Muscle sarcomere: A vs - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... "Crazy Glue": Strongest bonds are between Cytosine and Guanine, strong like Crazy Glue (3 H-bonds), whereas the A=T only have 2 H-bonds. ú This is relevant to DNA replication, as the weaker A=T will be the site where RNA primer makes the initial break. ...
... "Crazy Glue": Strongest bonds are between Cytosine and Guanine, strong like Crazy Glue (3 H-bonds), whereas the A=T only have 2 H-bonds. ú This is relevant to DNA replication, as the weaker A=T will be the site where RNA primer makes the initial break. ...
Forearm, Wrist, Hand Regions
... surfaces. Movement at the radiocarpal joint occurs primarily as result of sliding of the proximal carpal row in a direction opposite the direction of the distal movement. (i.e. carpals slide ulnarly with radial deviation; slide posteriorly with wrist flexion) To increase radiocarpal extension due to ...
... surfaces. Movement at the radiocarpal joint occurs primarily as result of sliding of the proximal carpal row in a direction opposite the direction of the distal movement. (i.e. carpals slide ulnarly with radial deviation; slide posteriorly with wrist flexion) To increase radiocarpal extension due to ...
Forearm and Wrist Regions
... surfaces. Movement at the radiocarpal joint occurs primarily as result of sliding of the proximal carpal row in a direction opposite the direction of the distal movement. (i.e. carpals slide ulnarly with radial deviation; slide posteriorly with wrist flexion) To increase radiocarpal extension due to ...
... surfaces. Movement at the radiocarpal joint occurs primarily as result of sliding of the proximal carpal row in a direction opposite the direction of the distal movement. (i.e. carpals slide ulnarly with radial deviation; slide posteriorly with wrist flexion) To increase radiocarpal extension due to ...
File
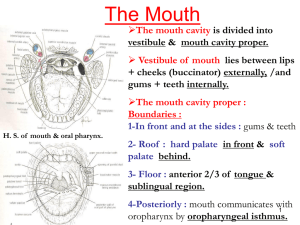
... The oral cavity has multiple functions: •it is the inlet for the digestive system involved with the initial processing of food, which is aided by secretions from salivary glands; •it manipulates sounds produced by the larynx and one outcome of this is speech; •it can be used for breathing because i ...
... The oral cavity has multiple functions: •it is the inlet for the digestive system involved with the initial processing of food, which is aided by secretions from salivary glands; •it manipulates sounds produced by the larynx and one outcome of this is speech; •it can be used for breathing because i ...
PDF - Anatomy Journal of Africa
... observed in studies such as Loukas’ et al (2013) which registered branch in 28% corpses the United States. Research conducted in Turkish population (Bekler et al, 2009) record percentage of occurrence of ulnar nerve contribution to the medial head of the triceps in 94.4% of the studied limbs. ...
... observed in studies such as Loukas’ et al (2013) which registered branch in 28% corpses the United States. Research conducted in Turkish population (Bekler et al, 2009) record percentage of occurrence of ulnar nerve contribution to the medial head of the triceps in 94.4% of the studied limbs. ...
sciatic ner
... clear as much as possible every point the doctor said it is important. As all anatomy lectures I will be exam oriented but as I know every student don’t have time to study all the sources so I will make understandable as much as I can and also try to cover most of the topic. ...
... clear as much as possible every point the doctor said it is important. As all anatomy lectures I will be exam oriented but as I know every student don’t have time to study all the sources so I will make understandable as much as I can and also try to cover most of the topic. ...
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Forearm cont.
... Deep: gluteal (L5, S1, S2) posterior gluteal line tuberosity on femur of iliac bone, dorsal surface of sacrum and ...
... Deep: gluteal (L5, S1, S2) posterior gluteal line tuberosity on femur of iliac bone, dorsal surface of sacrum and ...
Structure of the Posterior Abdominal Wall
... Catheter perforates arterial wall at a point where the artery turns downward toward the pelvis at the anterior abdominal wall. Catheter enters the thin-walled wider umbilical vein in stead of the thick-walled smaller artery. Catheter enters the thin-walled persistent urachus (urine is returned into ...
... Catheter perforates arterial wall at a point where the artery turns downward toward the pelvis at the anterior abdominal wall. Catheter enters the thin-walled wider umbilical vein in stead of the thick-walled smaller artery. Catheter enters the thin-walled persistent urachus (urine is returned into ...
Anatomy of the Head, Neck, Face, and Jaws.
... as the glenoid fossa, into which the mandible articulates. Just superior to this fossa, is a fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth o ...
... as the glenoid fossa, into which the mandible articulates. Just superior to this fossa, is a fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth o ...
ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FLAP
... reach the skin whereas in other cases they travel in the septum between the VL and RF. The more proximal portion of the anterolateral thigh skin is often supplied by a vessel from the transverse branch of the LCFA. Figure 1 This flap would necessarily have a shorter pedicle. ...
... reach the skin whereas in other cases they travel in the septum between the VL and RF. The more proximal portion of the anterolateral thigh skin is often supplied by a vessel from the transverse branch of the LCFA. Figure 1 This flap would necessarily have a shorter pedicle. ...
Ferrell autopsy report ()
... a blood soaked tee shirt, jeans, belt, underwear, and socks. Removal of the clothing reveals a welldeveloped, muscular male with multiple gunshot wound injuries as described below. There are corresponding defects in the tee shirt. Removal of the bags from the hands reveals small amount of liquid an ...
... a blood soaked tee shirt, jeans, belt, underwear, and socks. Removal of the clothing reveals a welldeveloped, muscular male with multiple gunshot wound injuries as described below. There are corresponding defects in the tee shirt. Removal of the bags from the hands reveals small amount of liquid an ...
A Rare Anatomical Variation of the Brachial Plexus Characterized by
... wide anatomical variations are expected [4, 5]. In this regard, some cases have reported many variations in the number of spinal nerves, communicating branches and ...
... wide anatomical variations are expected [4, 5]. In this regard, some cases have reported many variations in the number of spinal nerves, communicating branches and ...
Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Yeditepe Anatomy leg 2
... The deep fascia of the leg is called the crural fascia. The deep fascia surrounds the leg and is continuous above with the deep fascia of the thigh. Two intermuscular septa pass from its deep aspect to be attached to the fibula. These, together with the interosseous membrane, divide the leg into thr ...
... The deep fascia of the leg is called the crural fascia. The deep fascia surrounds the leg and is continuous above with the deep fascia of the thigh. Two intermuscular septa pass from its deep aspect to be attached to the fibula. These, together with the interosseous membrane, divide the leg into thr ...
Dissector Answers-Axilla-Shoulder-Arm
... into an anterior and posterior division. The posterior divisions of all three trunks unite to form the posterior cord. The anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunks unite to form the lateral cord. Finally, the anterior division of the inferior trunk forms the medial cord. (The medial aspe ...
... into an anterior and posterior division. The posterior divisions of all three trunks unite to form the posterior cord. The anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunks unite to form the lateral cord. Finally, the anterior division of the inferior trunk forms the medial cord. (The medial aspe ...
biology 2304/2101 human anatomy
... Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular system. Define a sarcomere and identify its major components Define and describe the neuromuscular junction and d ...
... Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular system. Define a sarcomere and identify its major components Define and describe the neuromuscular junction and d ...
INTRODUCTION - Austin Community College
... Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular system. Define a sarcomere and identify its major components Define and describe the neuromuscular junction and d ...
... Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle at the organ level List and describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscle Name and describe the functional unit of the muscular system. Define a sarcomere and identify its major components Define and describe the neuromuscular junction and d ...
The mandibular nerve
... The mylohyoid nerve is given off just before the mandibular foramen. It pierces the sphenomandibular ligament and runs in agroove ( the mylohyoid groove) which lies immediately below the mandibular foramen . the mylohyoid nerve may also contain sensory fibers that supply the skin of the chin and med ...
... The mylohyoid nerve is given off just before the mandibular foramen. It pierces the sphenomandibular ligament and runs in agroove ( the mylohyoid groove) which lies immediately below the mandibular foramen . the mylohyoid nerve may also contain sensory fibers that supply the skin of the chin and med ...
Anatomic considerations and the relationship between the piriformis
... Sciatica commonly defines a painful state resulting from the compression of the nerves forming the sciatic nerve (SN) by intervertebral disc herniation. This state may also occur as a result of non-discogenic disorders. Piriformis syndrome (PS) is one of the major causes of non-discogenic sciatica. ...
... Sciatica commonly defines a painful state resulting from the compression of the nerves forming the sciatic nerve (SN) by intervertebral disc herniation. This state may also occur as a result of non-discogenic disorders. Piriformis syndrome (PS) is one of the major causes of non-discogenic sciatica. ...
Anatomy of Larynx A Review - Otolaryngology Online Journal
... membrane of the larynx thus creating an internal framework. The fibroelastic membrane is divided into an upper and lower part by the presence of laryngeal ventricle. The upper membrane is also known as the quadrilateral membrane. It extends between the border of epiglottis and the arytenoid cartilag ...
... membrane of the larynx thus creating an internal framework. The fibroelastic membrane is divided into an upper and lower part by the presence of laryngeal ventricle. The upper membrane is also known as the quadrilateral membrane. It extends between the border of epiglottis and the arytenoid cartilag ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.