Cosmochemistry from Nanometers to Light- Years A Written by
... Studies of isotopes in chondrites and differentiated (melted) meteorites show that aluminum-26 (26Al) was present when the Solar System formed. Although not abundant (a few parts in 100,000) compared to the stable aluminum isotope (27Al), its half-life is so short (only 730,000 years) that its decay ...
... Studies of isotopes in chondrites and differentiated (melted) meteorites show that aluminum-26 (26Al) was present when the Solar System formed. Although not abundant (a few parts in 100,000) compared to the stable aluminum isotope (27Al), its half-life is so short (only 730,000 years) that its decay ...
Lab 2: The Planisphere
... RA-Dec coordinates are only good for storing the location of stars in reference books. This coordinate system, called the equatorial system, tells us nothing about how to actually find something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfill ...
... RA-Dec coordinates are only good for storing the location of stars in reference books. This coordinate system, called the equatorial system, tells us nothing about how to actually find something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfill ...
large PDF file
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
Chapter 20 Notes (smaller PDF file)
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
charts_set_8
... Rotation rate: few to many times per second!!! Magnetic field: 1010 x typical bar A neutron star over the Sandias? ...
... Rotation rate: few to many times per second!!! Magnetic field: 1010 x typical bar A neutron star over the Sandias? ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... http://www2.enel.ucalgary.ca/People/ciubotar/public_html/Starsevol/specbin-anim.gif ...
... http://www2.enel.ucalgary.ca/People/ciubotar/public_html/Starsevol/specbin-anim.gif ...
UNIT 4 - Galaxies XIV. The Milky Way A. Structure
... Interstellar gas and dust prevent observations of stars to great distances within the galaxy radio telescopes (long wavelengths) can "see" through the dust and allow astronomers to map the distribution of gas and dust in the galaxy - Milky Way has a spiral structure Spiral arms contain gas and dust ...
... Interstellar gas and dust prevent observations of stars to great distances within the galaxy radio telescopes (long wavelengths) can "see" through the dust and allow astronomers to map the distribution of gas and dust in the galaxy - Milky Way has a spiral structure Spiral arms contain gas and dust ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... The student is expected to explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components in the universe. ...
... The student is expected to explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components in the universe. ...
Mass determinations of PMS stars with the
... • We already had observations of BS Indi (K=6.6 mag) with AMBER but the signal resulted to be too faint (+ no standard observed) • In this period our brightest (HD113449) candidate will be observed with AMBER • We hope to observe all targets with the VLTI (UTs or ATs + fringe tracker) to put constra ...
... • We already had observations of BS Indi (K=6.6 mag) with AMBER but the signal resulted to be too faint (+ no standard observed) • In this period our brightest (HD113449) candidate will be observed with AMBER • We hope to observe all targets with the VLTI (UTs or ATs + fringe tracker) to put constra ...
N5128PNSydney
... Low mass (~0.7-7M ) סּmain sequence stars undergo a planetary nebula (PN) phase at ages 0.1-10Gyr depending on initial mass, following the red-giant branch (RGB) and asymptotic giant branch (AGB) to the white dwarf cooling track Length of PN phase ~104 yr (depending on core mass) Emission from the ...
... Low mass (~0.7-7M ) סּmain sequence stars undergo a planetary nebula (PN) phase at ages 0.1-10Gyr depending on initial mass, following the red-giant branch (RGB) and asymptotic giant branch (AGB) to the white dwarf cooling track Length of PN phase ~104 yr (depending on core mass) Emission from the ...
Nova
... In Algol-type binaries, one of the stars has evolved and expanded to fill a droplet-shaped potential surface, called the Roche lobe, within which material is gravitationally bound to the star (see Figure 1). The Roche surface is, therefore, the surface along which the gravitational potential is comm ...
... In Algol-type binaries, one of the stars has evolved and expanded to fill a droplet-shaped potential surface, called the Roche lobe, within which material is gravitationally bound to the star (see Figure 1). The Roche surface is, therefore, the surface along which the gravitational potential is comm ...
The Milky Way
... Galaxies seem to take one of four different appearances Ellipticals have no dust No cold gas: No star formation Made mostly of old stars ...
... Galaxies seem to take one of four different appearances Ellipticals have no dust No cold gas: No star formation Made mostly of old stars ...
Spagna
... Chamaeleon Star Forming Region The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
... Chamaeleon Star Forming Region The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
Role of column density in the formation of stars
... gas is compressed; this is true even if the photon-diffusion time is short, because an outward temperature gradient is still needed to drive photon diffusion. This is in contrast to normal star formation, where efficient cooling to very low temperatures during the early stages allows the gas to frag ...
... gas is compressed; this is true even if the photon-diffusion time is short, because an outward temperature gradient is still needed to drive photon diffusion. This is in contrast to normal star formation, where efficient cooling to very low temperatures during the early stages allows the gas to frag ...
Chemical Universe. - University of Texas Astronomy
... a planetary nebula. The star’s leftover core, at the heart of the nebula, becomes a white dwarf — a ball of matter only about as big as Earth, but containing most of the star’s mass. It no longer produces energy through nuclear reactions, but shines through the heat built up during its long life. Th ...
... a planetary nebula. The star’s leftover core, at the heart of the nebula, becomes a white dwarf — a ball of matter only about as big as Earth, but containing most of the star’s mass. It no longer produces energy through nuclear reactions, but shines through the heat built up during its long life. Th ...
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
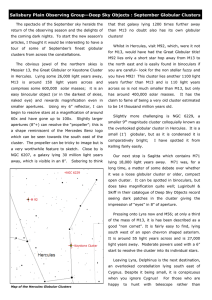
... Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of an open chevron shaped asterism. It is around 55 light years across and is 27,000 light years away. Moderate powers used with a 6” start ...
... Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of an open chevron shaped asterism. It is around 55 light years across and is 27,000 light years away. Moderate powers used with a 6” start ...
solar.gmu.edu
... 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies? 3. How are Seyfert galaxies and radio galaxies related to quasars? 4. How can material ejected from quasars appear to travel faster than light? 5. What could power the incredible energy output from active galaxies? 6. Why do many active ga ...
... 2. What evidence showed a link between quasars and galaxies? 3. How are Seyfert galaxies and radio galaxies related to quasars? 4. How can material ejected from quasars appear to travel faster than light? 5. What could power the incredible energy output from active galaxies? 6. Why do many active ga ...
Spectral Analysis Lab
... If you have ever looked closely at stars, you may have noticed that they are not all the same color. Scientists have found that they can learn a great deal about a star’s temperature and composition by analyzing the light it emits. How is this possible? When white light passes through a prism, it ap ...
... If you have ever looked closely at stars, you may have noticed that they are not all the same color. Scientists have found that they can learn a great deal about a star’s temperature and composition by analyzing the light it emits. How is this possible? When white light passes through a prism, it ap ...
Catherine Cress - CHPC Conference
... Another role for simulations in galaxy evolution studies Galaxy-scale simulations including gas ...
... Another role for simulations in galaxy evolution studies Galaxy-scale simulations including gas ...
Name
... 30) The helium fusion process that will occur in the lifetime of a Star with a mass similar to the Sun converts … A) four helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy B) four helium nuclei into two carbon nucleus plus energy C) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy D) two helium ...
... 30) The helium fusion process that will occur in the lifetime of a Star with a mass similar to the Sun converts … A) four helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy B) four helium nuclei into two carbon nucleus plus energy C) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy D) two helium ...
Name
... 30) The helium fusion process that will occur in the lifetime of a Star with a mass similar to the Sun converts … A) four helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy B) four helium nuclei into two carbon nucleus plus energy C) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy D) two helium ...
... 30) The helium fusion process that will occur in the lifetime of a Star with a mass similar to the Sun converts … A) four helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy B) four helium nuclei into two carbon nucleus plus energy C) two helium nuclei into one carbon nucleus plus energy D) two helium ...
Name - MIT
... C) Sunspot activity virtually ceased between the years 1645 and 1715. D) Gamma rays were released from the Sun at record lows in 1987 E) The energy output from the Sun was at a minimum from the years 1843 through 1902 27) Stars like the Sun probably do not form iron cores during their evolution beca ...
... C) Sunspot activity virtually ceased between the years 1645 and 1715. D) Gamma rays were released from the Sun at record lows in 1987 E) The energy output from the Sun was at a minimum from the years 1843 through 1902 27) Stars like the Sun probably do not form iron cores during their evolution beca ...
Name - MIT
... C) Sunspot activity virtually ceased between the years 1645 and 1715. D) Gamma rays were released from the Sun at record lows in 1987 E) The energy output from the Sun was at a minimum from the years 1843 through 1902 27) Stars like the Sun probably do not form iron cores during their evolution beca ...
... C) Sunspot activity virtually ceased between the years 1645 and 1715. D) Gamma rays were released from the Sun at record lows in 1987 E) The energy output from the Sun was at a minimum from the years 1843 through 1902 27) Stars like the Sun probably do not form iron cores during their evolution beca ...
Stellar Population Modeling of Galaxies in Nearby Groups
... dwarf galaxies are the best places to study the processes of star formation. SFHs of the Local Group dwarf galaxies were studied in details from deep images, which were obtained with large ground-based telescopes and the Hubble Space Telescope (see, for example, Holtzman et al. (2000), Han et al. (1 ...
... dwarf galaxies are the best places to study the processes of star formation. SFHs of the Local Group dwarf galaxies were studied in details from deep images, which were obtained with large ground-based telescopes and the Hubble Space Telescope (see, for example, Holtzman et al. (2000), Han et al. (1 ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.