EX - Uplift North Hills Prep
... EX: For a star, state the meaning of the following terms: (a) (i) Luminosity (ii) Apparent brightness (i) The luminosity is the total power emitted by the star. (ii) The apparent brightness is the incident power per unit area received at the surface of the Earth. (b) The spectrum and temperature of ...
... EX: For a star, state the meaning of the following terms: (a) (i) Luminosity (ii) Apparent brightness (i) The luminosity is the total power emitted by the star. (ii) The apparent brightness is the incident power per unit area received at the surface of the Earth. (b) The spectrum and temperature of ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... (d) [None of the above.] 27. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. (c) it is redshifted. (d) it is blueshifted. 28. What is the second most abundant chemical element in the main sequenc ...
... (d) [None of the above.] 27. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. (c) it is redshifted. (d) it is blueshifted. 28. What is the second most abundant chemical element in the main sequenc ...
How Close is our Nearest Neighbor
... galaxies that are members of the Local Group. To determine the distance to our nearest neighboring galaxies requires a clever astronomy experiment. When Shapley did his experiment, he had to measure the distances to globular clusters. To do this, he used Henrietta Leavitt’s discovery that certain va ...
... galaxies that are members of the Local Group. To determine the distance to our nearest neighboring galaxies requires a clever astronomy experiment. When Shapley did his experiment, he had to measure the distances to globular clusters. To do this, he used Henrietta Leavitt’s discovery that certain va ...
Galaxy Formation and Evolution Open Problems
... Helmi, White & Springel (2002, astro-ph/0201289) rescaled of a factor 10 the Springel’s simulation in order to study the evolution of CMD galactic halo and investigate the kinematics of CMD streams in the solar neighborhood. * Note: baryonic - CDM interactions (e.g. central bar) have been neglected. ...
... Helmi, White & Springel (2002, astro-ph/0201289) rescaled of a factor 10 the Springel’s simulation in order to study the evolution of CMD galactic halo and investigate the kinematics of CMD streams in the solar neighborhood. * Note: baryonic - CDM interactions (e.g. central bar) have been neglected. ...
The Lives of Stars
... formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are mov ...
... formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are mov ...
High molecular gas fractions in normal massive star
... D. Lutz1, T. Naab8, A. Omont11, A. Shapley12, A. Sternberg13 & B. Weiner4 ...
... D. Lutz1, T. Naab8, A. Omont11, A. Shapley12, A. Sternberg13 & B. Weiner4 ...
The Sun: Example of Radiation Laws
... Neutron Stars and Black Holes • If matter is forced to even higher densities than in a white dwarf, 106 times that of water, it collapses but could stabilize to form a neutron star with aid of additional pressure from nucleon degeneracy and the strong nuclear force. ...
... Neutron Stars and Black Holes • If matter is forced to even higher densities than in a white dwarf, 106 times that of water, it collapses but could stabilize to form a neutron star with aid of additional pressure from nucleon degeneracy and the strong nuclear force. ...
EarthComm_c1s9
... Scientists also search for examples of planetary nebulae. They want to understand when and how these events occur. Not only are these nebulae interesting, but they also show scientists what the fate of our solar system will be billions of years from now. What would happen if there were a supernova e ...
... Scientists also search for examples of planetary nebulae. They want to understand when and how these events occur. Not only are these nebulae interesting, but they also show scientists what the fate of our solar system will be billions of years from now. What would happen if there were a supernova e ...
Lecture 16
... Suppose the universe contained only lowmass stars. Would elements heavier than carbon exist? A. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. B. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolificall ...
... Suppose the universe contained only lowmass stars. Would elements heavier than carbon exist? A. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. B. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolificall ...
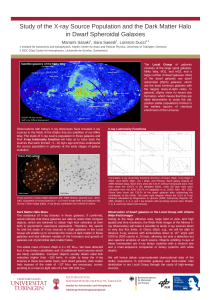
Study of the X-ray Source Population and the Dark Matter
... would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources in dSph galaxies in the Local Group will enable us to constrain t ...
... would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources in dSph galaxies in the Local Group will enable us to constrain t ...
Astronomers Find Extremely Large Planet
... young forming stars. The fact that the FLAMINGOS survey only found silhouette disks in clusters and not peppered thoughout the immense volume of the molecular clouds supports the point of view that such clusters of stars are the birthplace for most of the stars in our galaxy. “It’s surprising that t ...
... young forming stars. The fact that the FLAMINGOS survey only found silhouette disks in clusters and not peppered thoughout the immense volume of the molecular clouds supports the point of view that such clusters of stars are the birthplace for most of the stars in our galaxy. “It’s surprising that t ...
Origin of the Earth and of the Solar System
... years ago within the protosolar cloud (with an uncertainty of just 2 million years). Right: Ca/Al-rich inclusion within Allende-Meteorite with a diameter of ~1 cm (the oldest material, which could be dated so far). The first „Planetary-Embryos“ formed within just about 100 000 years. Roughly 10 mill ...
... years ago within the protosolar cloud (with an uncertainty of just 2 million years). Right: Ca/Al-rich inclusion within Allende-Meteorite with a diameter of ~1 cm (the oldest material, which could be dated so far). The first „Planetary-Embryos“ formed within just about 100 000 years. Roughly 10 mill ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... a. Giant molecular clouds do not contain enough material. b. General relativity does not allow such massive objects to exist. c. The rotation rate is so high that such an object splits into a pair of stars. d. Objects above this mass fuse hydrogen too rapidly and cannot stay together. e. Objects abo ...
... a. Giant molecular clouds do not contain enough material. b. General relativity does not allow such massive objects to exist. c. The rotation rate is so high that such an object splits into a pair of stars. d. Objects above this mass fuse hydrogen too rapidly and cannot stay together. e. Objects abo ...
ppt
... Cloud and star formation may have to be treated together Both magnetic and non-magnetic turbulence simulations are promising Observations of the large scale magnetic field strength are needed to judge its global support ...
... Cloud and star formation may have to be treated together Both magnetic and non-magnetic turbulence simulations are promising Observations of the large scale magnetic field strength are needed to judge its global support ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... . absorption in interstellar space (negligible for nearby stars) • Measurements from the Hipparcos satellite (1989– 1993) have yielded parallaxes accurate to 0.002 arcsec for about 100,000 stars. The largest stellar parallax ...
... . absorption in interstellar space (negligible for nearby stars) • Measurements from the Hipparcos satellite (1989– 1993) have yielded parallaxes accurate to 0.002 arcsec for about 100,000 stars. The largest stellar parallax ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... At least two supernovae have been detected in recent years in the nearby Whirlpool Galaxy, Messier 51. M51 is located at a distance of about 31 million light years (about 10 megaparsecs) in the direction of the constellation Canes Venatici. Stars can explode as supernovae in different ways, and the ...
... At least two supernovae have been detected in recent years in the nearby Whirlpool Galaxy, Messier 51. M51 is located at a distance of about 31 million light years (about 10 megaparsecs) in the direction of the constellation Canes Venatici. Stars can explode as supernovae in different ways, and the ...
colour
... . absorption in interstellar space (negligible for nearby stars) • Measurements from the Hipparcos satellite (1989– 1993) have yielded parallaxes accurate to 0.002 arcsec for about 100,000 stars. The largest stellar parallax ...
... . absorption in interstellar space (negligible for nearby stars) • Measurements from the Hipparcos satellite (1989– 1993) have yielded parallaxes accurate to 0.002 arcsec for about 100,000 stars. The largest stellar parallax ...
Galaxy Formation Leading questions for today • How do visible
... BT 7.1 abbreviated • dynamical friction slows down two galaxies meeting each other • even galaxies with hyperbolic orbits can merge ! ...
... BT 7.1 abbreviated • dynamical friction slows down two galaxies meeting each other • even galaxies with hyperbolic orbits can merge ! ...
The Milky Way
... Might be normal matter in a form that doesn’t emit much light – very small and dim star, little black holes • More likely it is elementary particles other than normal matter ...
... Might be normal matter in a form that doesn’t emit much light – very small and dim star, little black holes • More likely it is elementary particles other than normal matter ...
Supernovae - Michigan State University
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
Chapter 15: The Milky Way Galaxy
... How many stars does the Milky Way Galaxy contain? The Milky Way has about 200 billion stars. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way Galaxy? The solar system is between the Sagittarius and Perseus spiral arms about 26,000 ly from the center of the Galaxy. Is the Sun moving through the Mil ...
... How many stars does the Milky Way Galaxy contain? The Milky Way has about 200 billion stars. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way Galaxy? The solar system is between the Sagittarius and Perseus spiral arms about 26,000 ly from the center of the Galaxy. Is the Sun moving through the Mil ...
Slide 1
... Why don’t we do this? Why doesn’t everyone? First epoch M31 is from some of the “deepest-ever” images: 100 ksec= 28 hours per filter. Those images were also dithered. You probably need a few orbits per first-epoch in nearby objects, more than one field per object, and dithering (though you can relax ...
... Why don’t we do this? Why doesn’t everyone? First epoch M31 is from some of the “deepest-ever” images: 100 ksec= 28 hours per filter. Those images were also dithered. You probably need a few orbits per first-epoch in nearby objects, more than one field per object, and dithering (though you can relax ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... wavelength intervals were used when analyzing galaxy spectra to obtain the ages and metallicities of the stellar populations • For galaxies with old stellar populations, the Lick/IDS system of ~25 narrow-band indices is often used (Worthey1994. • For actively star-forming galaxies, the 4000A break(B ...
... wavelength intervals were used when analyzing galaxy spectra to obtain the ages and metallicities of the stellar populations • For galaxies with old stellar populations, the Lick/IDS system of ~25 narrow-band indices is often used (Worthey1994. • For actively star-forming galaxies, the 4000A break(B ...
Lecture 9
... As the helium core grows, it compresses. Helium doesn’t fuse to heavier elements for two reasons. (1) with 2 p+ per nucleus, the electric repulsion force is higher than was the case for H-fusion. This means that helium fusion requires a higher temperature than hydrogen fusion -- 100 million K ( ...
... As the helium core grows, it compresses. Helium doesn’t fuse to heavier elements for two reasons. (1) with 2 p+ per nucleus, the electric repulsion force is higher than was the case for H-fusion. This means that helium fusion requires a higher temperature than hydrogen fusion -- 100 million K ( ...
Lecture 10a Neutron Star and Black Holes (Test 2 overview)
... In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. ...
... In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.