Roman Republican Government
... Tribune – official of this assembly • Power of veto – can veto anything from Comitia Centuriata, Comitia Tributa, Concilium Plebis, or the Senate • Exercise veto in the case that the rights of the Plebeians are threatened • Negotiate with consuls & senate Veto power of Tribunes helped to abolish ...
... Tribune – official of this assembly • Power of veto – can veto anything from Comitia Centuriata, Comitia Tributa, Concilium Plebis, or the Senate • Exercise veto in the case that the rights of the Plebeians are threatened • Negotiate with consuls & senate Veto power of Tribunes helped to abolish ...
Focus Question: What values formed the basis of Roman society
... the Etruscans—a people who ruled most of central Italy for a time. The Romans learned from the Etruscans, studying their engineering techniques and adapting their alphabet. In 509 B.C., the Romans drove out the Etruscans and founded the state of Rome. They put in place a new form of government calle ...
... the Etruscans—a people who ruled most of central Italy for a time. The Romans learned from the Etruscans, studying their engineering techniques and adapting their alphabet. In 509 B.C., the Romans drove out the Etruscans and founded the state of Rome. They put in place a new form of government calle ...
Ancient Rome - Regents Review
... Collapse of the Republic • Sulla’s seizure of Rome led to 50 years of civil war. • Three men emerged victorious and became Rome’s first triumvirate. – Crassus- more a moneyed power than military power; especially since Pompey took credit for downing the Spartacus Rebellion – Pompey – military comma ...
... Collapse of the Republic • Sulla’s seizure of Rome led to 50 years of civil war. • Three men emerged victorious and became Rome’s first triumvirate. – Crassus- more a moneyed power than military power; especially since Pompey took credit for downing the Spartacus Rebellion – Pompey – military comma ...
PDF sample
... Augustus in 27 bc, I begin my story with the murder of Julius Caesar in 44 bc. As a dictator for life he laid the foundations for the imperial system. I conclude in 476 with Romulus Augustulus, the west-Roman emperor who was deposed by the German army officer Odoacer. In the east emperors remained i ...
... Augustus in 27 bc, I begin my story with the murder of Julius Caesar in 44 bc. As a dictator for life he laid the foundations for the imperial system. I conclude in 476 with Romulus Augustulus, the west-Roman emperor who was deposed by the German army officer Odoacer. In the east emperors remained i ...
starter activity. Study the information about Roman
... starter activity. Study the information about Roman Emperors. You have 2 mins and then your teacher will ask you 5 questions. ...
... starter activity. Study the information about Roman Emperors. You have 2 mins and then your teacher will ask you 5 questions. ...
www.leapfrog.com
... 1. The consuls shared the power. They served as judges, led the armies, and acted on behalf of all Roman citizens. 2. When necessary, a dictator was appointed, who served for six months. 3. Dictators were considered more powerful than the two consuls. D. A group of men called the senate advised the ...
... 1. The consuls shared the power. They served as judges, led the armies, and acted on behalf of all Roman citizens. 2. When necessary, a dictator was appointed, who served for six months. 3. Dictators were considered more powerful than the two consuls. D. A group of men called the senate advised the ...
Ancient Rome Unit Notes (WHI.6)
... o Set foreign policy • Consuls: o Two men who governed the city & had to agree on decisions. o Elected or one year and then not allowed to serve again for 10 years • Laws of Rome codified as Twelve Tables ...
... o Set foreign policy • Consuls: o Two men who governed the city & had to agree on decisions. o Elected or one year and then not allowed to serve again for 10 years • Laws of Rome codified as Twelve Tables ...
Ancient Roman Society
... Rome’s laws onto the Twelve Tables, which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens of Rome had a right to the protection of the law ...
... Rome’s laws onto the Twelve Tables, which were hung in the forum for all citizens to see The Twelve Tables were based on the idea that all citizens of Rome had a right to the protection of the law ...
Hail Caesar - Amazon Web Services
... few samples with contrasting perspectives: a lifetime portrait of Julius Caesar from Tusculum and a victory coin, both dating from around 44 BC; then two later representations – a portrait of Caesar from the Trajanic period and a sestertius minted by Octavian in 37 BC that depicts Caesar as ‘Divus J ...
... few samples with contrasting perspectives: a lifetime portrait of Julius Caesar from Tusculum and a victory coin, both dating from around 44 BC; then two later representations – a portrait of Caesar from the Trajanic period and a sestertius minted by Octavian in 37 BC that depicts Caesar as ‘Divus J ...
Overview of Roman Civilization, 509 BC
... eliminated, and poor volunteers flocked to the army. But the effect of this was to further undermine republican values. Service for profit meant soldiers pledged more loyalty to their commanders than to the republic itself. As a result, military leaders grew in power and threatened to become the ki ...
... eliminated, and poor volunteers flocked to the army. But the effect of this was to further undermine republican values. Service for profit meant soldiers pledged more loyalty to their commanders than to the republic itself. As a result, military leaders grew in power and threatened to become the ki ...
Rome - TeacherWeb
... PATRICIANS expelled the last Etruscan king and established a REPUBLIC. The power to rule was transferred to two new officials called CONSULS. Elected annually from the patrician class, the consul exercised their power in the interests of that class. ...
... PATRICIANS expelled the last Etruscan king and established a REPUBLIC. The power to rule was transferred to two new officials called CONSULS. Elected annually from the patrician class, the consul exercised their power in the interests of that class. ...
Year 13: Augustus and his rise to power: Introductory test
... “If Italy was to be fully integrated into the Roman Tradition, she must be made fully aware of and loyal to that tradition. But if she turned her eyes on the capital she would see much that was unworthy of Rome’s past. It is easy to draw an unpleasant picture of the Roman aristocracy at the end of t ...
... “If Italy was to be fully integrated into the Roman Tradition, she must be made fully aware of and loyal to that tradition. But if she turned her eyes on the capital she would see much that was unworthy of Rome’s past. It is easy to draw an unpleasant picture of the Roman aristocracy at the end of t ...
RD Milns Antiquities Museum Education Program
... Decebalus: Decebalus was the king of Dacia, who was involved in a series of campaigns against Rome. A peace was negotiated with Decebalus by the Emperor Domitian, under which he was established as non-threatening to Rome. The Emperor Trajan, however, desired military glory and grew suspicious of Dec ...
... Decebalus: Decebalus was the king of Dacia, who was involved in a series of campaigns against Rome. A peace was negotiated with Decebalus by the Emperor Domitian, under which he was established as non-threatening to Rome. The Emperor Trajan, however, desired military glory and grew suspicious of Dec ...
chapter 5 - SWR Global History
... historically valid? Why or why not? Why were the “common folk” less pleased than the officials at seeing the Dictator? What were their views of him likely to have been twenty days later? Were their fears accurate, but premature? Why or why not? What elements in the story of Cincinnatus inspired late ...
... historically valid? Why or why not? Why were the “common folk” less pleased than the officials at seeing the Dictator? What were their views of him likely to have been twenty days later? Were their fears accurate, but premature? Why or why not? What elements in the story of Cincinnatus inspired late ...
HERE - East Lynne 40 School District
... Before he reached Rome, Hannibal’s army suffered heavy losses trying to cross the Alps across northern Italy. Although he lost almost half his soldiers and all of the elephants, he still had a powerful army. ...
... Before he reached Rome, Hannibal’s army suffered heavy losses trying to cross the Alps across northern Italy. Although he lost almost half his soldiers and all of the elephants, he still had a powerful army. ...
Representative government of Rome:
... Representative government of Rome: The Roman Republic Vocabulary: patrician, republic, plebeian, consul, dictator, tribune Patricians under Etruscan rule became the new wealthy aristocratic class (Latin nobles). *Once the Etruscan rulers were driven out, the patricians declared Rome a republic- a co ...
... Representative government of Rome: The Roman Republic Vocabulary: patrician, republic, plebeian, consul, dictator, tribune Patricians under Etruscan rule became the new wealthy aristocratic class (Latin nobles). *Once the Etruscan rulers were driven out, the patricians declared Rome a republic- a co ...
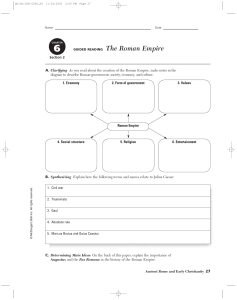
6.2 Roman Empire
... death of Alexander the Great. Though they had ruled Egypt for a long time, none of the family had ever bothered to learn Egyptian—until Cleopatra. Plutarch wrote that she learned so many languages she could speak to “Ethiopians, Troglodytes, Jews, Arabs, Syrians, Medes, and Parthians” in their own t ...
... death of Alexander the Great. Though they had ruled Egypt for a long time, none of the family had ever bothered to learn Egyptian—until Cleopatra. Plutarch wrote that she learned so many languages she could speak to “Ethiopians, Troglodytes, Jews, Arabs, Syrians, Medes, and Parthians” in their own t ...
Rome-RDG
... lead expeditions farther into modern day Germany and Britain, which were at that time completely unknown to the Romans. ...
... lead expeditions farther into modern day Germany and Britain, which were at that time completely unknown to the Romans. ...