Author Guidelines for 8 - Al
... Abstract—This paper shows the development in public-key digital signature schemes which are actually based on non deterministic polynomial mathematical hard problems (NP-Hard). In general, most of the currently used digital signature cryptosystems are computationally expensive with relatively length ...
... Abstract—This paper shows the development in public-key digital signature schemes which are actually based on non deterministic polynomial mathematical hard problems (NP-Hard). In general, most of the currently used digital signature cryptosystems are computationally expensive with relatively length ...
Chapter 10: Electronic Commerce Security
... today as Caesar Cyphers. The simplest replaces A with B, B with C etc. This is called a one-rotate code. The following is encrypted using a simple Caesar rotation cypher. See if you can decrypt it: ...
... today as Caesar Cyphers. The simplest replaces A with B, B with C etc. This is called a one-rotate code. The following is encrypted using a simple Caesar rotation cypher. See if you can decrypt it: ...
Introduction to quantum cryptography
... • and telescopes with 8-inch mirrors to send and receive photons over the air. • Using the quantum transmitted key messages were encrypted at the rate 1 million bits per second. The speed was impressive but the distance between two NIST buildings was only 730 ...
... • and telescopes with 8-inch mirrors to send and receive photons over the air. • Using the quantum transmitted key messages were encrypted at the rate 1 million bits per second. The speed was impressive but the distance between two NIST buildings was only 730 ...
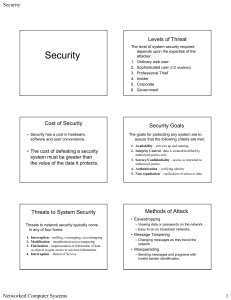
Do you know someone may be watching you?
... sources that are hacking into your system by using various techniques in computer science and mathematics. ...
... sources that are hacking into your system by using various techniques in computer science and mathematics. ...
Getting Security Right in Wireless Sensor Networks
... Fortunately, there are powerful tools for building secure, robust wireless communications networks. It takes diligence and attention to detail, but there is nothing fundamentally hard about it. Ciphers and Nonces The most basic cryptographic tool is the block cipher. As an example, AES-128 is a part ...
... Fortunately, there are powerful tools for building secure, robust wireless communications networks. It takes diligence and attention to detail, but there is nothing fundamentally hard about it. Ciphers and Nonces The most basic cryptographic tool is the block cipher. As an example, AES-128 is a part ...
Mod_7-Ch11
... – In cryptography, ciphertext (or cyphertext) is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm. Plaintext is what you have before encryption, and ciphertext is the encrypted result. ...
... – In cryptography, ciphertext (or cyphertext) is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm. Plaintext is what you have before encryption, and ciphertext is the encrypted result. ...
APT-Tactics
... We detail the typical intentions of an attacker and the tools and processes they would leverage to attain these goals. Lastly, the course presents key approaches to detect and terminate the process of an APT, and the infrastructure required for effective incident response. ...
... We detail the typical intentions of an attacker and the tools and processes they would leverage to attain these goals. Lastly, the course presents key approaches to detect and terminate the process of an APT, and the infrastructure required for effective incident response. ...
Section2.1notes
... Cryptanalysis of Shift Ciphers As the last two examples illustrate, one must know the key k used in a shift cipher when deciphering a message. This leads to an important question. How can we decipher a message in a shift cipher if we do not know the key k ? Cryptanalysis is the process of trying to ...
... Cryptanalysis of Shift Ciphers As the last two examples illustrate, one must know the key k used in a shift cipher when deciphering a message. This leads to an important question. How can we decipher a message in a shift cipher if we do not know the key k ? Cryptanalysis is the process of trying to ...
Enhancement of Security through a Cryptographic Algorithm
... Using this Decryption NNA (Natural number algorithm) private key technique, we can encrypt any size of file, as well as any kind of file, as NNA protocol can be implemented to any file as each of the characters are represented by natural numbers so any type of message can be sent. There might be lit ...
... Using this Decryption NNA (Natural number algorithm) private key technique, we can encrypt any size of file, as well as any kind of file, as NNA protocol can be implemented to any file as each of the characters are represented by natural numbers so any type of message can be sent. There might be lit ...
Packaging Information: Data Compression and
... encoded ciphertext Decryption keys are used to decode ciphertext and recover the original plaintext Decryption keys are sometimes discovered by brute force methods employing computers to search large potential key spaces ...
... encoded ciphertext Decryption keys are used to decode ciphertext and recover the original plaintext Decryption keys are sometimes discovered by brute force methods employing computers to search large potential key spaces ...
Lecture 6: Computational Security 1 Vernam Cipher (1917)
... 1. Fix an integer l > 0. Then the message space M, key space K, and ciphertext space C are all equal to {0, 1}l . 2. The key-generation algorithm Gen works by choosing a string k from {0, 1}l according to uniform distribution. 3. Encryption Enc works as follows: given a key k ∈ {0, 1}l and a message ...
... 1. Fix an integer l > 0. Then the message space M, key space K, and ciphertext space C are all equal to {0, 1}l . 2. The key-generation algorithm Gen works by choosing a string k from {0, 1}l according to uniform distribution. 3. Encryption Enc works as follows: given a key k ∈ {0, 1}l and a message ...
Section 2.1: Shift Ciphers and Modular Arithmetic
... • As the last two examples illustrate, one must know the key k used in a shift cipher when deciphering a message. This leads to an important question. How can we decipher a message in a shift cipher if we do not know the key k? Cryptanalysis is the process of trying to break a cipher by finding its ...
... • As the last two examples illustrate, one must know the key k used in a shift cipher when deciphering a message. This leads to an important question. How can we decipher a message in a shift cipher if we do not know the key k? Cryptanalysis is the process of trying to break a cipher by finding its ...
Codes, Ciphers, and Cryptography
... Algorithm—shift the alphabet. Key—how many places to shift! Thus, there are 26 keys for this cipher. ...
... Algorithm—shift the alphabet. Key—how many places to shift! Thus, there are 26 keys for this cipher. ...
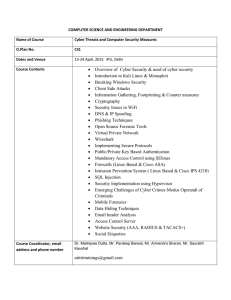
Course Learning Objectives:
... security model to prevent, detect and recover from the attacks. (ABET Outcomes: a, c, e, j, k) 2. Encrypt and decrypt messages using block ciphers, sign and verify messages using well known signature generation and verification algorithms. (ABET Outcomes: c, e, k) 3. Analyze existing authentication ...
... security model to prevent, detect and recover from the attacks. (ABET Outcomes: a, c, e, j, k) 2. Encrypt and decrypt messages using block ciphers, sign and verify messages using well known signature generation and verification algorithms. (ABET Outcomes: c, e, k) 3. Analyze existing authentication ...
(pdf)
... In the classical explanation of cryptography, Alice wishes to write a message to Bob, but Eve continues to intercept her messages. Alice and Bob decide to encrypt their messages. Alice and Bob can meet in person and exchange a key. With this information, they can both encrypt and decrypt messages to ...
... In the classical explanation of cryptography, Alice wishes to write a message to Bob, but Eve continues to intercept her messages. Alice and Bob decide to encrypt their messages. Alice and Bob can meet in person and exchange a key. With this information, they can both encrypt and decrypt messages to ...
CH 8 – Review - WordPress.com
... Public and private key are created using – very large prime numbers Asymmetric encryption uses – both a public key and a private key The author of the file creates a digital signature by running a program known as a – hashtag function veriSign is an example of a – certification authority who or what ...
... Public and private key are created using – very large prime numbers Asymmetric encryption uses – both a public key and a private key The author of the file creates a digital signature by running a program known as a – hashtag function veriSign is an example of a – certification authority who or what ...
Public Key Encryption
... suitable for processing large streams of data. The disadvantage of symmetric cryptography is that it presumes two parties have agreed on a key and been able to exchange that key in a secure manner prior to communication. This is a significant challenge. Thus, symmetric algorithms are usually mixed w ...
... suitable for processing large streams of data. The disadvantage of symmetric cryptography is that it presumes two parties have agreed on a key and been able to exchange that key in a secure manner prior to communication. This is a significant challenge. Thus, symmetric algorithms are usually mixed w ...
Cryptanalysis

Cryptanalysis (from the Greek kryptós, ""hidden"", and analýein, ""to loosen"" or ""to untie"") is the study of analyzing information systems in order to study the hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown.In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation.Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced computerized schemes of the present. Methods for breaking modern cryptosystems often involve solving carefully constructed problems in pure mathematics, the best-known being integer factorization.