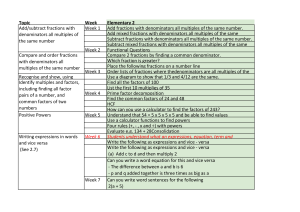
Factors, Fractions and Exponents
... • E.g., Simplify 6(4 + 3)2. First, do the operation within the parenthesis. We get 6(7)2. Second, do the exponent. Since 7 x 7 = 49, we get 6(49). Now multiply 6(49) = 294. – BTW: I multiplied 6(49) in my head by using the distributive property. 6(50 – 1) = 6(50) – 6(1) = 300 – 6 = 294. ...
... • E.g., Simplify 6(4 + 3)2. First, do the operation within the parenthesis. We get 6(7)2. Second, do the exponent. Since 7 x 7 = 49, we get 6(49). Now multiply 6(49) = 294. – BTW: I multiplied 6(49) in my head by using the distributive property. 6(50 – 1) = 6(50) – 6(1) = 300 – 6 = 294. ...
Standards from the NF Domain Calling for Word
... d. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. 4.NF.4 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a ...
... d. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. 4.NF.4 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a ...
Standard Index Form
... Standard Form without a Calculator To do calculations in standard form without a calculator you need to deal with the numbers and powers of 10 separately, applying the rules of indices. Example 1: Calculate 4.2 x 108 x 9 x 105 = 4.2 x 9 x 108 x 105 = 37.8 x 1013 = 3.78 x 101 x 1013 ...
... Standard Form without a Calculator To do calculations in standard form without a calculator you need to deal with the numbers and powers of 10 separately, applying the rules of indices. Example 1: Calculate 4.2 x 108 x 9 x 105 = 4.2 x 9 x 108 x 105 = 37.8 x 1013 = 3.78 x 101 x 1013 ...
Document
... should already know (all answers are even numbers). 4 times table is double the two times table (all answers are even numbers). 8 times table is double the four times table (if they can double two digit numbers quickly in their head this is a useful skill) (all answers are even numbers). 6 times tab ...
... should already know (all answers are even numbers). 4 times table is double the two times table (all answers are even numbers). 8 times table is double the four times table (if they can double two digit numbers quickly in their head this is a useful skill) (all answers are even numbers). 6 times tab ...
pptx
... A nibble (4 bits) ranges in value from 0…15, which is one hex digit – Range: 0000…1111 (binary) => 0x0 …0xF (hex) => 0…f ...
... A nibble (4 bits) ranges in value from 0…15, which is one hex digit – Range: 0000…1111 (binary) => 0x0 …0xF (hex) => 0…f ...
fract2
... overall geometric form and structure repeat at various scales they provide us with a “glimpse” into the wonderful way in which nature and mathematics meet. • Fractals often arise when investigating numerical solutions of differential (and other equations). … go to XAOS ...
... overall geometric form and structure repeat at various scales they provide us with a “glimpse” into the wonderful way in which nature and mathematics meet. • Fractals often arise when investigating numerical solutions of differential (and other equations). … go to XAOS ...
1 - MoodLearn
... 1. Subtract largest power of two less than or equal to number. 2. Put a one in the corresponding bit position. 3. Keep subtracting until result is zero. 4. Bits that haven't been filled – fill with zeros ...
... 1. Subtract largest power of two less than or equal to number. 2. Put a one in the corresponding bit position. 3. Keep subtracting until result is zero. 4. Bits that haven't been filled – fill with zeros ...
TX_G6_PerformanceTask_U1_TE
... All ___________________________ are also integers and rational numbers. All integers are also ___________________________ numbers. Not all ___________________________ are integers or whole numbers. Original content Copyright © by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Additions and changes to the original conte ...
... All ___________________________ are also integers and rational numbers. All integers are also ___________________________ numbers. Not all ___________________________ are integers or whole numbers. Original content Copyright © by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Additions and changes to the original conte ...
Name - Butler Area School District
... Numerator in a fraction is the top number or the number of equal parts you are talking about. ...
... Numerator in a fraction is the top number or the number of equal parts you are talking about. ...