29 Electronic Response to External Perturbations
... an external scalar potential and will derive general expressions that relate the dielectric function to the density–density response function and the dynamical structure factor introduced in the previous chapter. This will then allow us to get approximate expressions for the frequency and wave numbe ...
... an external scalar potential and will derive general expressions that relate the dielectric function to the density–density response function and the dynamical structure factor introduced in the previous chapter. This will then allow us to get approximate expressions for the frequency and wave numbe ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... There are a number of heuristic thought experiments that predict that electromagnetic and gravitational phenomena unify as the wavelength of a photon approaches the Planck length [5,6], since at this wavelength a quantum of light reaches an energy density comparable to a black hole of about this siz ...
... There are a number of heuristic thought experiments that predict that electromagnetic and gravitational phenomena unify as the wavelength of a photon approaches the Planck length [5,6], since at this wavelength a quantum of light reaches an energy density comparable to a black hole of about this siz ...
Transport of indirect excitons in high magnetic fields
... Composite bosons in the high magnetic field regime are particles with remarkable properties. In contrast to regular composite particles, their mass is determined not by the sum of the masses of their constituents, but by the effect of the magnetic field [1–4]. Such peculiarity should significantly m ...
... Composite bosons in the high magnetic field regime are particles with remarkable properties. In contrast to regular composite particles, their mass is determined not by the sum of the masses of their constituents, but by the effect of the magnetic field [1–4]. Such peculiarity should significantly m ...
slides:pptx - Experimental Elementary Particle Physics Group
... experiments and theory Comparison at the level of distributions ATLAS and CMS will unfold experimental effects and limitations independently – different ...
... experiments and theory Comparison at the level of distributions ATLAS and CMS will unfold experimental effects and limitations independently – different ...
LCAO principles
... polarisation of the valence states, but this is probably not the dominant term. The unpaired electron in the bond-centre is nodal at the muonium, so there should be zero isotropic hyperfine interaction in this form, but this is not the case – for the bondcentre, the isotropic contribution to the hyp ...
... polarisation of the valence states, but this is probably not the dominant term. The unpaired electron in the bond-centre is nodal at the muonium, so there should be zero isotropic hyperfine interaction in this form, but this is not the case – for the bondcentre, the isotropic contribution to the hyp ...
(pdf)
... beds with randomized particle configurations created via different schemes to obtain different microstructural details, and in inhomogeneous beds of randomized particle configurations created in three different ways. All the simulations were performed in fixed beds of particles in periodic domains, with t ...
... beds with randomized particle configurations created via different schemes to obtain different microstructural details, and in inhomogeneous beds of randomized particle configurations created in three different ways. All the simulations were performed in fixed beds of particles in periodic domains, with t ...
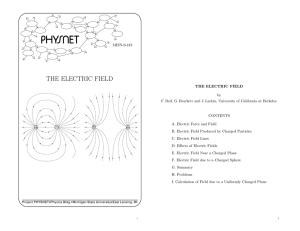
electric charge
... 6. Charge is conserved – In isolated system, total charge does not charge with time, though individual charges may charge i.e. charge can neither be created nor destroyed. It therefore, follows that simultaneously equal quantities of positive and negative charge can appear or disappear. This is what ...
... 6. Charge is conserved – In isolated system, total charge does not charge with time, though individual charges may charge i.e. charge can neither be created nor destroyed. It therefore, follows that simultaneously equal quantities of positive and negative charge can appear or disappear. This is what ...
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: UNDERSTANDING ELECTRIC FIELD-ENHANCED TRANSPORT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF
... including electrostatic force, image force and van der Waals force, are accounted for in the simulation. Using both experiment and simulation the effects of the particle size, electric field intensity, and the convective flow on coverage selectivity have been investigated. Coverage selectivity is mo ...
... including electrostatic force, image force and van der Waals force, are accounted for in the simulation. Using both experiment and simulation the effects of the particle size, electric field intensity, and the convective flow on coverage selectivity have been investigated. Coverage selectivity is mo ...
Electrokinetic colloid patterning characterization with a
... FIGURE A3 - Analysis data for experiment 1.................................................................. 76 FIGURE A4 - Analysis data for experiment 8.................................................................. 77 FIGURE A5 - Analysis data for experiment 9.................................. ...
... FIGURE A3 - Analysis data for experiment 1.................................................................. 76 FIGURE A4 - Analysis data for experiment 8.................................................................. 77 FIGURE A5 - Analysis data for experiment 9.................................. ...
Chapter 21 The Electric Field I: Discrete Charge Distributions
... (c) False. Electric field lines intersect any point in space occupied by a point charge. (d) True. An electric field partially polarizes the molecules; resulting in the separation of their charges and the creation of electric dipole moments. 17 ••• [SSM] Two molecules have dipole moments of equal ma ...
... (c) False. Electric field lines intersect any point in space occupied by a point charge. (d) True. An electric field partially polarizes the molecules; resulting in the separation of their charges and the creation of electric dipole moments. 17 ••• [SSM] Two molecules have dipole moments of equal ma ...
Dynamics of cold Fermi atoms in one
... framework of a microscopic approach directly by taking into account the electron-electron interactions and the electron-environment coupling. Both approaches have weak points: the first, phenomenological, model contains free parameters – the relevant relaxation constants, which may only be extracted ...
... framework of a microscopic approach directly by taking into account the electron-electron interactions and the electron-environment coupling. Both approaches have weak points: the first, phenomenological, model contains free parameters – the relevant relaxation constants, which may only be extracted ...
An Introduction to Mass Spectrometry
... (amu) and the dalton (Da). The amu is no longer acceptable because there are conflicting definitions. The dalton is frequently used for polymers, peptides and other large molecules. The elementary charge unit is defined as z is an integer equal to the number of electrons lost (or gained for negative ...
... (amu) and the dalton (Da). The amu is no longer acceptable because there are conflicting definitions. The dalton is frequently used for polymers, peptides and other large molecules. The elementary charge unit is defined as z is an integer equal to the number of electrons lost (or gained for negative ...
Lepton
A lepton is an elementary, half-integer spin (spin 1⁄2) particle that does not undergo strong interactions, but is subject to the Pauli exclusion principle. The best known of all leptons is the electron, which is directly tied to all chemical properties. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons), and neutral leptons (better known as neutrinos). Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed.There are six types of leptons, known as flavours, forming three generations. The first generation is the electronic leptons, comprising the electron (e−) and electron neutrino (νe); the second is the muonic leptons, comprising the muon (μ−) and muon neutrino (νμ); and the third is the tauonic leptons, comprising the tau (τ−) and the tau neutrino (ντ). Electrons have the least mass of all the charged leptons. The heavier muons and taus will rapidly change into electrons through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state. Thus electrons are stable and the most common charged lepton in the universe, whereas muons and taus can only be produced in high energy collisions (such as those involving cosmic rays and those carried out in particle accelerators).Leptons have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, spin, and mass. Unlike quarks however, leptons are not subject to the strong interaction, but they are subject to the other three fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism (excluding neutrinos, which are electrically neutral), and the weak interaction. For every lepton flavor there is a corresponding type of antiparticle, known as antilepton, that differs from the lepton only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. However, according to certain theories, neutrinos may be their own antiparticle, but it is not currently known whether this is the case or not.The first charged lepton, the electron, was theorized in the mid-19th century by several scientists and was discovered in 1897 by J. J. Thomson. The next lepton to be observed was the muon, discovered by Carl D. Anderson in 1936, which was classified as a meson at the time. After investigation, it was realized that the muon did not have the expected properties of a meson, but rather behaved like an electron, only with higher mass. It took until 1947 for the concept of ""leptons"" as a family of particle to be proposed. The first neutrino, the electron neutrino, was proposed by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930 to explain certain characteristics of beta decay. It was first observed in the Cowan–Reines neutrino experiment conducted by Clyde Cowan and Frederick Reines in 1956. The muon neutrino was discovered in 1962 by Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger, and the tau discovered between 1974 and 1977 by Martin Lewis Perl and his colleagues from the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The tau neutrino remained elusive until July 2000, when the DONUT collaboration from Fermilab announced its discovery.Leptons are an important part of the Standard Model. Electrons are one of the components of atoms, alongside protons and neutrons. Exotic atoms with muons and taus instead of electrons can also be synthesized, as well as lepton–antilepton particles such as positronium.