SOIL ORIGIN and DEVELOPMENT
... • HYDROLYSIS – Water reacts with minerals in rock create NEW, SOFTER COMPOUNDS ...
... • HYDROLYSIS – Water reacts with minerals in rock create NEW, SOFTER COMPOUNDS ...
waste management and remediation of contaminated areas
... hydrocarbons in the free phase (1,900 ton) ...
... hydrocarbons in the free phase (1,900 ton) ...
Soil entomology
... Using easily identified macrofaunal taxa for soil zoological site assessments C. Kantner, A. Bruckner During the last 100 years, limnologists have established an indicator system which evaluates water quality by analyzing the occurrence of aquatic organisms using representative taxa from nearly all ...
... Using easily identified macrofaunal taxa for soil zoological site assessments C. Kantner, A. Bruckner During the last 100 years, limnologists have established an indicator system which evaluates water quality by analyzing the occurrence of aquatic organisms using representative taxa from nearly all ...
Lesson 3 – Explore – Page 261 “Plant Processes”
... During photosynthesis, a plant produces sugar that it uses as food. Even organisms that don’t eat plants directly depend on plants because they eat other organisms that do eat plants. Organisms need energy for growth, repair, movement, and other life processes. Where does this energy come from ...
... During photosynthesis, a plant produces sugar that it uses as food. Even organisms that don’t eat plants directly depend on plants because they eat other organisms that do eat plants. Organisms need energy for growth, repair, movement, and other life processes. Where does this energy come from ...
to view and print the tri-fold brochure on Growing Hostas
... organic matter. Prepare your bed. Remove weeds. Till soil and add compost or peat moss so that you have a loose friable soil. Hosta should be planted so that the crown, where all the new growth buds are, is at the same depth as it is in the pot or ground. The eyes should be just below the surface. T ...
... organic matter. Prepare your bed. Remove weeds. Till soil and add compost or peat moss so that you have a loose friable soil. Hosta should be planted so that the crown, where all the new growth buds are, is at the same depth as it is in the pot or ground. The eyes should be just below the surface. T ...
LandSlides - European Soil Portal
... • Improvements in harmonisation are necessary because: - inventories do not follow any commonly agreed standards or methodologies until now - authorities in charge of inventories are either local, regional or national and can be civil engineers, soil scientists or geologists • Only landslides relate ...
... • Improvements in harmonisation are necessary because: - inventories do not follow any commonly agreed standards or methodologies until now - authorities in charge of inventories are either local, regional or national and can be civil engineers, soil scientists or geologists • Only landslides relate ...
Ch11
... 2. Monoculture: Large areas planted with a single species (entire crop vulnerable to disease, depletes soil of specific chemicals) ...
... 2. Monoculture: Large areas planted with a single species (entire crop vulnerable to disease, depletes soil of specific chemicals) ...
Lab 12
... INTRODUCTION Plants need at least 17 different chemical elements to grow. An element is a pure chemical that contains only one type of atom. Examples of common elements include iron, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Calcitic and dolomitic lime is examples of compounds. These substances consist ...
... INTRODUCTION Plants need at least 17 different chemical elements to grow. An element is a pure chemical that contains only one type of atom. Examples of common elements include iron, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Calcitic and dolomitic lime is examples of compounds. These substances consist ...
Avocado Root Rot - Avocadosource.com
... spores swim through water in the soil and attack the avocado roots. The oospores are presumably resistant spores, which have previously been reported only rarely with the cinnamon fungus. We found that oospores are produced readily in the presence of ...
... spores swim through water in the soil and attack the avocado roots. The oospores are presumably resistant spores, which have previously been reported only rarely with the cinnamon fungus. We found that oospores are produced readily in the presence of ...
2015-2016 Groundwater Virtual Lab
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
Communities & Biomes
... Range over which a population or organism can successfully survive & grow Too much or too little of an environmental factor can be limiting ...
... Range over which a population or organism can successfully survive & grow Too much or too little of an environmental factor can be limiting ...
biological nitrogen fixation (bnf) in legumes: importance in
... forms (NO3, NH4) as this requires less energy than making their N from BNF ( to use ‘N’ from the soil) . If it is a question of adding fertilizer ‘N’, BNF is the best alternative than adding inorganic fertilizer. Pulses high nitrogen requirement for protein synthesis Need to apply very large q ...
... forms (NO3, NH4) as this requires less energy than making their N from BNF ( to use ‘N’ from the soil) . If it is a question of adding fertilizer ‘N’, BNF is the best alternative than adding inorganic fertilizer. Pulses high nitrogen requirement for protein synthesis Need to apply very large q ...
BIOL 4120: Principles of Ecology Lecture 5: Terrestrial Environment
... in very dry climates and when loss of soil moisture due to ET exceeds PPT, water leaves the soil through the surface. The minerals (NaCl) dissolved move upward from the groundwater and result in a salt crust on the surface of the soil. ...
... in very dry climates and when loss of soil moisture due to ET exceeds PPT, water leaves the soil through the surface. The minerals (NaCl) dissolved move upward from the groundwater and result in a salt crust on the surface of the soil. ...
Chapter 12 * Weathering, Soil and Erosion
... Water and Chemical Weathering The chemical weathering by reaction of water with other substances is called hydrolysis. Water’s chemical effect on minerals is increased by the presence of acids that are dissolved in the water. When rainwater containing carbonic acid seeps into the ground, it ...
... Water and Chemical Weathering The chemical weathering by reaction of water with other substances is called hydrolysis. Water’s chemical effect on minerals is increased by the presence of acids that are dissolved in the water. When rainwater containing carbonic acid seeps into the ground, it ...
Soil
... What farming practices reduce soil loss? No-till Farming: The soil is not plowed each time a new planting takes place. The roots of the previous planting continue to hold the soil in place until the next planting. Strip Cropping: A crop that covers the ground such as wheat is planted in strips aroun ...
... What farming practices reduce soil loss? No-till Farming: The soil is not plowed each time a new planting takes place. The roots of the previous planting continue to hold the soil in place until the next planting. Strip Cropping: A crop that covers the ground such as wheat is planted in strips aroun ...
soil horizons
... down by physical, chemical and biological processes called weathering. Mature soils, or soils that have developed over a long time are arranged in a series of horizontal layers called soil horizons. ...
... down by physical, chemical and biological processes called weathering. Mature soils, or soils that have developed over a long time are arranged in a series of horizontal layers called soil horizons. ...
Soils
... • Is the soft material that covers the surface of the earth and provides a place for the growth of plant roots. • It also contains minerals, organic matter, air, and water. ...
... • Is the soft material that covers the surface of the earth and provides a place for the growth of plant roots. • It also contains minerals, organic matter, air, and water. ...
Study guide for Ecosystem Test 6 Levels of organization in ecology
... Population- all the organisms of one type in an area ex. all the rattlesnakes in a forest Community- all the populations of different organisms in an area ex. all the snakes, trees, grass, deer, etc. in a forest Ecosystem- all the different organisms AND the nonliving parts in an area ex. All the sn ...
... Population- all the organisms of one type in an area ex. all the rattlesnakes in a forest Community- all the populations of different organisms in an area ex. all the snakes, trees, grass, deer, etc. in a forest Ecosystem- all the different organisms AND the nonliving parts in an area ex. All the sn ...
Grasslands Unit Lecture Notes
... uptake enhanced by mycorrhizae "mined" from decaying organisms ...
... uptake enhanced by mycorrhizae "mined" from decaying organisms ...
objectives
... INTRODUCTION Plants need at least 16 different chemical elements to grow. An element is a pure chemical that contains only one type of atom. Examples of common elements include iron, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Calcite, dolomite, and lime are examples of compounds. These substances consis ...
... INTRODUCTION Plants need at least 16 different chemical elements to grow. An element is a pure chemical that contains only one type of atom. Examples of common elements include iron, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Calcite, dolomite, and lime are examples of compounds. These substances consis ...
1 - Madison Public Schools
... __________________________________________________________________ 7. Soil Color – determined by climate and composition 8. Soil Structure a. Ability of water to infiltrate soil – determined by how soil particles are arranged and if water can infiltrate (soak through) easily ...
... __________________________________________________________________ 7. Soil Color – determined by climate and composition 8. Soil Structure a. Ability of water to infiltrate soil – determined by how soil particles are arranged and if water can infiltrate (soak through) easily ...
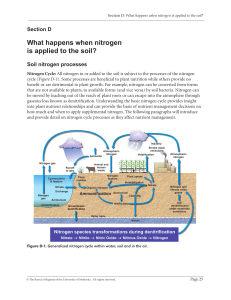
What happens when nitrogen is applied to the soil?
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
Y 11 AQA Biology: Uses of glucose crossword
... 2) Possible future use of some oil rich algal cells. (7) 6) This complex carbohydrate made from glucose is used to strengthen plant cell walls. (9) 7) Type of acid which is linked together to make proteins. (5) 8) Storage carbohydrate molecule made by plants from many glucose molecules. (6) 9) Proce ...
... 2) Possible future use of some oil rich algal cells. (7) 6) This complex carbohydrate made from glucose is used to strengthen plant cell walls. (9) 7) Type of acid which is linked together to make proteins. (5) 8) Storage carbohydrate molecule made by plants from many glucose molecules. (6) 9) Proce ...
Soil: Crucible of Life - American Society of Agronomy
... cascades through the soil and the plants growing in it. Heat is exchanged, water percolates through the intricate passages of the soil, plant roots suck up some of that water and transmit it to their leaves, which transpire it back to the atmosphere. The leaves absorb carbon dioxide from the air and ...
... cascades through the soil and the plants growing in it. Heat is exchanged, water percolates through the intricate passages of the soil, plant roots suck up some of that water and transmit it to their leaves, which transpire it back to the atmosphere. The leaves absorb carbon dioxide from the air and ...