 , ..., sN of the baker’s transformation, perturbed by a sequence p0 , p1 , ..., such that for all i, |pi | ≤ ε and si is between 0 and 1. Then it is easy to prove, by decreasing induction on i, that for all i, there exists a element s0i , such that |s0i − si | ...
... For instance, consider N iterations s0 , ..., sN of the baker’s transformation, perturbed by a sequence p0 , p1 , ..., such that for all i, |pi | ≤ ε and si is between 0 and 1. Then it is easy to prove, by decreasing induction on i, that for all i, there exists a element s0i , such that |s0i − si | ...
12 - NCETM
... Cancelling fractions to their lowest terms A fraction is said to be expressed in its lowest terms if the numerator and the denominator have no common factors. Which of these fractions are expressed in their lowest terms? ...
... Cancelling fractions to their lowest terms A fraction is said to be expressed in its lowest terms if the numerator and the denominator have no common factors. Which of these fractions are expressed in their lowest terms? ...
HOMEWORK 11.1 #`s 1-9
... Some problems have more than one case. One way to solve such problems is to establish cases that together cover all of the possibilities. Calculate the number of arrangements for each case and then add the values for all cases to obtain the total number of arrangements. e.g. Determine the number of ...
... Some problems have more than one case. One way to solve such problems is to establish cases that together cover all of the possibilities. Calculate the number of arrangements for each case and then add the values for all cases to obtain the total number of arrangements. e.g. Determine the number of ...