Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectroscopic observations for years in order to detect planetary systems. Of these 451 stars, 70 are reported to host planets and the rest, which we will designate as a comparison sample, (we often call them “sing ...
... stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectroscopic observations for years in order to detect planetary systems. Of these 451 stars, 70 are reported to host planets and the rest, which we will designate as a comparison sample, (we often call them “sing ...
second grade - Math/Science Nucleus
... light. While these objects also shine or reflect light during the day, we generally cannot see them because they are much dimmer than the bright light emitted by the nearby Sun. Most of the light we see at night comes from within our own galaxy, the Milky Way. Some points of light, however, are from ...
... light. While these objects also shine or reflect light during the day, we generally cannot see them because they are much dimmer than the bright light emitted by the nearby Sun. Most of the light we see at night comes from within our own galaxy, the Milky Way. Some points of light, however, are from ...
Lecture notes 11
... rising up into the chromosphere. Visible in Hα emission. Each one lasting about 5 – 15 min. ...
... rising up into the chromosphere. Visible in Hα emission. Each one lasting about 5 – 15 min. ...
Open access - ORBi
... observations with IOTA/IONIC at H band7 allowed us to constrain the nature of the dust grains with radiative transfer modelling, suggesting that the grains are very small (< 1µm), located close to their sublimation distance (around 0.2-0.5 AU depending on the grain size), with temperatures up to 170 ...
... observations with IOTA/IONIC at H band7 allowed us to constrain the nature of the dust grains with radiative transfer modelling, suggesting that the grains are very small (< 1µm), located close to their sublimation distance (around 0.2-0.5 AU depending on the grain size), with temperatures up to 170 ...
Practical cosmology with the Local Volume galaxies
... individual HII regions only. Therefore, evolutionary history of disks of galaxies looks to be driven mainly by internal SF processes. It is generally accepted that the enhanced star formation in galaxies is triggered by their interaction. But we did not find clear evidence for such suggestion. Curio ...
... individual HII regions only. Therefore, evolutionary history of disks of galaxies looks to be driven mainly by internal SF processes. It is generally accepted that the enhanced star formation in galaxies is triggered by their interaction. But we did not find clear evidence for such suggestion. Curio ...
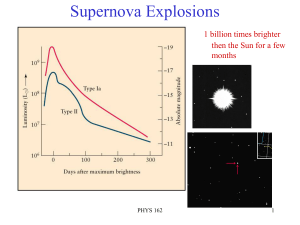
Supernovas 10/19
... In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. ...
... In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. ...
Impact on stellar properties of changing physics SAC Summer
... was originally created by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. It shows the relationship between the star’s luminosity or absolute magnitude versus its effective temperature or spectral type. In general, stars of greater luminosity populate the top of the diagram, while stars with higher surf ...
... was originally created by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. It shows the relationship between the star’s luminosity or absolute magnitude versus its effective temperature or spectral type. In general, stars of greater luminosity populate the top of the diagram, while stars with higher surf ...
The Evolution of Galaxy - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... ver since the big bang, the universe has been expanding. ago—and new clusters should still be forming and growing toAll objects not bound to one another by gravity or some day. But if the universe has only one quarter of the matter other force are being pulled apart. But will the cosmic expan- neede ...
... ver since the big bang, the universe has been expanding. ago—and new clusters should still be forming and growing toAll objects not bound to one another by gravity or some day. But if the universe has only one quarter of the matter other force are being pulled apart. But will the cosmic expan- neede ...
III Ionized Hydrogen (HII) Regions
... photons with energies above the Hydrogen ionization energy of 13.6eV. These objects include “Classical HII Regions” ionized by hot O or B stars (or clusters of such stars) and associated with regions of recent massive-star formation, and “Planetary Nebulae”, the ejected outer envelopes of AGB stars ...
... photons with energies above the Hydrogen ionization energy of 13.6eV. These objects include “Classical HII Regions” ionized by hot O or B stars (or clusters of such stars) and associated with regions of recent massive-star formation, and “Planetary Nebulae”, the ejected outer envelopes of AGB stars ...
Document
... 5-10 in each starburst galaxy observed *Whatever process ins forming these very luminous BHs is enhanced when many stars, particularly one of large mass and size, form simultaneously. And the production of the high-brightness X-ray sources goes away as fast as the star formation subsides. Recent stu ...
... 5-10 in each starburst galaxy observed *Whatever process ins forming these very luminous BHs is enhanced when many stars, particularly one of large mass and size, form simultaneously. And the production of the high-brightness X-ray sources goes away as fast as the star formation subsides. Recent stu ...
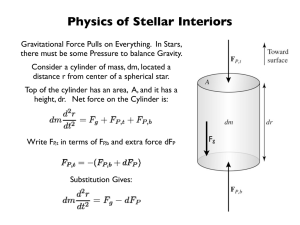
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 11 Notes: Stellar
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
MS-SCI-PS-Unit 4 -- Chapter 15- Stars, Galaxies
... light in the night sky. But they could see few details with their eyes alone. It was not until the invention of the telescope in 1608 that people could observe objects in the sky more closely. Recall that a telescope is a device that makes distant objects appear to be closer. The telescope revolutio ...
... light in the night sky. But they could see few details with their eyes alone. It was not until the invention of the telescope in 1608 that people could observe objects in the sky more closely. Recall that a telescope is a device that makes distant objects appear to be closer. The telescope revolutio ...
The Earth and Man In the Universe
... It has often been suggested that the stars are infinite in number and that the universe is therefore infinite in extent. But the latest investigations, telescopic as well as photographic, show that the proportion of increase in the number of the stars diminishes when the. lowest magnitudes are reach ...
... It has often been suggested that the stars are infinite in number and that the universe is therefore infinite in extent. But the latest investigations, telescopic as well as photographic, show that the proportion of increase in the number of the stars diminishes when the. lowest magnitudes are reach ...
The stellar populations in the low-luminosity, early
... test initial mass functions (IMF) in galaxies, supporting a steeper integrated galactic IMF with increasing galaxy mass and decreasing star formation rate (Recchi, Calura & Kroupa 2009). LLEs provide important tests of scaling relations with mass and luminosity in general, since they are at one extr ...
... test initial mass functions (IMF) in galaxies, supporting a steeper integrated galactic IMF with increasing galaxy mass and decreasing star formation rate (Recchi, Calura & Kroupa 2009). LLEs provide important tests of scaling relations with mass and luminosity in general, since they are at one extr ...
T Einstein’s Mirage Paul L. Schechter
... single quasar expected for a gravitational mirage was confirmed Perhaps the most important when a galaxy, the source of the needed gravitational potential, was observed between the two images. outstanding question about In the ensuing quarter century nearly a hundred cases of galaxy potentials produ ...
... single quasar expected for a gravitational mirage was confirmed Perhaps the most important when a galaxy, the source of the needed gravitational potential, was observed between the two images. outstanding question about In the ensuing quarter century nearly a hundred cases of galaxy potentials produ ...
chap8 (WP)
... passes by an observer stationary on the ground. What frequency does the observer hear if the train is traveling at 140 km/hr (a) towards and (b) away from the observer? (Use 342 m/s for the speed of sound in air) 2. A train blows its whistle at a frequency f as it approaches a tunnel. An observer st ...
... passes by an observer stationary on the ground. What frequency does the observer hear if the train is traveling at 140 km/hr (a) towards and (b) away from the observer? (Use 342 m/s for the speed of sound in air) 2. A train blows its whistle at a frequency f as it approaches a tunnel. An observer st ...
The extended structure of the dwarf irregular galaxy Sagittarius⋆⋆⋆
... of isolated dwarfs in the Local Group (LG) are expected to provide crucial insight into the impact of the various factors on shaping the current status of dSphs, since they may represent the test case of evolution without interactions and can give insight into the initial conditions at the epoch of ...
... of isolated dwarfs in the Local Group (LG) are expected to provide crucial insight into the impact of the various factors on shaping the current status of dSphs, since they may represent the test case of evolution without interactions and can give insight into the initial conditions at the epoch of ...
– 1 – 1. Historical Notes for Ay 123 1.1.
... Self gravitating sphere (or almost sphere) of gas with a finite definable radius, not easily deformed, not like a cloud in the Earth’s atmosphere Nuclear reactions occur at least to the point where 3 He is produced. radiates energy into the surrounding medium. Jupiter also does this, some internal h ...
... Self gravitating sphere (or almost sphere) of gas with a finite definable radius, not easily deformed, not like a cloud in the Earth’s atmosphere Nuclear reactions occur at least to the point where 3 He is produced. radiates energy into the surrounding medium. Jupiter also does this, some internal h ...
death_high_mass
... • Star is on main-sequence – Core converting hydrogen into helium. • Star is a Sub-giant -- Core is contracting releasing gravitational potential energy • Star is a Giant (III) – Core is contracting releasing gravitational potential energy and hydrogen into helium in a shell around the core. • Heliu ...
... • Star is on main-sequence – Core converting hydrogen into helium. • Star is a Sub-giant -- Core is contracting releasing gravitational potential energy • Star is a Giant (III) – Core is contracting releasing gravitational potential energy and hydrogen into helium in a shell around the core. • Heliu ...
Core-Halo Age Gradients and Star Formation in the Orion Nebula
... ages of massive stars are difficult to estimate as they quickly arrive on the main sequence while the PMS stars are on their Hayashi tracks. There is some evidence that massive stars in cluster cores are younger than more dispersed PMS stars in rich clusters (§4.1). But it is not clear whether this ...
... ages of massive stars are difficult to estimate as they quickly arrive on the main sequence while the PMS stars are on their Hayashi tracks. There is some evidence that massive stars in cluster cores are younger than more dispersed PMS stars in rich clusters (§4.1). But it is not clear whether this ...
Document
... clusters: gas stripping, star stripping, galaxy-galaxy encounters, interaction with the general tidal field. There’s a correlation between outer rotation-velocity gradients and distance from the cluster centre: inner-cluster galaxies show shallower rotation curves than do outer- cluster galaxies. (R ...
... clusters: gas stripping, star stripping, galaxy-galaxy encounters, interaction with the general tidal field. There’s a correlation between outer rotation-velocity gradients and distance from the cluster centre: inner-cluster galaxies show shallower rotation curves than do outer- cluster galaxies. (R ...
... NGC 253 is the jewel of Sculptor. It is a magnitude 7, nearly edgeon spiral galaxy. It is nearly half a degree long and while it can be picked up in binocular, an aperture of at least 100mm is required to just make out the smudge of the spiral arms. A medium aperture telescope will start to resolve ...
Abstract - chara - Georgia State University
... therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrared surveys are detecting a large number of these objects, which, due to magnitude limits, mostly turn out to be nearby. In the local stellar neighborhood they tend to dominate over more massive stars. This shows that the mass distribution function for ...
... therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrared surveys are detecting a large number of these objects, which, due to magnitude limits, mostly turn out to be nearby. In the local stellar neighborhood they tend to dominate over more massive stars. This shows that the mass distribution function for ...
STELLAR CLASSIFICATIONS: TYPE “O” STARS
... one of these stars would have to live close and be able to see heat. Lifespan: The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as th ...
... one of these stars would have to live close and be able to see heat. Lifespan: The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as th ...
Spring 2017 - Astronomers of Humboldt
... northern latitudes, but it is best viewed in the spring when it is high in the sky. M97 (Fig. 6) is located at the bottom of the bowl. This large planetary nebula is known as the Owl Nebula because of two large dark areas that resemble eyes. The galactic pair M81 and M82 (Fig. 7) are located about 1 ...
... northern latitudes, but it is best viewed in the spring when it is high in the sky. M97 (Fig. 6) is located at the bottom of the bowl. This large planetary nebula is known as the Owl Nebula because of two large dark areas that resemble eyes. The galactic pair M81 and M82 (Fig. 7) are located about 1 ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.