
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... concentrated in the central regions of the galaxy. The X-ray source could be another example of a veiled black hole associated with a Type 2 Quasar. This discovery adds to a CXO 0312 Fiore P3 (CXOUJ031238.9growing body of evidence that our 765134): A possible Type 2 quasar veiled black hole.(Credit: ...
... concentrated in the central regions of the galaxy. The X-ray source could be another example of a veiled black hole associated with a Type 2 Quasar. This discovery adds to a CXO 0312 Fiore P3 (CXOUJ031238.9growing body of evidence that our 765134): A possible Type 2 quasar veiled black hole.(Credit: ...
2.1 Hubble Space Telescope
... More than a decade after launch, The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) continues to produce excellent scientific results and stunning imagery. In the past year, the active instruments were the infrared camera NICMOS, the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) and the Fine Guidance Sensors (FGS). They are ...
... More than a decade after launch, The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) continues to produce excellent scientific results and stunning imagery. In the past year, the active instruments were the infrared camera NICMOS, the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) and the Fine Guidance Sensors (FGS). They are ...
Lecture 16 - Yet More Evolution of Stars
... • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off the new neutron star (also pushed outwards by the neutrinos) ...
... • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off the new neutron star (also pushed outwards by the neutrinos) ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a way to find Capella, the 6th brightest star in the sky, by "star hopping," or going step by step from the easier stars to the tougher ones. ...
... closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a way to find Capella, the 6th brightest star in the sky, by "star hopping," or going step by step from the easier stars to the tougher ones. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... generation and of a mass similar to that of our sun is f star ≈ 5 × 108 /1011 = 5 × 10−3 . This estimate is about 10 times lower than a similar one due to Hart [4]. Our considerations neglect some effects. For example, the gas from a supernova could all coagulate into another giant star which could ...
... generation and of a mass similar to that of our sun is f star ≈ 5 × 108 /1011 = 5 × 10−3 . This estimate is about 10 times lower than a similar one due to Hart [4]. Our considerations neglect some effects. For example, the gas from a supernova could all coagulate into another giant star which could ...
Page 1 Astronomy 110 Homework #08 Assigned: 03/13/2007 Due
... Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures thus far. Choose the correct response from those listed, along with at least a one (1) sentence justification for your answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations ...
... Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures thus far. Choose the correct response from those listed, along with at least a one (1) sentence justification for your answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
What is a Star
... What is a Star? A star is a luminous globe of glowing gas producing its own heat and light by nuclear reactions in the star's core. Stars vary in size, mass, brightness, temperature and colour. The smallest mass possible for a star is about 1/10 that of the Sun, while the brightest stars have masses ...
... What is a Star? A star is a luminous globe of glowing gas producing its own heat and light by nuclear reactions in the star's core. Stars vary in size, mass, brightness, temperature and colour. The smallest mass possible for a star is about 1/10 that of the Sun, while the brightest stars have masses ...
September Evening Skies
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
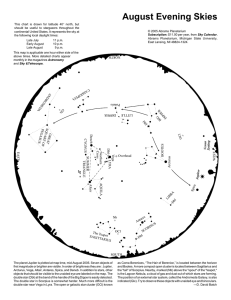
August Evening Skies
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
the lab handout here
... How many types of stars are shown on the HR Diagram? ___________________________ ...
... How many types of stars are shown on the HR Diagram? ___________________________ ...
Dust [12.1]
... where j,k are lower, upper levels, fjk is oscillator strength = effective number of oscillators participating in transition. ...
... where j,k are lower, upper levels, fjk is oscillator strength = effective number of oscillators participating in transition. ...
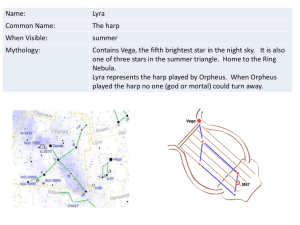
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
300 MHz - 3 GHz Yes, we`re interested
... Big Science Driver: Galaxy Assembly and Evolution • HI: heard several times about billion galaxies to z=1.5. And further… • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
... Big Science Driver: Galaxy Assembly and Evolution • HI: heard several times about billion galaxies to z=1.5. And further… • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
Uniqueness of the Earth, Lebo, 7-30
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
The Sky is Our Laboratory
... • Black holes are collapsed stars with M>= 3.2 M(Sun). Their gravitational pull is so large that not even the light can escape! We can only see them when surrounding matter spirals into the hole. ...
... • Black holes are collapsed stars with M>= 3.2 M(Sun). Their gravitational pull is so large that not even the light can escape! We can only see them when surrounding matter spirals into the hole. ...
Chapter 26 Book Questions
... C. The universe came into existence in an instant. D. The matter and energy in the universe has taken billions of years to form. 31. After the big bang, it is theorized that the universe __________________. 32. How large was the universe when the sun and solar system formed? 33. Circle the letter of ...
... C. The universe came into existence in an instant. D. The matter and energy in the universe has taken billions of years to form. 31. After the big bang, it is theorized that the universe __________________. 32. How large was the universe when the sun and solar system formed? 33. Circle the letter of ...
Before Reading
... How Many Stars in the Sky? • What are the problems the child encounters trying to count the stars in the sky? • Why is the country a better place than the city to see stars? • Do you think it is possible to count all the stars in the sky? Why or why not? ...
... How Many Stars in the Sky? • What are the problems the child encounters trying to count the stars in the sky? • Why is the country a better place than the city to see stars? • Do you think it is possible to count all the stars in the sky? Why or why not? ...
Uniqueness of the Earth, Lebo, 7-30
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
... Must be near, but not in, a spiral arm. We are at a corotation point far from our galactic center. Note: At the co-rotation point the Sun remains stationary and out of a spiral arm. Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locatio ...
7th Grade Astronomy Study Guide
... 1. An effect in which a star or galaxy appears to move quickly away from an observer is called ____________________. 2. A phenomenon in which sound seems to increase or decrease in relation to the direction it is moving is the ____________________. ...
... 1. An effect in which a star or galaxy appears to move quickly away from an observer is called ____________________. 2. A phenomenon in which sound seems to increase or decrease in relation to the direction it is moving is the ____________________. ...
The Universe - Solon City Schools
... a red giant and finishes as a dwarf star. Stars that are more massive go from a giant star to a supernova. ...
... a red giant and finishes as a dwarf star. Stars that are more massive go from a giant star to a supernova. ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.











![Dust [12.1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008843506_1-c0b3bc1292042697e2dbc020b2f06e1c-300x300.png)









