RTP
... multicast group and count the number of distinct end systems which sends packets,its unique identifier (SSRC) must be stored. Delay. As the group sizes grow, the time may become very large. This interval may easily exceed the duration of group membership. This means that timely reporting of QoS prob ...
... multicast group and count the number of distinct end systems which sends packets,its unique identifier (SSRC) must be stored. Delay. As the group sizes grow, the time may become very large. This interval may easily exceed the duration of group membership. This means that timely reporting of QoS prob ...
From Subnetting to VLSM - YSU Computer Science
... identify the network – CIDR transmitted as part of IP address – RFC 1517-1520 – Network portion not restricted to entire octet ...
... identify the network – CIDR transmitted as part of IP address – RFC 1517-1520 – Network portion not restricted to entire octet ...
IP Multicast
... • Flooding and pruning are repeated periodically, when the current state times out. • Between flooding rounds, a host can re-join a group by sending a graft message. • Intermediate routers propagates the graft message upstream until the path is re-connected. ...
... • Flooding and pruning are repeated periodically, when the current state times out. • Between flooding rounds, a host can re-join a group by sending a graft message. • Intermediate routers propagates the graft message upstream until the path is re-connected. ...
ppt
... Cache logic research: Internet protocol breakdown 1993 – 2006; Velocix: File-types on major P2P networks. ...
... Cache logic research: Internet protocol breakdown 1993 – 2006; Velocix: File-types on major P2P networks. ...
smesh.org
... • Half-duplex communication system between multiple participants that share a single communication channel. • Only one user is granted Permissionto-Speak at a time (floor-control). ...
... • Half-duplex communication system between multiple participants that share a single communication channel. • Only one user is granted Permissionto-Speak at a time (floor-control). ...
Topic 8 – LAN Fundamentals
... • A very simple service that does not involve any of the flow and error control mechanisms • Thus the delivery of data is not guaranteed – In most devices, there will be some higher layer of software that deals with reliability issues • Used for instances in which the overhead of connection establis ...
... • A very simple service that does not involve any of the flow and error control mechanisms • Thus the delivery of data is not guaranteed – In most devices, there will be some higher layer of software that deals with reliability issues • Used for instances in which the overhead of connection establis ...
Chapter04
... In a Class C address, only 8 bits are available for defining the hosts. Remember that subnet bits start at the left and go to the right, without skipping bits. This means that the only Class C subnet masks can be the following: Binary Decimal CIDR ...
... In a Class C address, only 8 bits are available for defining the hosts. Remember that subnet bits start at the left and go to the right, without skipping bits. This means that the only Class C subnet masks can be the following: Binary Decimal CIDR ...
Document
... Source node sends mobile agent to a connected RIMA node on the path with sufficient bandwidth and minimum delay At RIMA node: If destination is within a neighborhood or it is on the path to other RIMA node and feasible path exist, then RIMA node directly sends the mobile agent to destination node ...
... Source node sends mobile agent to a connected RIMA node on the path with sufficient bandwidth and minimum delay At RIMA node: If destination is within a neighborhood or it is on the path to other RIMA node and feasible path exist, then RIMA node directly sends the mobile agent to destination node ...
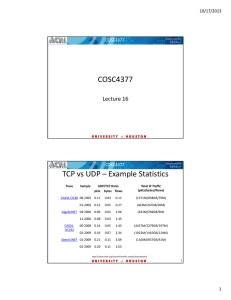
COSC4377 TCP vs UDP – Example Statistics
... – Stateless auto‐configuration requires no manual configuration of hosts, minimal (if any) configuration of routers, and no additional servers. The stateless mechanism allows a host to generate its own addresses using a combination of locally available information and information advertised by r ...
... – Stateless auto‐configuration requires no manual configuration of hosts, minimal (if any) configuration of routers, and no additional servers. The stateless mechanism allows a host to generate its own addresses using a combination of locally available information and information advertised by r ...
Chapter 21 - William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications
... "No ticket! Dear me, Watson, this is really very singular. According to my experience it is not possible to reach the platform of a Metropolitan train without exhibiting one's ticket.” —The Adventure of the Bruce-Partington Plans Sir Arthur Conan Doyle ...
... "No ticket! Dear me, Watson, this is really very singular. According to my experience it is not possible to reach the platform of a Metropolitan train without exhibiting one's ticket.” —The Adventure of the Bruce-Partington Plans Sir Arthur Conan Doyle ...
SNMP In Depth
... – 1271 - Remote LAN Monitoring MIB(Ethernet RMON) – 1284 - Ether-Like Interface Type MIB – 1285 - FDDI Interface Type MIB – 1286 - Bridge MIB – 1289 - DECnet Phase IV MIB extensions – 1304 - SMDS Interface Protocol(SIP) Interface Type MIB – 1315 - Frame Relay DTE Interface Type MIB – 1316 - Characte ...
... – 1271 - Remote LAN Monitoring MIB(Ethernet RMON) – 1284 - Ether-Like Interface Type MIB – 1285 - FDDI Interface Type MIB – 1286 - Bridge MIB – 1289 - DECnet Phase IV MIB extensions – 1304 - SMDS Interface Protocol(SIP) Interface Type MIB – 1315 - Frame Relay DTE Interface Type MIB – 1316 - Characte ...
Overview of work in TERENA
... • A mix of networking elements requiring a unified control plane and sophisticated management systems to seamlessly manage network and transport layer • several signalling protocols being standardised by IETF and ITU-T • Inter-operability, and multi-domain management still represent a challenge – Mo ...
... • A mix of networking elements requiring a unified control plane and sophisticated management systems to seamlessly manage network and transport layer • several signalling protocols being standardised by IETF and ITU-T • Inter-operability, and multi-domain management still represent a challenge – Mo ...
ppt - CS-CSIF - University of California, Davis
... Integrating Cellular Networks, WLANs and MANETs: A Futuristic Heterogeneous Wireless Network”, In IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, v12 i3. pp.30-41, June ...
... Integrating Cellular Networks, WLANs and MANETs: A Futuristic Heterogeneous Wireless Network”, In IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, v12 i3. pp.30-41, June ...
P2P
... the peers, Bob. r File is copied from Bob’s PC to Alice’s notebook: HTTP r While Alice downloads, other users uploading from Alice. r Alice’s peer is both a Web client and a transient Web server. All peers are servers = highly scalable! P2P ...
... the peers, Bob. r File is copied from Bob’s PC to Alice’s notebook: HTTP r While Alice downloads, other users uploading from Alice. r Alice’s peer is both a Web client and a transient Web server. All peers are servers = highly scalable! P2P ...
paper
... and Wavelength Assignment (RWA) algorithms from the vast body of already existing literature, less attention has been paid to the RSA algorithms in optical parallel transmission systems suitable for the Ethernet standards ( [6], [7], [8]). Forward Error Correction (FEC) codes are commonly applied in ...
... and Wavelength Assignment (RWA) algorithms from the vast body of already existing literature, less attention has been paid to the RSA algorithms in optical parallel transmission systems suitable for the Ethernet standards ( [6], [7], [8]). Forward Error Correction (FEC) codes are commonly applied in ...
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
... Reverse ARP : map MAC address to IP address for device that cannot store IP, usually diskless workstations Need to set up server with RARP table Use the same frame format – 0x0835 for Ethernet RARP request – operation 0x003 = RARP request 0x004 = RARP reply ...
... Reverse ARP : map MAC address to IP address for device that cannot store IP, usually diskless workstations Need to set up server with RARP table Use the same frame format – 0x0835 for Ethernet RARP request – operation 0x003 = RARP request 0x004 = RARP reply ...
Segment Routing - Technology and Use Cases
... – ecmp multi-hop shortest-path – in most topologies, any path can be expressed as list of node segments © 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ...
... – ecmp multi-hop shortest-path – in most topologies, any path can be expressed as list of node segments © 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ...
Efficient Data Transfer Protocols for Big Data
... [5] standard lets users take advantage of these efficient communication patterns, supported by protocols like InfiniBand, over widely-deployed Ethernet networks. In effect, RoCE is InfiniBand protocols made to work over Ethernet infrastructure. The notion of “converged Ethernet”, also known as enhan ...
... [5] standard lets users take advantage of these efficient communication patterns, supported by protocols like InfiniBand, over widely-deployed Ethernet networks. In effect, RoCE is InfiniBand protocols made to work over Ethernet infrastructure. The notion of “converged Ethernet”, also known as enhan ...
PPT
... Internet transport protocol • “Best effort” service, UDP segments may be: – Lost – Delivered out of order to app • Connectionless: – No handshaking between UDP sender, receiver – Each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... Internet transport protocol • “Best effort” service, UDP segments may be: – Lost – Delivered out of order to app • Connectionless: – No handshaking between UDP sender, receiver – Each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Chapter 06
... Interior routing protocols are designed for routing packets among networks within an organization and they route packets based on mathematical models Exterior routing protocols are designed for routing packets between networks controlled by different organizations and they route packets based on adm ...
... Interior routing protocols are designed for routing packets among networks within an organization and they route packets based on mathematical models Exterior routing protocols are designed for routing packets between networks controlled by different organizations and they route packets based on adm ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.