Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis
... • The Managed Devices contain the SNMP Agent and can consist of routers, switches, hubs, printers. They are responsible for collecting information and making it available to the NMSs. • The Agents contain software that have knowledge of management information and translates this information into a ...
... • The Managed Devices contain the SNMP Agent and can consist of routers, switches, hubs, printers. They are responsible for collecting information and making it available to the NMSs. • The Agents contain software that have knowledge of management information and translates this information into a ...
Optical Burst Switching.pdf
... Internet. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different networks. When data comes in on one of the lines, the router reads the address information in the packet to determine its ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table, it directs the packet to the next net ...
... Internet. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different networks. When data comes in on one of the lines, the router reads the address information in the packet to determine its ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table, it directs the packet to the next net ...
Slide 1
... – Use the network distributions to calculate similarity scores for the classes – Use the similarity scores to cluster the classes ...
... – Use the network distributions to calculate similarity scores for the classes – Use the similarity scores to cluster the classes ...
Packet switching
... – A header with information, such as destination address, source address, time to live (TTL), protocol. – A payload: The data to be sent. This may be a packet of an upper layer. ...
... – A header with information, such as destination address, source address, time to live (TTL), protocol. – A payload: The data to be sent. This may be a packet of an upper layer. ...
document
... Prevention – Policies & Assurances Violations of policy may define intrusion Except: ...
... Prevention – Policies & Assurances Violations of policy may define intrusion Except: ...
Optical Packet/Burst Switching
... However, the deployment of Ethernet in core networks faces problems such as low resource utilization and large recovery times after changes in the network topology or in the traffic demand. ...
... However, the deployment of Ethernet in core networks faces problems such as low resource utilization and large recovery times after changes in the network topology or in the traffic demand. ...
OSI model
... After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: Understand the rationale for the existence of networks. Distinguish between the three types of networks: LANs, MANs, and WANs. Understand the OSI model and TCP/IP. List different connecting devices and the OSI layers in which each device oper ...
... After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: Understand the rationale for the existence of networks. Distinguish between the three types of networks: LANs, MANs, and WANs. Understand the OSI model and TCP/IP. List different connecting devices and the OSI layers in which each device oper ...
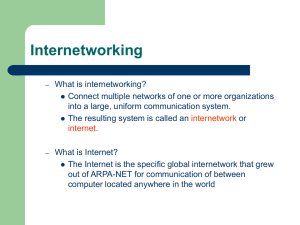
Internetworking
... What is internetworking? Connect multiple networks of one or more organizations into a large, uniform communication system. The resulting system is called an internetwork or internet. ...
... What is internetworking? Connect multiple networks of one or more organizations into a large, uniform communication system. The resulting system is called an internetwork or internet. ...
An Analytics Approach to Traffic Analysis in Network Virtualization
... switches are re-organized into trace slices that represent the life-time of packets. – offers versatile analytics features such as clustering, ranking, querying, verification as well as a graphical ...
... switches are re-organized into trace slices that represent the life-time of packets. – offers versatile analytics features such as clustering, ranking, querying, verification as well as a graphical ...
Slides - Nipun Arora
... switches are re-organized into trace slices that represent the life-time of packets. – offers versatile analytics features such as clustering, ranking, querying, verification as well as a graphical ...
... switches are re-organized into trace slices that represent the life-time of packets. – offers versatile analytics features such as clustering, ranking, querying, verification as well as a graphical ...
Networking Components
... Can integrate LANs and WANs running at different speeds and protocols. Operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI Model. For enterprise and home use Cost: $15 and up ...
... Can integrate LANs and WANs running at different speeds and protocols. Operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI Model. For enterprise and home use Cost: $15 and up ...
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications
... Ñ Control information is added to user data at each layer Ñ Transport layer may fragment user data Ñ Each fragment has a transport header added Ñ Destination SAP Ñ Sequence number Ñ Error detection code ...
... Ñ Control information is added to user data at each layer Ñ Transport layer may fragment user data Ñ Each fragment has a transport header added Ñ Destination SAP Ñ Sequence number Ñ Error detection code ...
CSCI6268L10 - Computer Science
... • IP is “best effort” – There is no tracking of packets – If something is dropped… oh well – If one fragment is dropped, many transport layer protocols (like TCP) will consider the whole thing lost and not ACK – This seems bad, but it’s one of the biggest successes of IP – UDP is IP with ports, so i ...
... • IP is “best effort” – There is no tracking of packets – If something is dropped… oh well – If one fragment is dropped, many transport layer protocols (like TCP) will consider the whole thing lost and not ACK – This seems bad, but it’s one of the biggest successes of IP – UDP is IP with ports, so i ...
Chapter 5 : The Internet: Addressing & Services
... CIX (Commercial Internet eXchange) was developed to provide commercial internetworking ...
... CIX (Commercial Internet eXchange) was developed to provide commercial internetworking ...
Midterm Review - UTK-EECS
... Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Protocol layers: rationale behind layering design, the Internet 5-layer protocol stack, difference between Internet and OSI protocol stacks, encapsulation ...
... Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Protocol layers: rationale behind layering design, the Internet 5-layer protocol stack, difference between Internet and OSI protocol stacks, encapsulation ...
23-wrapup
... • Little on undergraduate material • Supposedly you already know this, though some revisiting/overlap is unavoidable • Focus on the why, not the what ...
... • Little on undergraduate material • Supposedly you already know this, though some revisiting/overlap is unavoidable • Focus on the why, not the what ...
Networking | computer Network | TCP/IP
... • Little on undergraduate material • Supposedly you already know this, though some revisiting/overlap is unavoidable • Focus on the why, not the what ...
... • Little on undergraduate material • Supposedly you already know this, though some revisiting/overlap is unavoidable • Focus on the why, not the what ...
Chapter 4
... ‘Internet’ developed from the military network of the USA Department of Defense called ARPANET (Advanced research project agency). ...
... ‘Internet’ developed from the military network of the USA Department of Defense called ARPANET (Advanced research project agency). ...
Introduction to Distributed Systems & Networking
... Data Link: sending “frames” of bits and error detection Network Layer:” routing packets to the destination Transport Layer: reliable transmission of messages, disassembly/assembly, ordering, retransmission of lost packets • Session Layer; really part of transport, typ. Not impl. • Presentation Layer ...
... Data Link: sending “frames” of bits and error detection Network Layer:” routing packets to the destination Transport Layer: reliable transmission of messages, disassembly/assembly, ordering, retransmission of lost packets • Session Layer; really part of transport, typ. Not impl. • Presentation Layer ...
The Infrastructure Technologies
... • Messages have header and trailer carry information for delivering and ensuring the integrity of the message • These are used by application and communication protocols • The electronic form of a message is a signal ...
... • Messages have header and trailer carry information for delivering and ensuring the integrity of the message • These are used by application and communication protocols • The electronic form of a message is a signal ...
Internet History and Architectural Principles
... Q1: How should the network allocate resources to users? Q2: How should functionality be divided between the edge and the core? ...
... Q1: How should the network allocate resources to users? Q2: How should functionality be divided between the edge and the core? ...
TCP Review - Stanford University
... – Calculate Fi for each packet, or time it would complete being transmitted if we served just that flow – Next packet to transmit is one with lowest Fi timestamp – Packets will be sent out within one maximum packet transmission time of perfect “fairness” ...
... – Calculate Fi for each packet, or time it would complete being transmitted if we served just that flow – Next packet to transmit is one with lowest Fi timestamp – Packets will be sent out within one maximum packet transmission time of perfect “fairness” ...