DS35676681
... range of each other possible. 1.2 Some Issues in MANET Network An ad hoc network is a dynamic type of network with similarities and great differences to its parent fixed communication network. The properties of an ad hoc network will define its shortcomings and highlight security challenges [4] [5] ...
... range of each other possible. 1.2 Some Issues in MANET Network An ad hoc network is a dynamic type of network with similarities and great differences to its parent fixed communication network. The properties of an ad hoc network will define its shortcomings and highlight security challenges [4] [5] ...
Multicast - Virginia Tech
... •How to identify the receivers of a multicast datagram? •How to address a datagram sent to these receivers? Each multicast datagram to carry the IP addresses of all recipients? Not scalable for large number of recipients Use address indirection A single identifier used for a group of receivers ...
... •How to identify the receivers of a multicast datagram? •How to address a datagram sent to these receivers? Each multicast datagram to carry the IP addresses of all recipients? Not scalable for large number of recipients Use address indirection A single identifier used for a group of receivers ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Slide 1
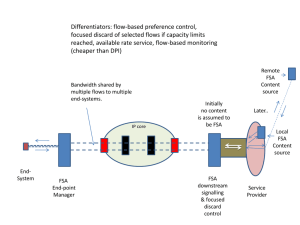
... For a minority of the most stringent applications (e.g. Broadcast TV or financial data applications), it is very unlikely that 1:N or even 1:1 network based protection switching will provide the required level of performance. For these applications the customer may require two diverse physical paths ...
... For a minority of the most stringent applications (e.g. Broadcast TV or financial data applications), it is very unlikely that 1:N or even 1:1 network based protection switching will provide the required level of performance. For these applications the customer may require two diverse physical paths ...
COMP211_Topic5_Network
... IPv6 datagram format priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” ...
... IPv6 datagram format priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” ...
ppt
... layering of abstractions: don’t sweat the details of the lower layer, only deal with lower layers ...
... layering of abstractions: don’t sweat the details of the lower layer, only deal with lower layers ...
AV200 Powerline Ethernet Wall Mount
... • Priority classification according to 802.1P tags, IP coding (IPv4 or IPv6) or TCP source/destination ports • Optimized support for broadcast and multicast traffic • MAC filtering - can discard Ethernet frames if they come from a source MAC address which is not present in a list of allowed MAC addr ...
... • Priority classification according to 802.1P tags, IP coding (IPv4 or IPv6) or TCP source/destination ports • Optimized support for broadcast and multicast traffic • MAC filtering - can discard Ethernet frames if they come from a source MAC address which is not present in a list of allowed MAC addr ...
Exploration CCNA4 - College of DuPage
... – Configure DHCP in an Enterprise branch network. This includes being able to explain DHCP features and benefits, the differences between BOOTP and DHCP, DHCP operation: and configuring, verifying, and troubleshooting DHCP. – Configure NAT on a Cisco router. This includes explaining key features and ...
... – Configure DHCP in an Enterprise branch network. This includes being able to explain DHCP features and benefits, the differences between BOOTP and DHCP, DHCP operation: and configuring, verifying, and troubleshooting DHCP. – Configure NAT on a Cisco router. This includes explaining key features and ...
Introduction - School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... – Self-healing - mechanisms that allow to detect, localize, and repair failures automatically; primarily distinguished by the cause of the failure – Self-configuration - methods for (re-)generating adequate configurations depending on the current situation in terms of environmental circumstances, e. ...
... – Self-healing - mechanisms that allow to detect, localize, and repair failures automatically; primarily distinguished by the cause of the failure – Self-configuration - methods for (re-)generating adequate configurations depending on the current situation in terms of environmental circumstances, e. ...
Cisco Unified Fabric with Automation: Acronyms and Abbreviations
... To provide a network overlay, leaf nodes must be aware of virtual machine network information. VDP is an IEEE protocol and communicates network information about a virtual machine from the virtual switch to the leaf switch; the leaf switch subsequently interprets this information and instantiates th ...
... To provide a network overlay, leaf nodes must be aware of virtual machine network information. VDP is an IEEE protocol and communicates network information about a virtual machine from the virtual switch to the leaf switch; the leaf switch subsequently interprets this information and instantiates th ...
Network Layer - Donald Bren School of Information and Computer
... DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol goal: allow host to dynamically obtain its IP address from network ...
... DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol goal: allow host to dynamically obtain its IP address from network ...
EE 122: Introduction To Communication Networks
... capacity for all of them at their peak transmission rate ...
... capacity for all of them at their peak transmission rate ...
www.c-jump.com
... – Enter static IP address, subnet mask, IP addresses of the default gateway, DNS servers if necessary – Configure the DHCP server – Provide static addresses for local PCs if necessary ...
... – Enter static IP address, subnet mask, IP addresses of the default gateway, DNS servers if necessary – Configure the DHCP server – Provide static addresses for local PCs if necessary ...
cs6551 computer networks - MET Engineering College
... transport layer and can directly use IP or any of the underlying networks. IP layer serves as focal point in the architecture. o It defines a common method for exchanging packets to any type of network o Segregates host-to-host delivery from process-to-process delivery. For any protocol to be added ...
... transport layer and can directly use IP or any of the underlying networks. IP layer serves as focal point in the architecture. o It defines a common method for exchanging packets to any type of network o Segregates host-to-host delivery from process-to-process delivery. For any protocol to be added ...
What is SAN:Storage area network is a dedicated centrally managed
... servers to be interconnected using similar elements as in LANs or WANs, routers, gateways, switches. ...
... servers to be interconnected using similar elements as in LANs or WANs, routers, gateways, switches. ...
DiscJuggler - Padus, Inc.
... prints could be achieved through more a more expensive, but centralized printer. A large percentage of desks did not require single-use printers, so a significant amount of savings was found by purchasing full-feature printers that could work over the network. The network technologies in DiscJuggler ...
... prints could be achieved through more a more expensive, but centralized printer. A large percentage of desks did not require single-use printers, so a significant amount of savings was found by purchasing full-feature printers that could work over the network. The network technologies in DiscJuggler ...
ch01
... – A small collection of computers that share common roles, such as sharing files or printers. – Also called a peer-to-peer network – Decentralized logons, security, and resource sharing – Easy to configure and works well for small groups of users (fewer than 10) – A Windows Server 2012/R2 server tha ...
... – A small collection of computers that share common roles, such as sharing files or printers. – Also called a peer-to-peer network – Decentralized logons, security, and resource sharing – Easy to configure and works well for small groups of users (fewer than 10) – A Windows Server 2012/R2 server tha ...
Cloud Edge 100
... l Obtain the IP address from your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Static addressing: l One IP address for the appliance. l Your network DNS server IP address. l Your network gateway IP address. ...
... l Obtain the IP address from your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Static addressing: l One IP address for the appliance. l Your network DNS server IP address. l Your network gateway IP address. ...
of the packet
... • One of the major roles of the Network layer - provide a mechanism for addressing hosts – As the number of hosts on the network grows, more planning is required to manage and address the network. – Rather than having all hosts everywhere connected to one vast global network, it is more practical an ...
... • One of the major roles of the Network layer - provide a mechanism for addressing hosts – As the number of hosts on the network grows, more planning is required to manage and address the network. – Rather than having all hosts everywhere connected to one vast global network, it is more practical an ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... OSPF “advanced” features (not in RIP) security: all OSPF messages authenticated (to prevent malicious intrusion) multiple same-cost paths allowed (only one path in RIP) for each link, multiple cost metrics for different TOS (e.g., satellite link cost set “low” for best effort ToS; high for real ...
... OSPF “advanced” features (not in RIP) security: all OSPF messages authenticated (to prevent malicious intrusion) multiple same-cost paths allowed (only one path in RIP) for each link, multiple cost metrics for different TOS (e.g., satellite link cost set “low” for best effort ToS; high for real ...
Unit 10
... – Clients keep a local copy of a file and flush modified copies of it to the server from time to time – Because there are multiple copies of the same file, files can become inconsistent ...
... – Clients keep a local copy of a file and flush modified copies of it to the server from time to time – Because there are multiple copies of the same file, files can become inconsistent ...
ch08
... Describe broadcast and unicast addressing Describe relay agent communications Discuss Microsoft DHCP scopes and classes Use DHCP troubleshooting utilities ...
... Describe broadcast and unicast addressing Describe relay agent communications Discuss Microsoft DHCP scopes and classes Use DHCP troubleshooting utilities ...
FS980M Datasheet
... it—at the network edge. Flexible and robust, the FS980M series provide total security and management features for enterprises of all sizes. They also support video surveillance and Point of Sale (POS) applications. Reduce network running costs by automating and simplifying many dayto-day tasks—an FS ...
... it—at the network edge. Flexible and robust, the FS980M series provide total security and management features for enterprises of all sizes. They also support video surveillance and Point of Sale (POS) applications. Reduce network running costs by automating and simplifying many dayto-day tasks—an FS ...
Ethernet - Faculty - Genesee Community College
... ___________ used when a frame is sent from a ______________ __________________________ ______________ device. In the example shown, a host with IP address 192.168.1.5 (source) requests a web page from the server at IP address ...
... ___________ used when a frame is sent from a ______________ __________________________ ______________ device. In the example shown, a host with IP address 192.168.1.5 (source) requests a web page from the server at IP address ...
$doc.title
... • UDP between an intermediate peer – One or both hosts with a NAT – Neither host’s network blocks UDP traffic – Solu]on: direct UDP packets through another node ...
... • UDP between an intermediate peer – One or both hosts with a NAT – Neither host’s network blocks UDP traffic – Solu]on: direct UDP packets through another node ...
Document
... – WiFi: 2 11(b) 54(a/g) 600(n) 1000(VHT) Mb/s – WiMAX: 75 Mb/s, radius{ 50km [LOS], 2-5km [NLOS] } 100 Mb/s in 802.16m for high-mobility (250km/h) users – Significant differences in the coverage area ...
... – WiFi: 2 11(b) 54(a/g) 600(n) 1000(VHT) Mb/s – WiMAX: 75 Mb/s, radius{ 50km [LOS], 2-5km [NLOS] } 100 Mb/s in 802.16m for high-mobility (250km/h) users – Significant differences in the coverage area ...