AnwerkeyTypes-of-stars-and-HR-diagram
... White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors from hottest to Coldest: __Blue, white ...
... White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors from hottest to Coldest: __Blue, white ...
Astronomy 115 Homework Set #1 – Due: Thursday, Feb
... 1. What is the average density of the Sun? How does this compare with the average density of Jupiter? 2. How many hydrogen atoms are converted to helium each second in order to power the Sun’s luminosity? To arrive at the solution, answer the following: (a) What is the mass of 4 hydrogen atoms? (b) ...
... 1. What is the average density of the Sun? How does this compare with the average density of Jupiter? 2. How many hydrogen atoms are converted to helium each second in order to power the Sun’s luminosity? To arrive at the solution, answer the following: (a) What is the mass of 4 hydrogen atoms? (b) ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #1
... Assume for the time being that the Galaxy has no dust, and that we are observing along a line of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central ...
... Assume for the time being that the Galaxy has no dust, and that we are observing along a line of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central ...
Lecture 12
... These two stars have about the same luminosity— which one appears brighter (i.e. has a larger apparent brightness) ? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity— which one appears brighter (i.e. has a larger apparent brightness) ? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
Russell Diagram
... Star A has a brightness of 1.0 μW/m2 and is known to be 4.0 ly away. Star B is 9.0 ly away and has a brightness of 3.0 μW/m2. How much more luminous is star B than star A? ...
... Star A has a brightness of 1.0 μW/m2 and is known to be 4.0 ly away. Star B is 9.0 ly away and has a brightness of 3.0 μW/m2. How much more luminous is star B than star A? ...
Sequence of Stars Notes
... H-R Diagram: shows the relationship between a star’s absolute magnitude and temperature ...
... H-R Diagram: shows the relationship between a star’s absolute magnitude and temperature ...
SOLUTIONS ASTROPHYSICS – OPTION D 2015-17
... Non rotating star = straight line = no movement = no Doppler shift Rotating star = moving toward and away = Doppler Shift ...
... Non rotating star = straight line = no movement = no Doppler shift Rotating star = moving toward and away = Doppler Shift ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the man on the left? • W ...
... • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the man on the left? • W ...
Solutions2
... at different distances from us. Star A has parallax 10−3 ”, and radius 108 m. It appears 25 times brighter than Star B. a) What are the distances to stars A and B? Star A has d=1/p”=1000 parsecs. Star B is 25 times fainter, so must be 5 times farther away (inverse square law), 5000 parsecs. b) Star ...
... at different distances from us. Star A has parallax 10−3 ”, and radius 108 m. It appears 25 times brighter than Star B. a) What are the distances to stars A and B? Star A has d=1/p”=1000 parsecs. Star B is 25 times fainter, so must be 5 times farther away (inverse square law), 5000 parsecs. b) Star ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... - It relies on an objective classification – i.e. measurement-based classification - It is possible to classify every object by measuring the flux through standard filters. - Avoids ‘digitisation’ of the HR diagram, as classification not based on presence or absence of discrete features in spectrum. ...
... - It relies on an objective classification – i.e. measurement-based classification - It is possible to classify every object by measuring the flux through standard filters. - Avoids ‘digitisation’ of the HR diagram, as classification not based on presence or absence of discrete features in spectrum. ...
No Slide Title
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... The luminosity (L) of a star is the energy radiated from all of its surface in one second. The absolute magnitude (M) is used usually to measure the luminosity of the stars; it is related to the stellar luminosity by an approximate relation: L star M 2.5log ...
... The luminosity (L) of a star is the energy radiated from all of its surface in one second. The absolute magnitude (M) is used usually to measure the luminosity of the stars; it is related to the stellar luminosity by an approximate relation: L star M 2.5log ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... The difference between absolute magnitude, and apparent magnitude The rule for numbers that determine the brightness of stars How to interpret the H-R diagram. This includes comparing the characteristics of main sequence stars, giants, super giants, and white dwarfs ...
... The difference between absolute magnitude, and apparent magnitude The rule for numbers that determine the brightness of stars How to interpret the H-R diagram. This includes comparing the characteristics of main sequence stars, giants, super giants, and white dwarfs ...
Lecture 7 Stars and Galaxies and Nebula, (Oh My!) Feb 18 2003
... Clumps of old stars, about the same age and distance away. Found in the halo of our own galaxy (as well as the halo of other galaxies, but I digress). Very old stars. (low abundance of heavy metals) ...
... Clumps of old stars, about the same age and distance away. Found in the halo of our own galaxy (as well as the halo of other galaxies, but I digress). Very old stars. (low abundance of heavy metals) ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram Star Data Table
... which type of star? (hint: red giant, main sequence, white dwarf) ...
... which type of star? (hint: red giant, main sequence, white dwarf) ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 5
... 18. Which of the stars in the diagram above has the brightest absolute visual magnitude? ...
... 18. Which of the stars in the diagram above has the brightest absolute visual magnitude? ...
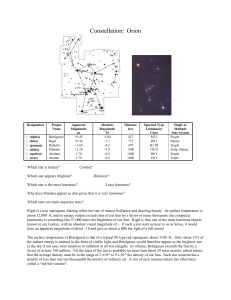
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
chapter 17 measuring the stars
... Astronomers use luminosity and surface temperature to classify stars Figure 17.13 plots luminosity versus temperature for well-known stars We abbreviate Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram to H-R Diagram o H-R Diagrams: A plot of luminosity against temperature (or spectral class) for a group of stars (see i ...
... Astronomers use luminosity and surface temperature to classify stars Figure 17.13 plots luminosity versus temperature for well-known stars We abbreviate Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram to H-R Diagram o H-R Diagrams: A plot of luminosity against temperature (or spectral class) for a group of stars (see i ...
Announcements
... Visible (Balmer) lines of H due to Electron transitions to 2nd energy level Medium Temperature Stars (~104K) -> hot enough for collisions to knock electron up to 2nd level, not hot enough to knock electron free of atom. ...
... Visible (Balmer) lines of H due to Electron transitions to 2nd energy level Medium Temperature Stars (~104K) -> hot enough for collisions to knock electron up to 2nd level, not hot enough to knock electron free of atom. ...
Distances to Stars: Parsecs and Light Years
... distance of 1.5 miles • The Light Year = (2.9979E+08 m/sec)*(3.156E+07 sec) = 9.461E+15 m. Alpha Centauri is 4.3 light years away • 1 parsec = 3.26 ly ...
... distance of 1.5 miles • The Light Year = (2.9979E+08 m/sec)*(3.156E+07 sec) = 9.461E+15 m. Alpha Centauri is 4.3 light years away • 1 parsec = 3.26 ly ...
File
... Absolute magnitude – how much light energy is being released from an object o The smaller, or more negative the number, the more energy is being released. Example A star called Becrux has an absolute magnitude of -3.92. Another star called Altair has an absolute magnitude of 2.22. Becrux is giving ...
... Absolute magnitude – how much light energy is being released from an object o The smaller, or more negative the number, the more energy is being released. Example A star called Becrux has an absolute magnitude of -3.92. Another star called Altair has an absolute magnitude of 2.22. Becrux is giving ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... Experiment: How does a stars’ mass affect how long stars live? Hypothesis: If a star has a (circle one: greater / lesser) mass, then its life will be longer. Independent Variable: ___________________________ (what variable will you be changing?) Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What ...
... Experiment: How does a stars’ mass affect how long stars live? Hypothesis: If a star has a (circle one: greater / lesser) mass, then its life will be longer. Independent Variable: ___________________________ (what variable will you be changing?) Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What ...
Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... Although we don’t see it because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
... Although we don’t see it because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... further means to measure the distance to far away stars in our galaxy (Spectroscopic parallax) RUNG 4 Procedure: •Determine the star’s spectral type from spectroscopy and measure the star’s apparent brightness. •Use the main sequence to get the star’s luminosity. •Use the Inverse Square Law for Br ...
... further means to measure the distance to far away stars in our galaxy (Spectroscopic parallax) RUNG 4 Procedure: •Determine the star’s spectral type from spectroscopy and measure the star’s apparent brightness. •Use the main sequence to get the star’s luminosity. •Use the Inverse Square Law for Br ...
Malmquist bias
The Malmquist bias is an effect in observational astronomy which leads to the preferential detection of intrinsically bright objects. It was first described in 1922 by Swedish astronomer Gunnar Malmquist (1893–1982), who then greatly elaborated upon this work in 1925. In statistics, this bias is referred to as a selection bias and affects the survey results in a brightness limited survey, where stars below a certain apparent brightness are not included. Since observed stars and galaxies appear dimmer when farther away, the brightness that is measured will fall off with distance until their brightness falls below the observational threshold. Objects which are more luminous, or intrinsically brighter, can be observed at a greater distance, creating a false trend of increasing intrinsic brightness, and other related quantities, with distance. This effect has led to many spurious claims in the field of astronomy. Properly correcting for these effects has become an area of great focus.