1 Molecular Cell Biology
... Large K+ concentration gradient ([K+]i:[K+]o ≈ 30) Plasma membrane contains spontaneously active K+ channels ⇒ K+ move freely out of cell As K+ moves out of cell, leaves negative charge build up ⇒ opposes further K+ exit At equilibrium, electrical force balances concentration gradient and electroche ...
... Large K+ concentration gradient ([K+]i:[K+]o ≈ 30) Plasma membrane contains spontaneously active K+ channels ⇒ K+ move freely out of cell As K+ moves out of cell, leaves negative charge build up ⇒ opposes further K+ exit At equilibrium, electrical force balances concentration gradient and electroche ...
magnesium sulfate (epsom salt)
... • Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. • Magnesium sulfate may be used orally or as a soak. Follow your doctor's instructions or the directions on the package. • To take magnesium sulfate ...
... • Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. • Magnesium sulfate may be used orally or as a soak. Follow your doctor's instructions or the directions on the package. • To take magnesium sulfate ...
Elucidating the complete reaction cycle for membrane
... Elucidating the complete reaction cycle for membrane-bound pyrophosphatases Craig Wilkinson, Nita Shah and Adrian Goldman ...
... Elucidating the complete reaction cycle for membrane-bound pyrophosphatases Craig Wilkinson, Nita Shah and Adrian Goldman ...
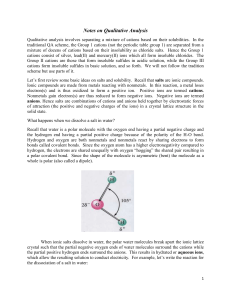
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... Those salts that dissociate into aqueous ions when placed in water are said to be soluble. Those salts that do not dissociate into aqueous ions (or dissociate to a very small extent – not enough to conduct an electric current) are said to be insoluble. For now we won’t be too concerned about the sol ...
... Those salts that dissociate into aqueous ions when placed in water are said to be soluble. Those salts that do not dissociate into aqueous ions (or dissociate to a very small extent – not enough to conduct an electric current) are said to be insoluble. For now we won’t be too concerned about the sol ...
ST110 Chemistry, Cellular Structure, and Function_BB
... difference, but usually not. A food calorie contains 4,184 joules. A can of soda containing 200 food calories contains 200,000 regular calories, or 200 kilocalories. A gallon of gasoline contains 31,000 kilocalories. • The same applies to exercise -- when a fitness chart says you burn about 100 calo ...
... difference, but usually not. A food calorie contains 4,184 joules. A can of soda containing 200 food calories contains 200,000 regular calories, or 200 kilocalories. A gallon of gasoline contains 31,000 kilocalories. • The same applies to exercise -- when a fitness chart says you burn about 100 calo ...
Practice Exam for learning objectives 1-21
... Practice Exam for Unit II 1. The DNA that codes for proteins that regulate the activity of structural genes is contained in a(n): a. operon b. regulatory gene c. inducer d. intron 2. An inducible operon is turned _______ unless a(n) _______ binds to the _______. a. on, inducer, repressor b. on, repr ...
... Practice Exam for Unit II 1. The DNA that codes for proteins that regulate the activity of structural genes is contained in a(n): a. operon b. regulatory gene c. inducer d. intron 2. An inducible operon is turned _______ unless a(n) _______ binds to the _______. a. on, inducer, repressor b. on, repr ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... All of life exists within an electric potential window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in ho ...
... All of life exists within an electric potential window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in ho ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... All of life exists within an electric potential window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in ho ...
... All of life exists within an electric potential window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in ho ...
Plant Structure and Function
... • Both apical and lateral meristems rely on totipotent cell divisions for growth ...
... • Both apical and lateral meristems rely on totipotent cell divisions for growth ...
MLAB 1315-Hematology Fall 2007 Keri Brophy
... hexose monophosphate shunt and glycolytic pathway ...
... hexose monophosphate shunt and glycolytic pathway ...
The Plant Kingdom - UNT's College of Education
... Apical Meristem (Produces new cells for growth) Zone of Elongation (Cells elongate allowing the root to grow longer) Zone of Maturation (Cells develop into tissues) ...
... Apical Meristem (Produces new cells for growth) Zone of Elongation (Cells elongate allowing the root to grow longer) Zone of Maturation (Cells develop into tissues) ...
Unit 5 Lesson 8
... Energy storage and transfer Cell division, and enlargement Promotes early root formation and growth Improves quality of fruits, vegetables, and grains Vital to seed formation Helps plants survive harsh winter conditions Increases water-use efficiency Hastens maturity ...
... Energy storage and transfer Cell division, and enlargement Promotes early root formation and growth Improves quality of fruits, vegetables, and grains Vital to seed formation Helps plants survive harsh winter conditions Increases water-use efficiency Hastens maturity ...
Parts of a Plant
... axillary bud - a bud that develops in the axil. flower - the reproductive unit of angiosperms. flower stalk - the structure that supports the flower. internode - the area of the stem between any two adjacent nodes. lateral shoot (branch) - an offshoot of the stem of a plant. leaf - an outgrowth of a ...
... axillary bud - a bud that develops in the axil. flower - the reproductive unit of angiosperms. flower stalk - the structure that supports the flower. internode - the area of the stem between any two adjacent nodes. lateral shoot (branch) - an offshoot of the stem of a plant. leaf - an outgrowth of a ...
1 - SchoolNotes
... 8. Describe the pH scale 9. Why does a coastal area have a moderate climate? 10. Describe polar covalent bonds 11. What contributes to acid rain? 12. If the pH of cytoplasm is 7.2 then the cytoplasm is _______ 13. What carbohydrate is found in the cell walls of plants? 14. What type of molecule is u ...
... 8. Describe the pH scale 9. Why does a coastal area have a moderate climate? 10. Describe polar covalent bonds 11. What contributes to acid rain? 12. If the pH of cytoplasm is 7.2 then the cytoplasm is _______ 13. What carbohydrate is found in the cell walls of plants? 14. What type of molecule is u ...
STUDY GUIDE –Intro to Cell Biology
... In dehydration synthesis, 2 monomers are brought together to make a dimer or polymer, this can only happen when water is removed. What is a monomer? Smallest sub unit or building block (ex= individual lego) What is a polymer? Polymers are large molecules made of many monomers (ex= huge lego house) W ...
... In dehydration synthesis, 2 monomers are brought together to make a dimer or polymer, this can only happen when water is removed. What is a monomer? Smallest sub unit or building block (ex= individual lego) What is a polymer? Polymers are large molecules made of many monomers (ex= huge lego house) W ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... 1. Compare and discuss how cells store energy and release energy using ATP. Be specific! You may draw the cycle. ...
... 1. Compare and discuss how cells store energy and release energy using ATP. Be specific! You may draw the cycle. ...
The following two questions relate to a cell that has an electrical
... 19. Consider the characteristics of an integral protein that is located within the interior of the plasma membrane. The amino acids of this protein that are embedded in the plasma membrane would likely have a. ionic side chains b. non-polar side chains c. polar side chains 20. Consider a poison that ...
... 19. Consider the characteristics of an integral protein that is located within the interior of the plasma membrane. The amino acids of this protein that are embedded in the plasma membrane would likely have a. ionic side chains b. non-polar side chains c. polar side chains 20. Consider a poison that ...
Transport in Plants I - Western Washington University
... …the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, – water (free) moves from a region of higher H2O concentration, to a region of lower H2O concentration, until in equilibrium, ...
... …the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, – water (free) moves from a region of higher H2O concentration, to a region of lower H2O concentration, until in equilibrium, ...
Assignment 5 Bioenergy/ Photosynthesis
... membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to dissipate back across the membrane via a protein complex called ATP Synthase (or I can make ATP doggoneitase) to yield an ATP molecule from ADP and Pi. D. The oxygen from ...
... membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to dissipate back across the membrane via a protein complex called ATP Synthase (or I can make ATP doggoneitase) to yield an ATP molecule from ADP and Pi. D. The oxygen from ...
Roots
... Hydrogen bonds among water molecules resist rupturing (cohesion) so water is pulled upward ...
... Hydrogen bonds among water molecules resist rupturing (cohesion) so water is pulled upward ...
Root, Stem, and Leaf Lecture
... • Tasty fruits and seeds are eaten and deposited in a nice pile of “fertilizer” • Stickery fruits hang on to fur and britches • Aerodynamic fruits are blown • Floaty fruits disperse by water ...
... • Tasty fruits and seeds are eaten and deposited in a nice pile of “fertilizer” • Stickery fruits hang on to fur and britches • Aerodynamic fruits are blown • Floaty fruits disperse by water ...
PACKAGE LEAFLET ALMAGEL A ATC code:AO2A B O2
... aluminium chloride. Under the effect of the alkaline intestinal content the latter is transformed into alkaline aluminium salts which are absorbed with difficulty and in practice do not change the concentration of aluminium ions in the blood. Aluminium hydroxide reduces the serum levels of the phosp ...
... aluminium chloride. Under the effect of the alkaline intestinal content the latter is transformed into alkaline aluminium salts which are absorbed with difficulty and in practice do not change the concentration of aluminium ions in the blood. Aluminium hydroxide reduces the serum levels of the phosp ...
P-glycoprotein Activation Monitored via ATP Hydrolysis and ATP
... upon P-glycoprotein activation for several structurally different drugs, including local anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release of inorganic phosphate in inside-out cellular vesicles of MDR1-transfected cells and AT ...
... upon P-glycoprotein activation for several structurally different drugs, including local anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release of inorganic phosphate in inside-out cellular vesicles of MDR1-transfected cells and AT ...
1 1) What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most
... A) Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. B) Enzymes display specificity for certain molecules with which they interact. C) Enzymes raise the activation energy for the reactions they catalyze. D) An enzyme may be used many times over for a specific reaction. ...
... A) Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. B) Enzymes display specificity for certain molecules with which they interact. C) Enzymes raise the activation energy for the reactions they catalyze. D) An enzyme may be used many times over for a specific reaction. ...
Magnesium in biology

Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must be bound to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.Over 300 enzymes require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including all enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other nucleotides to synthesize DNA and RNA.In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthesis.