Glencoe Earth Science
... The color of a star indicates its temperature. For example, hot stars are a blue-white color. A relatively cool star looks orange or red. Stars that have the same temperature as the Sun have a yellow color. Astronomers study the composition of stars by observing their spectra. When fitted into a tel ...
... The color of a star indicates its temperature. For example, hot stars are a blue-white color. A relatively cool star looks orange or red. Stars that have the same temperature as the Sun have a yellow color. Astronomers study the composition of stars by observing their spectra. When fitted into a tel ...
RADIO OBSERVATIONS RELATED TO STAR FORMATION P. G.
... procedure; we introduce the review of observations (Sect. II) by outlining a working hypothesis for the evolutionary sequence of Ο and Β stars. This sequence is based on radio and IR observations of the giant HII region W3 (reviewed by Mezger and Wink, 1974) and on model calculations of dust-filled ...
... procedure; we introduce the review of observations (Sect. II) by outlining a working hypothesis for the evolutionary sequence of Ο and Β stars. This sequence is based on radio and IR observations of the giant HII region W3 (reviewed by Mezger and Wink, 1974) and on model calculations of dust-filled ...
Importance of the bonus lines (depends on excitation)
... Very simple geometry which allows detailed modeling ...
... Very simple geometry which allows detailed modeling ...
WFIRST-2.4: What Every Astronomer Should Know
... matched to the i-band depth of LSST. The AB magnitude limits for LSST in g and r are fainter; however, a typical z>1 LSST weak lensing source galaxy has r-J or i-H color of about 1.2, so even here the WFIRST-2.4 imaging depth remains well matched, and of course the angular resolution is much higher. ...
... matched to the i-band depth of LSST. The AB magnitude limits for LSST in g and r are fainter; however, a typical z>1 LSST weak lensing source galaxy has r-J or i-H color of about 1.2, so even here the WFIRST-2.4 imaging depth remains well matched, and of course the angular resolution is much higher. ...
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... This is the most popular and accessible method in astronomy. Photometry is the measurement of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation usually expressed in apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude is a numerical scale to describe how bright each star appears in the sky. The lower the magnitude, the ...
... This is the most popular and accessible method in astronomy. Photometry is the measurement of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation usually expressed in apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude is a numerical scale to describe how bright each star appears in the sky. The lower the magnitude, the ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... (not even light) can escape them. • We can find them because…. – Stars that are close to them are “pulled” by the gravity of the black hole. – Gases in the area are pulled in so fast (like a drain in a sink) that they spin around the black hole and we see the heat given off. ...
... (not even light) can escape them. • We can find them because…. – Stars that are close to them are “pulled” by the gravity of the black hole. – Gases in the area are pulled in so fast (like a drain in a sink) that they spin around the black hole and we see the heat given off. ...
The Distribution of Stars Most Likely to Harbor Intelligent Life
... of the habitable star that divides the distribution into fractions f and (1 − f ). The thick solid curve corresponds to f = 1/2 in Eqs. (11) and (13) and gives the median intelligent star lifetime as a function of the specified Ti ; i.e., in the set consisting of all civilizations that have the same ...
... of the habitable star that divides the distribution into fractions f and (1 − f ). The thick solid curve corresponds to f = 1/2 in Eqs. (11) and (13) and gives the median intelligent star lifetime as a function of the specified Ti ; i.e., in the set consisting of all civilizations that have the same ...
Life Stages of High
... Lower Limit on a Star’s Mass • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. • Is ...
... Lower Limit on a Star’s Mass • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. • Is ...
SOME CONSTRAINTS ON GALAXY EVOLUTION IMPOSED BY
... removal) S (ellipticals) • 3 S (spirals), one would expect the population of metalrich globulars in ellipticals to be (on average) twice as large as that of the metalpoor primordial ones. What little information is presently available suggests that metal-rich and metal-poor clusters actually occur w ...
... removal) S (ellipticals) • 3 S (spirals), one would expect the population of metalrich globulars in ellipticals to be (on average) twice as large as that of the metalpoor primordial ones. What little information is presently available suggests that metal-rich and metal-poor clusters actually occur w ...
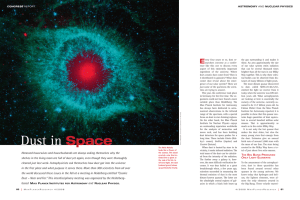
Dust in Space - Max-Planck
... 163,000 light-years away. A year after supernova 1987A, astronomers watched how the first dust arose in the gas cloud. However, this phase was already complete after one further year. “There is only a very small window of time in which the dust can be created,” says Cherchneff. The reason seems plau ...
... 163,000 light-years away. A year after supernova 1987A, astronomers watched how the first dust arose in the gas cloud. However, this phase was already complete after one further year. “There is only a very small window of time in which the dust can be created,” says Cherchneff. The reason seems plau ...
PowerPoint
... below 80 Jupiter masses. • The central density and temperature do not get large enough for nuclear fusion to occur. • These failed stars, gradually cool down and contract. • Recently, there have been a number of discovered brown dwarves. ...
... below 80 Jupiter masses. • The central density and temperature do not get large enough for nuclear fusion to occur. • These failed stars, gradually cool down and contract. • Recently, there have been a number of discovered brown dwarves. ...
PEGASUS, THE FLYING HORSE Pegasus is a constellation in the
... with a redshift of 0.0027. It was discovered by musician-astronomer William Herschel in 1784 and was later one of the first nebulous objects to be described as "spiral" by William Parsons. Another of Pegasus's galaxies is NGC 7742, a Type 2 Seyfert galaxy. Located at a distance of 77 million light-y ...
... with a redshift of 0.0027. It was discovered by musician-astronomer William Herschel in 1784 and was later one of the first nebulous objects to be described as "spiral" by William Parsons. Another of Pegasus's galaxies is NGC 7742, a Type 2 Seyfert galaxy. Located at a distance of 77 million light-y ...
Educator`s Guide to the Cullman Hall of the Universe, Heilbrunn
... is mostly empty space. These galaxies range in size from thousands of times smaller to a hundred times larger than our own Milky Way Galaxy, which alone contains more than 100 billion stars. Like our Sun, many of these stars have planets, asteroids, meteoroids, and comets in orbit around them. Howev ...
... is mostly empty space. These galaxies range in size from thousands of times smaller to a hundred times larger than our own Milky Way Galaxy, which alone contains more than 100 billion stars. Like our Sun, many of these stars have planets, asteroids, meteoroids, and comets in orbit around them. Howev ...
Opakování z minulého cvičení
... Traditionally, spectroscopy dealt with visible light, but it has been extended to cover other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation and even to measurements of the distribution of energy among particles, such as cosmic rays. The first spectroscopy does is to tell us what stars , galaxies and so o ...
... Traditionally, spectroscopy dealt with visible light, but it has been extended to cover other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation and even to measurements of the distribution of energy among particles, such as cosmic rays. The first spectroscopy does is to tell us what stars , galaxies and so o ...
Leo Powerpoint
... Regulus, shining at the heart of Leo the Lion, is near the end of the list of first magnitude stars. At a distance of only 79 light years, it shines in our sky at magnitude 1.35. The Latin name means "the little king," the reference to a kingly star going back to ancient times. Regulus marks the end ...
... Regulus, shining at the heart of Leo the Lion, is near the end of the list of first magnitude stars. At a distance of only 79 light years, it shines in our sky at magnitude 1.35. The Latin name means "the little king," the reference to a kingly star going back to ancient times. Regulus marks the end ...
PPT
... iterative processing for 1 million stars (final results April 2002) platform for further development/experimentation ...
... iterative processing for 1 million stars (final results April 2002) platform for further development/experimentation ...
Frantic Finish - Max-Planck
... imum as conventional Type II supernovae. The problem is: “These objects are all extremely far away. We can often register only the light curves, and the spectra are not conclusive in detail,” says Hans-Thomas Janka. What causes these supernovae? The researchers can only speculate. After an initial e ...
... imum as conventional Type II supernovae. The problem is: “These objects are all extremely far away. We can often register only the light curves, and the spectra are not conclusive in detail,” says Hans-Thomas Janka. What causes these supernovae? The researchers can only speculate. After an initial e ...
The Extragalactic Group of MPE and USM
... of Massive Galaxies in the FORS Deep and GOODS South fields • Study evolution of galaxies with broadband deep U to K surveys. • LFs, Mass Functions, SFRs do not require spectroscopy but can be derived with accurate photometric redshifts. • Advantage of photo z: no color selection bias, fainter lumin ...
... of Massive Galaxies in the FORS Deep and GOODS South fields • Study evolution of galaxies with broadband deep U to K surveys. • LFs, Mass Functions, SFRs do not require spectroscopy but can be derived with accurate photometric redshifts. • Advantage of photo z: no color selection bias, fainter lumin ...
Are Gamma-Ray Bursts good Star Formation Indicators?
... evolution of baryonic matter in the universe. Although significant progress has been made in recent years, there remains debate about the fraction of star-formation occurring in obscured mode, which is hard to study directly, and uncertainty about the star formation occurring at very high redshifts ...
... evolution of baryonic matter in the universe. Although significant progress has been made in recent years, there remains debate about the fraction of star-formation occurring in obscured mode, which is hard to study directly, and uncertainty about the star formation occurring at very high redshifts ...
Constellation ARA
... Ara contains several notable deep sky objects: the Stingray Nebula, the open cluster NGC 6193 and the globular cluster NGC 6397. NGC 6193 is a large open cluster that contains 27 stars, many of them binaries. The cluster lies eight degrees west and one degree north of Alpha Arae. Its estimated age i ...
... Ara contains several notable deep sky objects: the Stingray Nebula, the open cluster NGC 6193 and the globular cluster NGC 6397. NGC 6193 is a large open cluster that contains 27 stars, many of them binaries. The cluster lies eight degrees west and one degree north of Alpha Arae. Its estimated age i ...
“And God Said, Let There Be Lights in the Firmament of Heaven”
... for reasons not fully understood the sun reaches a minimum temperature just outside its visual surface from that minimum of about 4500 degrees centigrade the temperature of the gas around the sun climbs rapidly to a million plus degrees centigrade this hot gas surrounds the sun in a tenuous corona w ...
... for reasons not fully understood the sun reaches a minimum temperature just outside its visual surface from that minimum of about 4500 degrees centigrade the temperature of the gas around the sun climbs rapidly to a million plus degrees centigrade this hot gas surrounds the sun in a tenuous corona w ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... values. 3. The second step is to estimate the age of the cluster. As the cluster ages, the shape of its CMD also changes. By selecting Tools → Isochrones you can add an isochrone on your CMD, which is a theoretical prediction of how the stars should be distributed at a certain age of the cluster. Yo ...
... values. 3. The second step is to estimate the age of the cluster. As the cluster ages, the shape of its CMD also changes. By selecting Tools → Isochrones you can add an isochrone on your CMD, which is a theoretical prediction of how the stars should be distributed at a certain age of the cluster. Yo ...
Baryons at Low Densities: The Stellar Halos around Galaxies
... clusters) survey. The high angular resolution of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) allows the detection of single stars in halos at larger distances and in denser regions — hence investigating the transition regions between the disc and halo. All MW-like galaxies observed by GHOSTS have extended stel ...
... clusters) survey. The high angular resolution of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) allows the detection of single stars in halos at larger distances and in denser regions — hence investigating the transition regions between the disc and halo. All MW-like galaxies observed by GHOSTS have extended stel ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.