The expansion of Roman power took place over approximately 500
... lands. Romans often treated them very harshly which led to slave rebellions. A slave named Spartacus led a famous revolt in 73 B.C. E. After crushing his army and killing Spartacus in battle, the Romans put thousands of surviving rebels to death on crosses. With so many slaves to do the work, thousa ...
... lands. Romans often treated them very harshly which led to slave rebellions. A slave named Spartacus led a famous revolt in 73 B.C. E. After crushing his army and killing Spartacus in battle, the Romans put thousands of surviving rebels to death on crosses. With so many slaves to do the work, thousa ...
Rome
... Voted in groups (like House of Representatives) Voted on ruler and granted “imperium” (right to command) ...
... Voted in groups (like House of Representatives) Voted on ruler and granted “imperium” (right to command) ...
Roman Republics. Harriet I. Flower
... University Press. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form by any electronic or mechanical means (including photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval) without permission in writing from the publisher, except for reading and browsing via the World Wi ...
... University Press. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form by any electronic or mechanical means (including photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval) without permission in writing from the publisher, except for reading and browsing via the World Wi ...
part one caius octavius (thurinus) 63–44 bc
... This brief mention in the Christmas story must have been the first time I heard of Augustus, and although it is hard to be precise with such early memories I must have been very young. Like most people who hear or read these words, I doubt that I thought much of them, and it was only later that my l ...
... This brief mention in the Christmas story must have been the first time I heard of Augustus, and although it is hard to be precise with such early memories I must have been very young. Like most people who hear or read these words, I doubt that I thought much of them, and it was only later that my l ...
Activity 1: Roman Aqueducts: Construction and Use.
... Censor Appius Claudius Caecus: A Roman politician who lived from 340 BC – 273 BC. He was censor in 312 BC, who did not follow the usual procedure of serving as consul first. He sought support from the lower classes, allowing sons of freedmen to serve in the senate, and extended voting privileges to ...
... Censor Appius Claudius Caecus: A Roman politician who lived from 340 BC – 273 BC. He was censor in 312 BC, who did not follow the usual procedure of serving as consul first. He sought support from the lower classes, allowing sons of freedmen to serve in the senate, and extended voting privileges to ...
Creating a Poster About Ancient Rome
... Your poster must be created to support you answer to this question: What are the most important ideas that you learned about Ancient Rome? The poster will have 4 sections each of which represents a topic covered in the unit. For each topic below you must describe and illustrate four key ideas that y ...
... Your poster must be created to support you answer to this question: What are the most important ideas that you learned about Ancient Rome? The poster will have 4 sections each of which represents a topic covered in the unit. For each topic below you must describe and illustrate four key ideas that y ...
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline
... to a foreign country to make peace or to proclaim war, this too is the business of the Senate. As a result, many foreign kings imagine the constitution is a complete aristocracy because nearly all the business they had with Rome was settled by the Senate. After all this, someone would naturally ask ...
... to a foreign country to make peace or to proclaim war, this too is the business of the Senate. As a result, many foreign kings imagine the constitution is a complete aristocracy because nearly all the business they had with Rome was settled by the Senate. After all this, someone would naturally ask ...
The Roman REpublic - Warren County Schools
... 2. Who were the patricians? How much power did they have? small group of wealthy landowners. They held all the power. 3. Who were the plebeians? How much power did they have? peasants, laborers, craftspeople, and shopkeepers. They had very little voice in the government. Section 33.3 1. Summarize th ...
... 2. Who were the patricians? How much power did they have? small group of wealthy landowners. They held all the power. 3. Who were the plebeians? How much power did they have? peasants, laborers, craftspeople, and shopkeepers. They had very little voice in the government. Section 33.3 1. Summarize th ...
Origins of Democratic Thought and Practice A Legacy
... In Ancient Rome: 1. The Roman Republic was founded in 509 B.C. as a representative democracy. 2. In Rome males of noble and common birth had citizenship. A foreigner or non-citizen could be “made” a citizen through action of the government (a form of “naturalized” citizenship). For the most part wom ...
... In Ancient Rome: 1. The Roman Republic was founded in 509 B.C. as a representative democracy. 2. In Rome males of noble and common birth had citizenship. A foreigner or non-citizen could be “made” a citizen through action of the government (a form of “naturalized” citizenship). For the most part wom ...
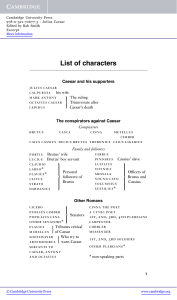
Cassius will now describe an event which he feels proves Caesar`s
... For once, upon a raw and gusty day, the troubled Tiber chafing with her shores, Caesar said to me 'darest thou, Cassius, now leap in with me into this angry flood, and swim to yonder point?' Upon the word, accoutered as I was, I plunged in and bade him follow; so indeed he did. The torrent roared, a ...
... For once, upon a raw and gusty day, the troubled Tiber chafing with her shores, Caesar said to me 'darest thou, Cassius, now leap in with me into this angry flood, and swim to yonder point?' Upon the word, accoutered as I was, I plunged in and bade him follow; so indeed he did. The torrent roared, a ...
Notes 20 The Roman
... − 46 BCE: Julius Caesar takes Rome, names himself dictator − but for life, not the usual 6 month term − took land from conservatives and gave it to supporters − started big building projects in Rome to provide employment for the poor (sound familiar?) − gave Roman citizenship to provincial subjects ...
... − 46 BCE: Julius Caesar takes Rome, names himself dictator − but for life, not the usual 6 month term − took land from conservatives and gave it to supporters − started big building projects in Rome to provide employment for the poor (sound familiar?) − gave Roman citizenship to provincial subjects ...
ancient rome - WMLGalaxy
... 3) known as Latins, spoke Latin, were herders and farmers, harvested wheat, grapes, and olives ...
... 3) known as Latins, spoke Latin, were herders and farmers, harvested wheat, grapes, and olives ...
YEAR 4: JULIUS CAESAR AND IMPERIAL ROME (5 lessons)
... Lesson 4. Rome’s first Emperor The Senate hoped that killing Caesar would allow Rome once again to become a republic. However, the empire was now too large to be ruled in such a democratic way. Two of Caesar’s best friends, Mark Antony and Octavian, became joint rulers of Rome. They fell out after ...
... Lesson 4. Rome’s first Emperor The Senate hoped that killing Caesar would allow Rome once again to become a republic. However, the empire was now too large to be ruled in such a democratic way. Two of Caesar’s best friends, Mark Antony and Octavian, became joint rulers of Rome. They fell out after ...
What is History? - CLIO History Journal
... enclosed in a bundle of rods) • Toga praetexta - with a purple band • Auspicium - right to take the auspices • Each consul had the right of veto • Only one year in office, ten years before eligible for reelection ...
... enclosed in a bundle of rods) • Toga praetexta - with a purple band • Auspicium - right to take the auspices • Each consul had the right of veto • Only one year in office, ten years before eligible for reelection ...
Ch.2 Rome: Power, Authority and Sovereignty
... adopted until quite late on. It constituted an established elite which was social, economic and political, asserting aristocratic descent from an ancestry as old as Rome itself, though the order did (like most aristocracies) admit newcomers in later years. The supremacy of the patrician order had it ...
... adopted until quite late on. It constituted an established elite which was social, economic and political, asserting aristocratic descent from an ancestry as old as Rome itself, though the order did (like most aristocracies) admit newcomers in later years. The supremacy of the patrician order had it ...
Bellringer - Warren County Schools
... They were elected annually. Each one had their own duties ranging from being judges to managing finances, or organizing games/festivals. ...
... They were elected annually. Each one had their own duties ranging from being judges to managing finances, or organizing games/festivals. ...
Rome / Roman Empire
... 3. Why is it important to settle on a peninsula? 2 reasons. 4. Which two men are given credit for founding Rome, in 753 BC? 5. Which three groups were the first to settle Rome? 6. What were some of the new ideas/achievements introduced to Rome by the Etruscans? 7. True/False: Early Roman government ...
... 3. Why is it important to settle on a peninsula? 2 reasons. 4. Which two men are given credit for founding Rome, in 753 BC? 5. Which three groups were the first to settle Rome? 6. What were some of the new ideas/achievements introduced to Rome by the Etruscans? 7. True/False: Early Roman government ...
Julius Caesar - Beck-Shop
... other powers and honours. There was even a statue of him placed in one of the Roman temples with the inscription ‘To the Unconquerable God’. Caesar was now sole ruler of Rome and its Empire. He was king in all but name. Caesar was, however, surprisingly merciful to most of his defeated Roman opponen ...
... other powers and honours. There was even a statue of him placed in one of the Roman temples with the inscription ‘To the Unconquerable God’. Caesar was now sole ruler of Rome and its Empire. He was king in all but name. Caesar was, however, surprisingly merciful to most of his defeated Roman opponen ...
The Reforms of Julius Caesar A. Julius Caesar created ______
... Rome was a Republic; it had no kings. But it was not very democratic. Most of the power was in the hands of the Senate. It members were patricians, and most of them were rich land owners. For many years, the plebeians fought for a greater voice in the government. They won many important rights and e ...
... Rome was a Republic; it had no kings. But it was not very democratic. Most of the power was in the hands of the Senate. It members were patricians, and most of them were rich land owners. For many years, the plebeians fought for a greater voice in the government. They won many important rights and e ...
Ancient Rome Webquest
... 1. How was Rome ruled in the first and second centuries BC? What were the various branches of government? Which one was the most powerful part of the legislative branch? ...
... 1. How was Rome ruled in the first and second centuries BC? What were the various branches of government? Which one was the most powerful part of the legislative branch? ...
The Rise of Rome - msking-phs
... First War- Rome wins control of Sicily Second War- Hannibal, brilliant Carthaginian general invaded northern Italy • Took on brilliant Rome commander Scipio • Rome finishes Triumphant ...
... First War- Rome wins control of Sicily Second War- Hannibal, brilliant Carthaginian general invaded northern Italy • Took on brilliant Rome commander Scipio • Rome finishes Triumphant ...