3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Devices & Internet - The Computer Engineers` Blog
... Guidelines for Planning Router Connectivity ...
... Guidelines for Planning Router Connectivity ...
Document
... managed when the migration is done in 3 phases: 1. Baseline inventory established -- all application elements are inventoried including source code, data files, test data, and test results 2. Migration process can now begin 3. Final system test, parallel runs, and production cutover phase ...
... managed when the migration is done in 3 phases: 1. Baseline inventory established -- all application elements are inventoried including source code, data files, test data, and test results 2. Migration process can now begin 3. Final system test, parallel runs, and production cutover phase ...
"Detection and mitigation of soft failure due to polarization-mode dispersion in optical networks"
... Optical rerouting using GMPLS has recently been demonstrated with IP routers and photonic cross connects in an installed dense WDM network [2]. In addition, coordination of the GMPLS control, measurement, and data planes has been used to ensure the quality of a 40 Gb/s WDM network that was impaired ...
... Optical rerouting using GMPLS has recently been demonstrated with IP routers and photonic cross connects in an installed dense WDM network [2]. In addition, coordination of the GMPLS control, measurement, and data planes has been used to ensure the quality of a 40 Gb/s WDM network that was impaired ...
Packet data in the Ericsson CDMA2000 radio access network
... and a fundamental channel (FCH) to provide an initial packet-data rate of 9.6 kbit/s. To ensure backward compatibility with cdmaOne, the fundamental channel in CDMA2000 is similar to that in cdmaOne. The fundamental channel is mainly used for voice services, but in CDMA2000 it also supports low-data ...
... and a fundamental channel (FCH) to provide an initial packet-data rate of 9.6 kbit/s. To ensure backward compatibility with cdmaOne, the fundamental channel in CDMA2000 is similar to that in cdmaOne. The fundamental channel is mainly used for voice services, but in CDMA2000 it also supports low-data ...
Architecting Information Centric ETSI-M2M systems
... Networking (CCN) rationale [11] that assumes hierarchical content names, receiver initiated sessions, content level security schema, and in-network caching mechanisms. The NDN architecture is born to natively support mobile applications and multicast data dissemination while, at the same time, to im ...
... Networking (CCN) rationale [11] that assumes hierarchical content names, receiver initiated sessions, content level security schema, and in-network caching mechanisms. The NDN architecture is born to natively support mobile applications and multicast data dissemination while, at the same time, to im ...
The OSI and TCP/IP Models
... • The Application layer of the TCP/IP Model encompasses the same functions as the Application, Presentation, and Session layers of the OSI Model. • The Transport layer of the TCP/IP Model functions the same as the Transport layer in OSI Model and part of Session layer. • The Internet of layer of the ...
... • The Application layer of the TCP/IP Model encompasses the same functions as the Application, Presentation, and Session layers of the OSI Model. • The Transport layer of the TCP/IP Model functions the same as the Transport layer in OSI Model and part of Session layer. • The Internet of layer of the ...
Resource Optimization of Spatial TDMA in Ad Hoc Radio Networks
... allocation when designing link access schemes. One access scheme for ad hoc networks is Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), in which the transmission resource of a radio frequency is divided into time slots, and a unit may transmit in one or several time slots. It is known that, although simple to ...
... allocation when designing link access schemes. One access scheme for ad hoc networks is Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), in which the transmission resource of a radio frequency is divided into time slots, and a unit may transmit in one or several time slots. It is known that, although simple to ...
Medium - Message
... In a network, when two or more stations attempt to transmit a packet across the network at the same time, a packet collision occurs. This is not uncommon in a shared medium such as an Ethernet that has many computers in the same network segment. When a packet collision occurs, the packets are either ...
... In a network, when two or more stations attempt to transmit a packet across the network at the same time, a packet collision occurs. This is not uncommon in a shared medium such as an Ethernet that has many computers in the same network segment. When a packet collision occurs, the packets are either ...
Network Layer
... • Pure flooding :: every incoming packet to a node is sent out on every outgoing line. – Obvious adjustment – do not send out on arriving link (assuming full-duplex links). – The routing algorithm can use a hop counter (e.g., TTL) to dampen the flooding. – Selective flooding :: only send on those li ...
... • Pure flooding :: every incoming packet to a node is sent out on every outgoing line. – Obvious adjustment – do not send out on arriving link (assuming full-duplex links). – The routing algorithm can use a hop counter (e.g., TTL) to dampen the flooding. – Selective flooding :: only send on those li ...
Slides - Indico
... – Operations divisions typically have strong resistance to change the network topology because of the potential for: • route flaps, and • drastic changes in the end-end packet latency (e.g., > 10ms) – For these reasons, while theoretically management-plane traffic and network engineering is a potent ...
... – Operations divisions typically have strong resistance to change the network topology because of the potential for: • route flaps, and • drastic changes in the end-end packet latency (e.g., > 10ms) – For these reasons, while theoretically management-plane traffic and network engineering is a potent ...
20060717-phoebus-almes
... In our early work, each of these transport connections is a conventional TCP connection Each transport-level gateway (depot) receives data from one connection and pipes it to the next connection in the chain ...
... In our early work, each of these transport connections is a conventional TCP connection Each transport-level gateway (depot) receives data from one connection and pipes it to the next connection in the chain ...
Lecture 8 - CS Smith
... 1KB pkt every 30 msec -> 33kB/sec thruput over 1 Gbps link network protocol limits use of physical resources! ...
... 1KB pkt every 30 msec -> 33kB/sec thruput over 1 Gbps link network protocol limits use of physical resources! ...
Introduction to Sensor Networks
... – X and Y co-ordinates are encoded by two 4-byte quantities. ...
... – X and Y co-ordinates are encoded by two 4-byte quantities. ...
The 27 level cascaded H-Bridge multilevel inverter
... Figure 3 shows the structure of an abstract neuron with n inputs. Each input channel i can transmit a real value xi. The primitive function f computed in the body of the abstract neuron can be selected arbitrarily. Usually the input channels have an associated weight, which means that the incoming i ...
... Figure 3 shows the structure of an abstract neuron with n inputs. Each input channel i can transmit a real value xi. The primitive function f computed in the body of the abstract neuron can be selected arbitrarily. Usually the input channels have an associated weight, which means that the incoming i ...
EECS 700: Network Security
... – It could send recursive queries to those name servers, thereby obliging them to find the answer and return it. – it could send iterative queries and possibly be referred to other name servers "closer" to the domain name it's looking for. – Current implementations are polite and do the latter, foll ...
... – It could send recursive queries to those name servers, thereby obliging them to find the answer and return it. – it could send iterative queries and possibly be referred to other name servers "closer" to the domain name it's looking for. – Current implementations are polite and do the latter, foll ...
Datacenter Network Topologies
... Novel Layer 2 solutions • TRILL – IETF standard in the making – Layer 2.5 – Switches are as “Routing Bridges” – Run IS-IS between them to compute multiple paths • ECMP to place packets on different flows! ...
... Novel Layer 2 solutions • TRILL – IETF standard in the making – Layer 2.5 – Switches are as “Routing Bridges” – Run IS-IS between them to compute multiple paths • ECMP to place packets on different flows! ...
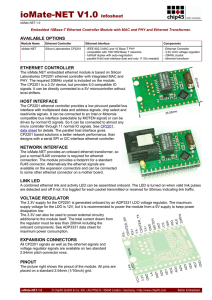
ioMate-NET V1.0 Infosheet
... In this manual are descriptions for copyrighted products that are not explicitly indicated as such. The absence of the trademark (™) and copyright (©) symbols does not imply that a product is not protected. Additionally, registered patents and trademarks are similarly not expressly indicated in this ...
... In this manual are descriptions for copyrighted products that are not explicitly indicated as such. The absence of the trademark (™) and copyright (©) symbols does not imply that a product is not protected. Additionally, registered patents and trademarks are similarly not expressly indicated in this ...
Networking
... Conversion of application-level data is left up to the presentation layer. But hold on !!! How do lower level layers communicate if they all represent values differently ? (data length fields in headers) A fixed byte order is used (called network byte order) for all control data. ...
... Conversion of application-level data is left up to the presentation layer. But hold on !!! How do lower level layers communicate if they all represent values differently ? (data length fields in headers) A fixed byte order is used (called network byte order) for all control data. ...
Chapter 3
... UDP: more • often used for streaming multimedia apps Length, in – loss tolerant bytes of UDP segment, – rate sensitive including • reliable transfer over header UDP: add reliability at application layer – application-specific error recovery! ...
... UDP: more • often used for streaming multimedia apps Length, in – loss tolerant bytes of UDP segment, – rate sensitive including • reliable transfer over header UDP: add reliability at application layer – application-specific error recovery! ...