Assessing the biocompatibility of click
... modified bases into the whole genes and genomes. An alternative approach to DNA assembly may be envisaged that instead of enzymes, uses highly efficient chemical reactions for the ligation of oligonucleotides (5–7). Such an approach would not only eliminate the need for enzymatic ligation and cloning ...
... modified bases into the whole genes and genomes. An alternative approach to DNA assembly may be envisaged that instead of enzymes, uses highly efficient chemical reactions for the ligation of oligonucleotides (5–7). Such an approach would not only eliminate the need for enzymatic ligation and cloning ...
Comparison Between Currently Used Blood Samples And New
... hundred microliters of 95% ethanol were added; the sample was mixed by inversion at least five times and incubated at 10 min at room temperature. The sample was then centrifuged for 1 min at 13,000 rpm at room temperature, the supernatant was discarded, and the DNA was dissolved in 100 μL TE buffer ...
... hundred microliters of 95% ethanol were added; the sample was mixed by inversion at least five times and incubated at 10 min at room temperature. The sample was then centrifuged for 1 min at 13,000 rpm at room temperature, the supernatant was discarded, and the DNA was dissolved in 100 μL TE buffer ...
THREE-BASE DELETION IN EXON 3 OF THE /3
... antisense strand), are deleted from the mutant allele of the petient. Ladders represent the nucleotide sequence of the antisense strand (anti). Clone A and clone 8 derived from themutant and normal alleles. respectively. The nucleotide sequence of the sense strand (sense), their corresponding amino ...
... antisense strand), are deleted from the mutant allele of the petient. Ladders represent the nucleotide sequence of the antisense strand (anti). Clone A and clone 8 derived from themutant and normal alleles. respectively. The nucleotide sequence of the sense strand (sense), their corresponding amino ...
dna TRANSCRIPTION AND tRANSLATION
... containing RNA and proteins Sequence hypothesis – Initially proposed by Francis Crick in 1958, this hypothesis states that the DNA sequence codes for the amino acid sequence Transcription – The process of making an mRNA sequence from a gene sequence (DNA) template Translation – The process of transl ...
... containing RNA and proteins Sequence hypothesis – Initially proposed by Francis Crick in 1958, this hypothesis states that the DNA sequence codes for the amino acid sequence Transcription – The process of making an mRNA sequence from a gene sequence (DNA) template Translation – The process of transl ...
A Review on Y-Chromosomal based DNA Profiling and Bayesian
... particular gender then the tandem repeats of 2-5 base pair long are checked on the Y-Chromosome in case of male and on the autosomal chromosomes in case of females. If the DNA found is contaminated then we can use mitochondrial part of the cell for better results. The process for Y-STR analysis has ...
... particular gender then the tandem repeats of 2-5 base pair long are checked on the Y-Chromosome in case of male and on the autosomal chromosomes in case of females. If the DNA found is contaminated then we can use mitochondrial part of the cell for better results. The process for Y-STR analysis has ...
DNA and RNA Extraction Controls Performance Summary
... 0.5mM EDTA 1mM EDTA 2mM EDTA 2.5mM EDTA 3mM EDTA 3.5mM EDTA 4mM EDTA ...
... 0.5mM EDTA 1mM EDTA 2mM EDTA 2.5mM EDTA 3mM EDTA 3.5mM EDTA 4mM EDTA ...
Chapter 7 Molecular Genetics: From DNA to Proteins Worksheets
... _____ 1. The process in which cells make proteins is called protein expression. _____ 2. Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. _____ 3. Splicing removes introns from mRNA. _____ 4. A codon can be described as a three-letter genetic “word.” _____ 5. UAG, U ...
... _____ 1. The process in which cells make proteins is called protein expression. _____ 2. Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. _____ 3. Splicing removes introns from mRNA. _____ 4. A codon can be described as a three-letter genetic “word.” _____ 5. UAG, U ...
TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit
... Introduction TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit is based on silica membrane technology and provides special buffer system for many kinds of sample’s gDNA extraction. The spin column is made of new type silica membrane can bind DNA optimally on given salt and pH conditions. Simple centrifugation processing com ...
... Introduction TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit is based on silica membrane technology and provides special buffer system for many kinds of sample’s gDNA extraction. The spin column is made of new type silica membrane can bind DNA optimally on given salt and pH conditions. Simple centrifugation processing com ...
IMPROVING ENANTIOSELECTIVITY OF ENZYMES THROUGH
... An S specific nitrilase will convert the non-labeled group to the carboxylic acid, while an R specific nitrilase will convert the labeled group to the carboxylic acid with loss of the 15N label. The one mass unit difference is detectable by mass spectrometry. Extensive screening led to many variants ...
... An S specific nitrilase will convert the non-labeled group to the carboxylic acid, while an R specific nitrilase will convert the labeled group to the carboxylic acid with loss of the 15N label. The one mass unit difference is detectable by mass spectrometry. Extensive screening led to many variants ...
SMIC Biology
... answers to questions. When time is up, peer leaders should bring up any items their groups were unable to resolve. Part 6: Scholarly Definitions Team leader: Divide the work amongst the group, including yourself. Your team should evaluate the definitions that follow by circling any parts that are in ...
... answers to questions. When time is up, peer leaders should bring up any items their groups were unable to resolve. Part 6: Scholarly Definitions Team leader: Divide the work amongst the group, including yourself. Your team should evaluate the definitions that follow by circling any parts that are in ...
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation | Principles of Biology from Nature
... RNA polymerases in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ. Prokaryotes use a single type of RNA polymerase, but eukaryotes have at least three different types of RNA polymerase. All of the genetic information contained within prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered their genome. In some cases, the cells ...
... RNA polymerases in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ. Prokaryotes use a single type of RNA polymerase, but eukaryotes have at least three different types of RNA polymerase. All of the genetic information contained within prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered their genome. In some cases, the cells ...
SFP 982319
... Multidrug-resistant TB with not yet appreciated circulation of the Hypervirulent TB strains, and proposes to consider them as a combined problem of increasing propagation of MDR-HV TB strains. Methodologically, this project aims to develop, evaluate and implement a fast, high-throughput and inexpens ...
... Multidrug-resistant TB with not yet appreciated circulation of the Hypervirulent TB strains, and proposes to consider them as a combined problem of increasing propagation of MDR-HV TB strains. Methodologically, this project aims to develop, evaluate and implement a fast, high-throughput and inexpens ...
Biology 321 Answers to Problem Set 6
... a. Review definition of polymorphism in earlier lecture b. silent or same sense mutation c. Neutral missense mutation (note legend at bottom of table that indicates that all people genotyped were healthy non-NIDDM) d. Examination of a normal control group is important because some sequence variation ...
... a. Review definition of polymorphism in earlier lecture b. silent or same sense mutation c. Neutral missense mutation (note legend at bottom of table that indicates that all people genotyped were healthy non-NIDDM) d. Examination of a normal control group is important because some sequence variation ...
7 - Anaerobic Respiration
... until after exercise finishes, or if exercise intensity drops significantly (as high levels of O2 availability are required for aerobic respiration) – fatigue occurs. •If exercise continues after the depletion of the PCr stores then other energy systems must be used to resynthesise ATP. •Only 1 ATP ...
... until after exercise finishes, or if exercise intensity drops significantly (as high levels of O2 availability are required for aerobic respiration) – fatigue occurs. •If exercise continues after the depletion of the PCr stores then other energy systems must be used to resynthesise ATP. •Only 1 ATP ...
RNA analysis on non-denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis
... Do not use high voltage to avoid RNA degradation during electrophoresis. ...
... Do not use high voltage to avoid RNA degradation during electrophoresis. ...
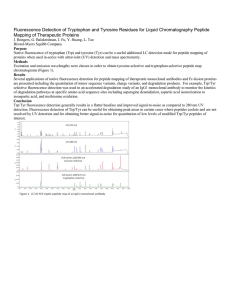
Fluorescence Detection of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues for
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
Assay Standards Working Group Recommendations, November 2012
... with two or more biological replicates, unless there is a compelling reason indicating that this is impractical or wasteful (e.g. overlapping time points with high temporal resolution). A biological replicate is defined as cells/tissue obtained from an independent human subject and subsequent analys ...
... with two or more biological replicates, unless there is a compelling reason indicating that this is impractical or wasteful (e.g. overlapping time points with high temporal resolution). A biological replicate is defined as cells/tissue obtained from an independent human subject and subsequent analys ...
Real-time polymerase chain reaction

A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (Quantitative real-time PCR), semi-quantitatively, i.e. above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules (Semi quantitative real-time PCR) or qualitatively (Qualitative real-time PCR).Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence.The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation qPCR be used for quantitative real-time PCR and that RT-qPCR be used for reverse transcription–qPCR [1]. The acronym ""RT-PCR"" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention.