Investigating the role of cell cycle control by Fbxo7 in the
... The deregulation of the G1/S phase transition occurs regularly in multiple cancer subtypes, including T cell malignancies (1). This can happen as a result of direct mutations, including inactivation of tumour suppressor genes, like the INK4 family members of cyclin dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor ...
... The deregulation of the G1/S phase transition occurs regularly in multiple cancer subtypes, including T cell malignancies (1). This can happen as a result of direct mutations, including inactivation of tumour suppressor genes, like the INK4 family members of cyclin dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor ...
ﺟﺎﻣﻌﺔ اﻻﺳﮐﻧدرﯾﺔ ﮐﻟﯾﺔ اﻟطب Module (3): Introduction to Medical Sciences
... جامعة االسكندرية كلية الطب The full contents (Practical, Lectures& ILA of the Integrated curriculum Of the Histology Department 2014-2015 First Year ...
... جامعة االسكندرية كلية الطب The full contents (Practical, Lectures& ILA of the Integrated curriculum Of the Histology Department 2014-2015 First Year ...
Cell City Worksheet – high school
... _______________________. It has a ____________________ membrane. The inner membrane is where most _______________ respiration occurs. The inner membranes is __________ with a very large surface area. These ruffles are called ___________. Mitochondria have their own ________ and manufacture some of t ...
... _______________________. It has a ____________________ membrane. The inner membrane is where most _______________ respiration occurs. The inner membranes is __________ with a very large surface area. These ruffles are called ___________. Mitochondria have their own ________ and manufacture some of t ...
Structure
... – Attachment sites for molecules needing to enter, or for messenger molecules such as hormones. – These are very specific to each person and play a role in recognizing our own cells (organ transplants) ...
... – Attachment sites for molecules needing to enter, or for messenger molecules such as hormones. – These are very specific to each person and play a role in recognizing our own cells (organ transplants) ...
section 3-3 notes
... Define) of an animal and plant cell from pages 56-57 in your science book. • First draw or sketch out plant and animal cell with pencil first. • Next, label ALL parts of both cells and give a BRIEF description of each on the back, bottom, or sides of your DLC. • Last, please color both cells. • Not ...
... Define) of an animal and plant cell from pages 56-57 in your science book. • First draw or sketch out plant and animal cell with pencil first. • Next, label ALL parts of both cells and give a BRIEF description of each on the back, bottom, or sides of your DLC. • Last, please color both cells. • Not ...
Cell parts powerpoint
... • The membrane around the nucleus is what separates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. ...
... • The membrane around the nucleus is what separates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. ...
Cell-testRvwPPT_Answers to Questions
... site of cellular respiration (ATP production) • Golgi Apparatus – “fedEx of Cell”, packages proteins for delivery in/out of cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum – “highway of the cell”, transports proteins throughout cell. – Rough E.R. = has Ribosomes – Smooth E.R. = no ribosomes ...
... site of cellular respiration (ATP production) • Golgi Apparatus – “fedEx of Cell”, packages proteins for delivery in/out of cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum – “highway of the cell”, transports proteins throughout cell. – Rough E.R. = has Ribosomes – Smooth E.R. = no ribosomes ...
File
... Complete each statement. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. cell membrane nucleus lysosome ribosome organelle Golgi complex mitochondria organs prokaryotic 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s ...
... Complete each statement. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. cell membrane nucleus lysosome ribosome organelle Golgi complex mitochondria organs prokaryotic 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s ...
Biology Study Guide: 7
... Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? ...
... Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? ...
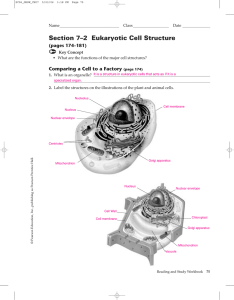
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Students’ flowcharts should include RNA moving out of the nucleus, the production of proteins in ribosomes, modification in rough ER, proteins moving into the Golgi apparatus, proteins sent to their final destinations. ...
... Students’ flowcharts should include RNA moving out of the nucleus, the production of proteins in ribosomes, modification in rough ER, proteins moving into the Golgi apparatus, proteins sent to their final destinations. ...
organelle function ws. - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... $IP38.-arestructuresthatcontaindigestiveenzymes. o ffi 9. In addition to a cell membrane, plant cells also have a that serves to ...
... $IP38.-arestructuresthatcontaindigestiveenzymes. o ffi 9. In addition to a cell membrane, plant cells also have a that serves to ...
Cell Organelles
... the center of the cell. • In most houses, the living room is where the most action happens; families and friends gather, entertainment is produced and much more. • In a cell, some of the more important things happen in the nucleus; transcription, translation and replication. ...
... the center of the cell. • In most houses, the living room is where the most action happens; families and friends gather, entertainment is produced and much more. • In a cell, some of the more important things happen in the nucleus; transcription, translation and replication. ...
Cell Organelles
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
Cell Organelles - Cloudfront.net
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
Slide 1 - ParklandNatSciWiki
... degree of specificity • Binding and release between receptor and ligand relatively rapid • Ligands alter receptor structureconformational change • Once a ligand is released, the receptor is no longer activated ...
... degree of specificity • Binding and release between receptor and ligand relatively rapid • Ligands alter receptor structureconformational change • Once a ligand is released, the receptor is no longer activated ...
Key Term Review: Cell Structure and Function
... Key Term Review: Cell Structure and Function Match each term in Column B with its description in Column A. Write the correct letter in the space provided. Column B ...
... Key Term Review: Cell Structure and Function Match each term in Column B with its description in Column A. Write the correct letter in the space provided. Column B ...
Chap 4 sec 2 Fact Review Sheet
... 14. The cell membrane has two layers of phospholipids. 15. A phospholipid is a type of lipid. 16. Each phospholipid has a hydrophobic, or “water fearing,” end and a hydrophilic, or “water loving,” end. The “water fearing” ends form the outer part of the membrane. 17. This structure makes it difficul ...
... 14. The cell membrane has two layers of phospholipids. 15. A phospholipid is a type of lipid. 16. Each phospholipid has a hydrophobic, or “water fearing,” end and a hydrophilic, or “water loving,” end. The “water fearing” ends form the outer part of the membrane. 17. This structure makes it difficul ...
Cell Parts - Humble ISD
... Cell Membrane Protects the cell Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell ...
... Cell Membrane Protects the cell Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell ...
Growth Factor Receptors
... proliferation. Most soluble growth factors are made by one cell type and act on a neighboring cell to stimulate proliferation (paracrine action). Many cancer cells, however, acquire the ability to synthesize the same growth factors to which they are responsive, generating an autocrine loop. For exam ...
... proliferation. Most soluble growth factors are made by one cell type and act on a neighboring cell to stimulate proliferation (paracrine action). Many cancer cells, however, acquire the ability to synthesize the same growth factors to which they are responsive, generating an autocrine loop. For exam ...
The Incredible Edible Cell
... √ Are all the organelles included? (10 for plants cells, 9 for animal cells) √ Are the organelles correctly labeled? Each organelle must be labeled with its name and function. You may label each organelle or use a key. √ Are the relationships between the parts (if any) shown correctly? Are the ribos ...
... √ Are all the organelles included? (10 for plants cells, 9 for animal cells) √ Are the organelles correctly labeled? Each organelle must be labeled with its name and function. You may label each organelle or use a key. √ Are the relationships between the parts (if any) shown correctly? Are the ribos ...
The Parts of the Cell - St. Pius X High School
... Vesicles – small membrane sacs, function - transport --'bud' off of ER to transport proteins to Golgi --'bud' off Golgi to transport contents to plasma membrane for export ...
... Vesicles – small membrane sacs, function - transport --'bud' off of ER to transport proteins to Golgi --'bud' off Golgi to transport contents to plasma membrane for export ...
The Cell (2)
... 36. Microtubules are thin hollow pipes. They are made up of proteins known as tubulins. They help the cell maintain shape. They are found in structures such as cilia and flagella that help some organisms to swim. 37. Proteins are made on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are small units of RNA and protein fo ...
... 36. Microtubules are thin hollow pipes. They are made up of proteins known as tubulins. They help the cell maintain shape. They are found in structures such as cilia and flagella that help some organisms to swim. 37. Proteins are made on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are small units of RNA and protein fo ...
Parts of the Cell Plant and Animal
... • Since an animal cell does not have a cell wall, the cell membrane forms a barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell; however, plants have a cell membrane as well. The cell membrane protects the cell and regulates what substances enter and leave the cell. ...
... • Since an animal cell does not have a cell wall, the cell membrane forms a barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell; however, plants have a cell membrane as well. The cell membrane protects the cell and regulates what substances enter and leave the cell. ...
Apoptosis

Apoptosis (/ˌæpəˈtoʊsɪs/; from Ancient Greek ἀπό apo, ""by, from, of, since, than"" and πτῶσις ptōsis, ""fall"") is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay.In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bodies that phagocytic cells are able to engulf and quickly remove before the contents of the cell can spill out onto surrounding cells and cause damage.Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. For an average child between the ages of 8 and 14, approximately 20 billion to 30 billion cells die a day.Research in and around apoptosis has increased substantially since the early 1990s. In addition to its importance as a biological phenomenon, defective apoptotic processes have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases. Excessive apoptosis causes atrophy, whereas an insufficient amount results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, such as cancer.Some factors like Fas receptor, caspases (C-cysteine rich, asp- aspartic acid moiety containing, ase – proteases) etc. promote apoptosis, while members of Bcl-2 inhibit apoptosis.