ap404e
... The vision of the Global Soil Partnership is for a healthy and productive soils for a food secure world. The mission of the GSP is to build capacities and exchanges knowledge and technologies for sustainable management of soil resources at all levels to enhance food security in an era of climate cha ...
... The vision of the Global Soil Partnership is for a healthy and productive soils for a food secure world. The mission of the GSP is to build capacities and exchanges knowledge and technologies for sustainable management of soil resources at all levels to enhance food security in an era of climate cha ...
Soil Formation
... Biological activity produces the organic material in soil. Humus forms from the remains of plants and animals. It is an extremely important part of the soil. Humus coats the mineral grains. It binds them together into clumps that hold the soil together. This gives the soil its structure. Soils with ...
... Biological activity produces the organic material in soil. Humus forms from the remains of plants and animals. It is an extremely important part of the soil. Humus coats the mineral grains. It binds them together into clumps that hold the soil together. This gives the soil its structure. Soils with ...
1 - Madison Public Schools
... __________________________________________________________________ 7. Soil Color – determined by climate and composition 8. Soil Structure a. Ability of water to infiltrate soil – determined by how soil particles are arranged and if water can infiltrate (soak through) easily ...
... __________________________________________________________________ 7. Soil Color – determined by climate and composition 8. Soil Structure a. Ability of water to infiltrate soil – determined by how soil particles are arranged and if water can infiltrate (soak through) easily ...
Soils in the Environment Review
... Soils in the Environment Review Three Different Types of Soil 1. sand - loose, tiny grains of crushed or worn rock 2. loam - soil that has almost equal parts of sand, silt, and clay 3. clay - very fine pieces of earth that are much smaller than pieces of sand. ...
... Soils in the Environment Review Three Different Types of Soil 1. sand - loose, tiny grains of crushed or worn rock 2. loam - soil that has almost equal parts of sand, silt, and clay 3. clay - very fine pieces of earth that are much smaller than pieces of sand. ...
Soils
... -Probably high rainfall and possibly high in organic matter. -Use lime to raise pH -Many fertilizers have an acid affect on the soil. ...
... -Probably high rainfall and possibly high in organic matter. -Use lime to raise pH -Many fertilizers have an acid affect on the soil. ...
Soil Conservation
... • Describe three important benefits that soil provides. • Describe four methods of preventing soil damage and loss. ...
... • Describe three important benefits that soil provides. • Describe four methods of preventing soil damage and loss. ...
Testing the Visual Soil Assessment tool on Estonian farm fields
... samples were collected from the depth of 5–10 cm and 25–30 cm. The study revealed that results of a visually assessed soil physical parameters, such a soil structure, soil structural stability, soil porosity, presence of tillage pan, were confirmed by laboratory measurements in most cases. Soil wate ...
... samples were collected from the depth of 5–10 cm and 25–30 cm. The study revealed that results of a visually assessed soil physical parameters, such a soil structure, soil structural stability, soil porosity, presence of tillage pan, were confirmed by laboratory measurements in most cases. Soil wate ...
Chapter 12 * Weathering, Soil and Erosion
... reacts chemically with many common minerals. Acid rain also increases the rate of chemical weathering, and can cause structures made of concrete and stone to wear out more quickly. ...
... reacts chemically with many common minerals. Acid rain also increases the rate of chemical weathering, and can cause structures made of concrete and stone to wear out more quickly. ...
slides
... • AM fungi thrive on decomposing organic matter and obtain large amounts of nitrogen from it. • The fungus itself is much richer in N than plant roots, and calculations suggest that there is as much nitrogen in AM fungi globally as in roots. • Since fungal hyphae (the threads of which the fungus is ...
... • AM fungi thrive on decomposing organic matter and obtain large amounts of nitrogen from it. • The fungus itself is much richer in N than plant roots, and calculations suggest that there is as much nitrogen in AM fungi globally as in roots. • Since fungal hyphae (the threads of which the fungus is ...
Weathering and Soil Formation - PAMS-Doyle
... • Each horizon is different. A cross section is called a soil profile. • Soil that has 3 layers is mature (takes many thousands of years and the right conditions. • Factors: surface features, time, climate and type • Soil that has 2 layers is immature. ...
... • Each horizon is different. A cross section is called a soil profile. • Soil that has 3 layers is mature (takes many thousands of years and the right conditions. • Factors: surface features, time, climate and type • Soil that has 2 layers is immature. ...
CH. 8 EARTH SYSTEMS
... • Organisms-Plants remove nutrients from the soil and excrete organic acids that speed chemical weathering. Animals that burrow: earthworms, gophers, voles, mix the soil distributing organic and mineral matter. • Time-As soil ages, and has organic matter in it over time, they become deep and fertile ...
... • Organisms-Plants remove nutrients from the soil and excrete organic acids that speed chemical weathering. Animals that burrow: earthworms, gophers, voles, mix the soil distributing organic and mineral matter. • Time-As soil ages, and has organic matter in it over time, they become deep and fertile ...
Soil Formation and Composition notes
... B. Occurs most rapidly in warm, wet climates. C. Limestone weathers more quickly than Granite in warm, wet climates. ...
... B. Occurs most rapidly in warm, wet climates. C. Limestone weathers more quickly than Granite in warm, wet climates. ...
Materials and Practices Guidelines for Lake Whatcom
... Topsoil. Choose topsoils with a relatively low level of organic material content (ideally, with organic content of a maximum of 10% by volume). Topsoils can be highly variable in phosphorus content and fecal bacteria depending on their source and composition. Home‐generated materials. Materia ...
... Topsoil. Choose topsoils with a relatively low level of organic material content (ideally, with organic content of a maximum of 10% by volume). Topsoils can be highly variable in phosphorus content and fecal bacteria depending on their source and composition. Home‐generated materials. Materia ...
DOC
... put up their hands to find a new partner. They are moving about the room to do this. 5. The process is allowed to continue for as long as you wish. It may be repeated on other days and the children do get better with time. You may like to explain that if they get the same question again it does not ...
... put up their hands to find a new partner. They are moving about the room to do this. 5. The process is allowed to continue for as long as you wish. It may be repeated on other days and the children do get better with time. You may like to explain that if they get the same question again it does not ...
Soil Survey
... 3) tables giving physical and chemical data and interpretations for various uses. ...
... 3) tables giving physical and chemical data and interpretations for various uses. ...
Glacial Rock Dust - Nature`s Footprint
... over many thousands of years by glacial action. As a glacier recedes, it leaves behind deposits of “glacial moraine”. These deposits are mined, dried and screened for agricultural and horticultural re-mineralization. Glacial Rock Dust can replace key elements that have been depleted from the soil ov ...
... over many thousands of years by glacial action. As a glacier recedes, it leaves behind deposits of “glacial moraine”. These deposits are mined, dried and screened for agricultural and horticultural re-mineralization. Glacial Rock Dust can replace key elements that have been depleted from the soil ov ...
Abstract
... serve as reservoirs of resistance determinants that can be mobilized into the humanassociated microbial community. On a molecular level, antibiotic resistance may evolve from either spontaneous mutation of genes, or by inter- or intra-species horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of existing antibiotic res ...
... serve as reservoirs of resistance determinants that can be mobilized into the humanassociated microbial community. On a molecular level, antibiotic resistance may evolve from either spontaneous mutation of genes, or by inter- or intra-species horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of existing antibiotic res ...
Assessment of grass root effects on soil piping in sandy soils using
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
Mechanical Weathering
... Time, Climate, Organisms and Slope Time: Important in all geologic processes. The longer a soil has been forming, the thicker it becomes. ...
... Time, Climate, Organisms and Slope Time: Important in all geologic processes. The longer a soil has been forming, the thicker it becomes. ...
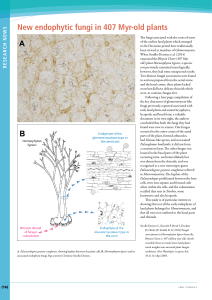
Research News
... had Glomus-like spores, and was named Palaeoglomus boullardii; it did not form a continuous layer. The other fungus was located in the basal parts of the plant occurring intra- and intercellularly but was absent from the rhizoids, and was recognized as a new monotypic genus ...
... had Glomus-like spores, and was named Palaeoglomus boullardii; it did not form a continuous layer. The other fungus was located in the basal parts of the plant occurring intra- and intercellularly but was absent from the rhizoids, and was recognized as a new monotypic genus ...
in 1,5
... derived from rocks. Organic soils form from the accumulation of plant material, usually in water-saturated, anaerobic conditions that retard decomposition. Mineral matter is described as texture and comprises half the volume of mineral soils. The other half of the soil volume is composed of voids or ...
... derived from rocks. Organic soils form from the accumulation of plant material, usually in water-saturated, anaerobic conditions that retard decomposition. Mineral matter is described as texture and comprises half the volume of mineral soils. The other half of the soil volume is composed of voids or ...
GEOSEA V Proceedings Vol. !, Geol. Soc. Malaysia, Bulletin
... A set of two river terraces (T1 and T 2 ) occurs along the main river channels. T 1 is mostly cut-and-filled in T 2 -deposits. A short distance upstream the watergaps, due to the bunding effect of the latter, the younger T 1 -deposits can locally overlap the T 2 deposits. The T 2 -terrace level belo ...
... A set of two river terraces (T1 and T 2 ) occurs along the main river channels. T 1 is mostly cut-and-filled in T 2 -deposits. A short distance upstream the watergaps, due to the bunding effect of the latter, the younger T 1 -deposits can locally overlap the T 2 deposits. The T 2 -terrace level belo ...