Neurotransmitters and Sleep
... example, one of the results of inhibiting sleep in lab animals is that they lose the ability to regulate their body temperature. In addition, brain and body temperature vary across stages of sleep. The basal forebrain area forms an important sleep and thermoregulation circuit with two nuclei in the ...
... example, one of the results of inhibiting sleep in lab animals is that they lose the ability to regulate their body temperature. In addition, brain and body temperature vary across stages of sleep. The basal forebrain area forms an important sleep and thermoregulation circuit with two nuclei in the ...
SLEEP AND EEG
... Adenosine is produced from the ATP during awake state (increased adenosine when we are awake more). Adenosine inhibits arousal center, this can bring NREM sleep (injection of adenosine induces normal sleep). Adenosine level decreases during sleep as brain uses this adenosine for replenishing its ...
... Adenosine is produced from the ATP during awake state (increased adenosine when we are awake more). Adenosine inhibits arousal center, this can bring NREM sleep (injection of adenosine induces normal sleep). Adenosine level decreases during sleep as brain uses this adenosine for replenishing its ...
Lecture 7 Rhythms of the Brain
... • Sleep appears to be necessary for survival. – All vertebrates and reptiles sleep, and fish and amphibians show periods of quiescence. – Sleep has not disappeared even where it interferes with survival, but not without adaptations. • Uni-hemisphere sleep, multiple naps, etc. ...
... • Sleep appears to be necessary for survival. – All vertebrates and reptiles sleep, and fish and amphibians show periods of quiescence. – Sleep has not disappeared even where it interferes with survival, but not without adaptations. • Uni-hemisphere sleep, multiple naps, etc. ...
presentation ( format)
... • Goes to bed at night, stares at ceiling for 4-5 hours. • Feels exhausted in the morning • No problems with roommates or outside noise • Hard to concentrate in classes due to fatigue. • Denies symptoms of depression/anxiety. ...
... • Goes to bed at night, stares at ceiling for 4-5 hours. • Feels exhausted in the morning • No problems with roommates or outside noise • Hard to concentrate in classes due to fatigue. • Denies symptoms of depression/anxiety. ...
The Relationship Between Insomnia and Major Depressive Disorder
... regular monitoring of sleep status may allow for treatment ...
... regular monitoring of sleep status may allow for treatment ...
z2f001152923s1 - American Psychological Association
... by A. G. Harvey et al., 2015, Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0038655 Supplementary Description of CBTI-BP CBTI-BP. During a treatment development phase, we found that the unique features of sleep in bipolar disorder necessitated modifications to CBT-I, includi ...
... by A. G. Harvey et al., 2015, Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0038655 Supplementary Description of CBTI-BP CBTI-BP. During a treatment development phase, we found that the unique features of sleep in bipolar disorder necessitated modifications to CBT-I, includi ...
REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder
... check if you have any other sleep problems contributing to the RBD, for example obstructive sleep apnoea. Most of the time this assessment will involve an overnight sleep study. This is done in a hospital and includes a video recording. ...
... check if you have any other sleep problems contributing to the RBD, for example obstructive sleep apnoea. Most of the time this assessment will involve an overnight sleep study. This is done in a hospital and includes a video recording. ...
Exam practice answers 1
... in the amount of stage 4 sleep experienced. Many also find it more difficult to feel refreshed on awakening. Lifestyle activities may play a role here, such as drinking more alcohol and putting on weight, which leads to snoring and frequent awakening. However, there is a lack of incisive research ev ...
... in the amount of stage 4 sleep experienced. Many also find it more difficult to feel refreshed on awakening. Lifestyle activities may play a role here, such as drinking more alcohol and putting on weight, which leads to snoring and frequent awakening. However, there is a lack of incisive research ev ...
Slide 1
... • Exaggerated startle response • Sleep Disturbance- (difficulty falling or staying asleep or restless sleep) ...
... • Exaggerated startle response • Sleep Disturbance- (difficulty falling or staying asleep or restless sleep) ...
Sleep Deficit and School Performance
... REM 2. Night Terrors - anxiety or fear that occurs during slow wave sleep 3. Sleep walking 4. Confusional arousals ...
... REM 2. Night Terrors - anxiety or fear that occurs during slow wave sleep 3. Sleep walking 4. Confusional arousals ...
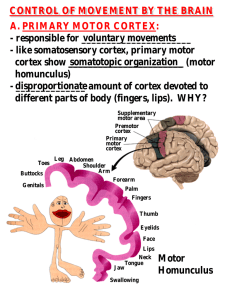
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... - projects to basal cholinergic system - desynchronized EEG of REM ...
... - projects to basal cholinergic system - desynchronized EEG of REM ...
(2014). Treating comorbid - Scientific Research Publishing
... Similarly, the best evidence for the non-pharmacological insomnia treatment in older adults exists for sleep restriction/sleep compression and stimulus control [25]-[30]. In particularly, the method of stimulus control appears to be effective which results in both the remission of insomnia in older ...
... Similarly, the best evidence for the non-pharmacological insomnia treatment in older adults exists for sleep restriction/sleep compression and stimulus control [25]-[30]. In particularly, the method of stimulus control appears to be effective which results in both the remission of insomnia in older ...
Rhythms of Waking and Sleep 2 Day Circadian Examples
... hallucinations. Often triggered by emotion. May have mutation of a gene which in turn reduces orexin (a “stayawake” transmitter) • Animal Model of narcolepsy allows research Several meds can decrease sleep attacks of narcolepsy: -stimulants like Ritalin or amphetamine or the ...
... hallucinations. Often triggered by emotion. May have mutation of a gene which in turn reduces orexin (a “stayawake” transmitter) • Animal Model of narcolepsy allows research Several meds can decrease sleep attacks of narcolepsy: -stimulants like Ritalin or amphetamine or the ...
The Use Of Medication In Autism
... intervention • Behavior has a negative impact on function • Medication-responsive problem • Benefits outweigh potential side effects • Understanding it is symptomatic treatment, not a cure • Not a substitute for appropriate educational and behavioral programming ...
... intervention • Behavior has a negative impact on function • Medication-responsive problem • Benefits outweigh potential side effects • Understanding it is symptomatic treatment, not a cure • Not a substitute for appropriate educational and behavioral programming ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file (28 KB )
... MBs, sleep-promoting neurons (e.g. 201Y) are normally most active at night, and wake promoting/sleep-inhibiting neurons (e.g. c309/MBSwitch) are normally most active during the day (diurnal influences are indicated by upward and downward deflections in sinusoids). Antagonistic signals from these two ...
... MBs, sleep-promoting neurons (e.g. 201Y) are normally most active at night, and wake promoting/sleep-inhibiting neurons (e.g. c309/MBSwitch) are normally most active during the day (diurnal influences are indicated by upward and downward deflections in sinusoids). Antagonistic signals from these two ...
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers
... • REM is called paradoxical sleep as brain waves are similar to waking state (Beta/Alpha) , but a person is deeply asleep and unable to move (muscle atonia) • Most vivid dreaming takes place during REM sleep • REM stage lengthens as night progresses • When deprived of REM sleep = REM rebound ...
... • REM is called paradoxical sleep as brain waves are similar to waking state (Beta/Alpha) , but a person is deeply asleep and unable to move (muscle atonia) • Most vivid dreaming takes place during REM sleep • REM stage lengthens as night progresses • When deprived of REM sleep = REM rebound ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF SLEEP By Dr. Mohammad
... • The diurnal change in melatonin secretion from serotonin in the pineal gland functions as a timing signal to coordinate events with the light– dark cycle, including the sleep–wake cycle. ...
... • The diurnal change in melatonin secretion from serotonin in the pineal gland functions as a timing signal to coordinate events with the light– dark cycle, including the sleep–wake cycle. ...
How much sleep do I need? Why is sleep important for good mental
... of our life. It helps us to feel well, focused and happy. Most people experience a bad night’s sleep now and again, but if you regularly don’t get enough sleep it can really affect how you feel and what you can get done during the day. ...
... of our life. It helps us to feel well, focused and happy. Most people experience a bad night’s sleep now and again, but if you regularly don’t get enough sleep it can really affect how you feel and what you can get done during the day. ...
2 - New Page 1
... • More time spent in Stage 4 and REM • Less time spent in Stages 1 and 2 • Rats die in 2-3 weeks if sleep deprived, 4-6 weeks if REM deprived • Deep, Stage 3-4, slow-wave (delta) sleep may be needed for recovery from oxidative stress • High metabolism during awake activity produces overabundance of ...
... • More time spent in Stage 4 and REM • Less time spent in Stages 1 and 2 • Rats die in 2-3 weeks if sleep deprived, 4-6 weeks if REM deprived • Deep, Stage 3-4, slow-wave (delta) sleep may be needed for recovery from oxidative stress • High metabolism during awake activity produces overabundance of ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... - projects to basal cholinergic system - desynchronized EEG of REM ...
... - projects to basal cholinergic system - desynchronized EEG of REM ...
Chapter 4 - States of Consciousness
... Describe the stages of sleep. Explain why REM sleep is also called paradoxical sleep. Define the sleep disorders of insomnia, narcolepsy, and apnea. Explain the theories of the nature and content of dreams. Explain the difference between substance abuse and substance ...
... Describe the stages of sleep. Explain why REM sleep is also called paradoxical sleep. Define the sleep disorders of insomnia, narcolepsy, and apnea. Explain the theories of the nature and content of dreams. Explain the difference between substance abuse and substance ...
Minh Tran - Dr Magrann
... peptide promotes wakefulness, inhibits REM sleep, and associates with motor control Narcoleptics generally do not have as many neurons that secrete hypocretin, which inhibits the ability to fully control alertness and accounts for tendency to fall asleep ...
... peptide promotes wakefulness, inhibits REM sleep, and associates with motor control Narcoleptics generally do not have as many neurons that secrete hypocretin, which inhibits the ability to fully control alertness and accounts for tendency to fall asleep ...