The Scale of the Cosmos
... a star, large enough to be spherical and to have cleared its orbital zone of other objects 7. Star – a self-luminous ball of has gas that generates its own energy by nuclear fusion ...
... a star, large enough to be spherical and to have cleared its orbital zone of other objects 7. Star – a self-luminous ball of has gas that generates its own energy by nuclear fusion ...
Document
... Gas clouds rear-end one another Both cause cloud collapse & forming new stars, especially hot, luminous (OB) stars. These light up the spiral arms. ...
... Gas clouds rear-end one another Both cause cloud collapse & forming new stars, especially hot, luminous (OB) stars. These light up the spiral arms. ...
How Far is far ?
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
Scientific Results Summary
... discovered a circumstellar disk in an odd butterfly shape. Their discovery showed that massive stars form the same way lower-mass stars like the Sun. A very young protostar located in the Omega Nebula (M17) was found to be surrounded by an envelope of dust and gas. The relevance of their discovery w ...
... discovered a circumstellar disk in an odd butterfly shape. Their discovery showed that massive stars form the same way lower-mass stars like the Sun. A very young protostar located in the Omega Nebula (M17) was found to be surrounded by an envelope of dust and gas. The relevance of their discovery w ...
Guide to Deep Space Poster PDF
... These dark structures are columns of cool gas, mainly hydrogen and dust, that serve as incubators for new stars. Astronomers have detected blobs of much denser gas inside the Pillars, these appear to be forming solar systems. Eventually the new star will become visible as their radiation blows away ...
... These dark structures are columns of cool gas, mainly hydrogen and dust, that serve as incubators for new stars. Astronomers have detected blobs of much denser gas inside the Pillars, these appear to be forming solar systems. Eventually the new star will become visible as their radiation blows away ...
Lecture8
... The glowing gas cloud in this Hubble Space Telescope image lies 210,000 lightyears away in the constellation Tucana (the Toucan). Hot stars within the nebula emit high-energy, ultraviolet photons, which are absorbed by the surrounding gas and heat the gas to high temperature. This heated gas prod ...
... The glowing gas cloud in this Hubble Space Telescope image lies 210,000 lightyears away in the constellation Tucana (the Toucan). Hot stars within the nebula emit high-energy, ultraviolet photons, which are absorbed by the surrounding gas and heat the gas to high temperature. This heated gas prod ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... A supernova is when a very big star explodes. This happens when a star totally runs out of energy to make heat and light. They are very big and because of gravity they press on their centers very hard and use up their energy very quickly, so they usually only live for a few million years. Then they ...
... A supernova is when a very big star explodes. This happens when a star totally runs out of energy to make heat and light. They are very big and because of gravity they press on their centers very hard and use up their energy very quickly, so they usually only live for a few million years. Then they ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... A supernova is when a very big star explodes. This happens when a star totally runs out of energy to make heat and light. They are very big and because of gravity they press on their centers very hard and use up their energy very quickly, so they usually only live for a few million years. Then they ...
... A supernova is when a very big star explodes. This happens when a star totally runs out of energy to make heat and light. They are very big and because of gravity they press on their centers very hard and use up their energy very quickly, so they usually only live for a few million years. Then they ...
Extragalactic AO Science
... OII, 4000 Break in J band This is probably the formation epoch of MW-like disks (1” diameter). ...
... OII, 4000 Break in J band This is probably the formation epoch of MW-like disks (1” diameter). ...
1128/1130 Discussion Notes
... on this one.) The force of gravity from the material outside of the orbit is in all different directions, so it practically cancels out. The force of gravity from the material within the orbit is all in the same direction, so it adds up. ...
... on this one.) The force of gravity from the material outside of the orbit is in all different directions, so it practically cancels out. The force of gravity from the material within the orbit is all in the same direction, so it adds up. ...
Friday, November 7 - Otterbein University
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
PSC100 Transparant Replacement for Chapter 8 Measurement of
... ** Finds distance to most distant galaxies ...
... ** Finds distance to most distant galaxies ...
Astronomy 12: Introduction to Astronomy
... b. The region on the H-R diagram where, once they are formed. new stars rest for most of their lives. c. The sequence of events a star follows from its formation to supernova. d. The region on the H-R diagram where protostars first appear. 3. Define hydrogen burning. a. The formation of a hydrogen g ...
... b. The region on the H-R diagram where, once they are formed. new stars rest for most of their lives. c. The sequence of events a star follows from its formation to supernova. d. The region on the H-R diagram where protostars first appear. 3. Define hydrogen burning. a. The formation of a hydrogen g ...
Document
... The closest ones are being disrupted, but where is this material going? An important link to galaxy formation and evolution which we will look at in more detail next week! ...
... The closest ones are being disrupted, but where is this material going? An important link to galaxy formation and evolution which we will look at in more detail next week! ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... five senses to gather information. Inference- a possible explanation or solution to a problem based on observations. ...
... five senses to gather information. Inference- a possible explanation or solution to a problem based on observations. ...
Cosmology, galaxies, stars and the sun
... As size increases, the temperature decreases because the heat of nuclear fusion is spread out over such an enormous volume! ...
... As size increases, the temperature decreases because the heat of nuclear fusion is spread out over such an enormous volume! ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
Stars presentation by lauren
... over 150 times BIGGER than that!! Scientists have discovered that on the other side of the galaxy, there are much bigger stars. That is where the biggest star in the galaxy is.So our sun is actually not that big compared to other stars. ...
... over 150 times BIGGER than that!! Scientists have discovered that on the other side of the galaxy, there are much bigger stars. That is where the biggest star in the galaxy is.So our sun is actually not that big compared to other stars. ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
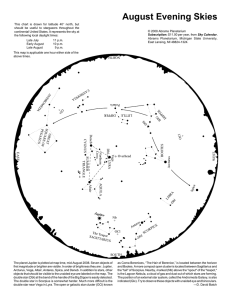
August Evening Skies
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
Recent advances in star
... note that the calculations of Lim, Falle and Hartquist, which do attempt to be more realistic in terms of the microphysics, suggest that the gross macroscopic behaviour of the gas is greatly modified by its microscopic properties. The safest conclusion at present seems to be that we have not yet arr ...
... note that the calculations of Lim, Falle and Hartquist, which do attempt to be more realistic in terms of the microphysics, suggest that the gross macroscopic behaviour of the gas is greatly modified by its microscopic properties. The safest conclusion at present seems to be that we have not yet arr ...
Volume 20 Number 4 March 2012 - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... Peering deep inside the hub of the Andromeda galaxy, the Hubble Space Telescope has uncovered a large, rare population of hot, bright stars. Blue is typically an indicator of hot, young stars but these stellar oddities are aging, Sun-like stars that have prematurely cast off their outer layers of ma ...
... Peering deep inside the hub of the Andromeda galaxy, the Hubble Space Telescope has uncovered a large, rare population of hot, bright stars. Blue is typically an indicator of hot, young stars but these stellar oddities are aging, Sun-like stars that have prematurely cast off their outer layers of ma ...
Astronomy 10B List of Concepts– by Chapter
... o How long will they be doing this (what fraction of their lives)? o Relation between stellar mass and main sequence lifetime • Red Giants – and the red giant branch o What are the stars doing? o How big do they get? Why? o How long will they be there? • Evolutionary stages of a low-mass star • Evol ...
... o How long will they be doing this (what fraction of their lives)? o Relation between stellar mass and main sequence lifetime • Red Giants – and the red giant branch o What are the stars doing? o How big do they get? Why? o How long will they be there? • Evolutionary stages of a low-mass star • Evol ...
From galaxies to stars
... and the whole core compacts down to a ball of neutrons only 20 km across: a neutron star. Meanwhile, the outer layers of the star fall inwards until they hit the newborn neutron star. When they meet the core they “bounce” off it so hard that they are ejected outwards in blast wave which explodes the ...
... and the whole core compacts down to a ball of neutrons only 20 km across: a neutron star. Meanwhile, the outer layers of the star fall inwards until they hit the newborn neutron star. When they meet the core they “bounce” off it so hard that they are ejected outwards in blast wave which explodes the ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.