Organelle Worksheet - Allen County Schools
... Review of 1/7/13 Nucleus, ER, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplast, cell wall, cell membrane PLACE THE ORGANELLE NEXT TO THE FUNCTION 1. What cell part controls the cell? 2. What organelle is a passageway through the cytoplasm? 3. What organelle is a storage tank for cells? 4. What covers an animal c ...
... Review of 1/7/13 Nucleus, ER, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplast, cell wall, cell membrane PLACE THE ORGANELLE NEXT TO THE FUNCTION 1. What cell part controls the cell? 2. What organelle is a passageway through the cytoplasm? 3. What organelle is a storage tank for cells? 4. What covers an animal c ...
Pre-AP Biology Cell Transport Worksheet
... Cell Transport Worksheet 1. A cell was poisoned by a substance that destroyed all of its mitochondria. Circle all of the cell transport processes listed that would still be able to continue. a. Osmosis d. Exocytosis b. Diffusion e. Pinocytosis c. Facilitated diffusion f. Phagocytosis ...
... Cell Transport Worksheet 1. A cell was poisoned by a substance that destroyed all of its mitochondria. Circle all of the cell transport processes listed that would still be able to continue. a. Osmosis d. Exocytosis b. Diffusion e. Pinocytosis c. Facilitated diffusion f. Phagocytosis ...
CH 3 Part 2 - Catherine Huff`s Site
... •Located near cell surface on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart ...
... •Located near cell surface on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart ...
THROUGH THE CELL MEMBRANE!!!
... passageway or pore from the outside of the cell to the inside of the cell. - Small molecules like H2O, O2, CO2 & glucose are able to DIFFUSE through the cell membrane b/w the lipid molecules. ...
... passageway or pore from the outside of the cell to the inside of the cell. - Small molecules like H2O, O2, CO2 & glucose are able to DIFFUSE through the cell membrane b/w the lipid molecules. ...
Enveroment dep 1 st Lec 1 The plant cell The cell is basic unit of life
... ribosomes. In plant cell the DNA in the nucleus is organized into complex thread like structures called chromosomes , each it consists of many genes 2- Ribosomes bulid proteins : ribosomes are organelles that are formed in the cytoplasm and direct the synthesis of proteins , using genetic instructio ...
... ribosomes. In plant cell the DNA in the nucleus is organized into complex thread like structures called chromosomes , each it consists of many genes 2- Ribosomes bulid proteins : ribosomes are organelles that are formed in the cytoplasm and direct the synthesis of proteins , using genetic instructio ...
CELL (Introduction)
... • Formation of high energy compound Adenosine Tri phosphate (ATP). • Mitochondria has its own cellular DNA and replicates independently of the cell in which it is found. ...
... • Formation of high energy compound Adenosine Tri phosphate (ATP). • Mitochondria has its own cellular DNA and replicates independently of the cell in which it is found. ...
Cell Organelles
... water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
MITOTIC CELL DIVISION
... pulled to the poll by the contraction of the spindle fibers • chromatids are separated at the centromere ...
... pulled to the poll by the contraction of the spindle fibers • chromatids are separated at the centromere ...
Golgi Apparatus 2
... The front is called the cis face Usually found near the ER Materials enter the Golgi body in transport vesicles that come from the ER ...
... The front is called the cis face Usually found near the ER Materials enter the Golgi body in transport vesicles that come from the ER ...
1 Lecture 34 – Cell Cycle Control and Cancer Genetics I. Cancers
... IV. Apoptosis – programmed cell death A. excess cells produced during development destined to die - example: webbing between digits B. cells that may become cancerous also can be killed by apoptosis - better to lose a few cells than to develop cancer - intracellular proteases degrade proteins, kill ...
... IV. Apoptosis – programmed cell death A. excess cells produced during development destined to die - example: webbing between digits B. cells that may become cancerous also can be killed by apoptosis - better to lose a few cells than to develop cancer - intracellular proteases degrade proteins, kill ...
Plant PCD In vegetative development Suspensor degradation
... 1. Autoimmune, other defects in immune system 2. Defective signaling ...
... 1. Autoimmune, other defects in immune system 2. Defective signaling ...
Cullen Lecture 6: Signal Transduction in Fungi Filamentous Growth
... Msb2 w/o the Mucin Domain is Hyperactive ...
... Msb2 w/o the Mucin Domain is Hyperactive ...
4_ Cells and cell di..
... system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm Smooth ER transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made prote ...
... system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm Smooth ER transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made prote ...
1 Do cell-intrinsic (lineage) or cell
... •little cell migration (cell sliding possible) Cells of same parentage are also neighbours ...
... •little cell migration (cell sliding possible) Cells of same parentage are also neighbours ...
Introduction to the Cell
... ● may contain soluble pigments in some cells (red and blue pigments in flowers); ● help protect from predators by storing waste products that may also be poisonous compounds ● contractile vacuole: specialized vacuole that pumps excess water out of cell. ...
... ● may contain soluble pigments in some cells (red and blue pigments in flowers); ● help protect from predators by storing waste products that may also be poisonous compounds ● contractile vacuole: specialized vacuole that pumps excess water out of cell. ...
V. Lecture Section 5 A. Review of the mitotic cell cycle and cell death
... 1. Internal activation of apoptosis = Intrinsic apoptotic pathway 2. External activation of apopotosis = Extrinsic apoptotic pathway 3. Activation of Caspase Cascade 4. Characteristics include cessation of DNA repair mechanisms, cell shrinkage, nuclear membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, and death ...
... 1. Internal activation of apoptosis = Intrinsic apoptotic pathway 2. External activation of apopotosis = Extrinsic apoptotic pathway 3. Activation of Caspase Cascade 4. Characteristics include cessation of DNA repair mechanisms, cell shrinkage, nuclear membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, and death ...
Mitochondrion File
... generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.[4] Mitochondria are commonly between 0.75 and 3μm in diameter[5] but vary considerably in size and structure. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. In addition to supplying cellular ...
... generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.[4] Mitochondria are commonly between 0.75 and 3μm in diameter[5] but vary considerably in size and structure. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. In addition to supplying cellular ...
Wellness and Illness
... telomere shortening → abnormal chromosome structure → malfunction or apoptosis ...
... telomere shortening → abnormal chromosome structure → malfunction or apoptosis ...
Incredible Edible Cell
... Purpose: You will use several different food items representing the various organelles or cell structures found in plant and animal cells to construct an edible cell model. This activity will help you learn more about the different parts of a cell and their functions. Background: All cells have a ce ...
... Purpose: You will use several different food items representing the various organelles or cell structures found in plant and animal cells to construct an edible cell model. This activity will help you learn more about the different parts of a cell and their functions. Background: All cells have a ce ...
A Cell in a Bag Project
... A cell is really like a plastic bag with some interesting “stuff” inside of it. The “stuff” in the bag also works like the inside of a car to be sure that the cell is able survive. This project will help you to visualize the cell as a 3D structure with the machinery necessary to sustain life. Proced ...
... A cell is really like a plastic bag with some interesting “stuff” inside of it. The “stuff” in the bag also works like the inside of a car to be sure that the cell is able survive. This project will help you to visualize the cell as a 3D structure with the machinery necessary to sustain life. Proced ...
REVISED Handout
... Purpose: You will use several different food items representing the various organelles or cell structures found in plant and animal cells to construct an edible cell model. This activity will help you learn more about the different parts of a cell and their functions. Background: All cells have a ce ...
... Purpose: You will use several different food items representing the various organelles or cell structures found in plant and animal cells to construct an edible cell model. This activity will help you learn more about the different parts of a cell and their functions. Background: All cells have a ce ...
Cell Division (Mitosis) and Death
... Contain hundreds to thousands of repeats of a 6base DNA sequence added by telomerase ...
... Contain hundreds to thousands of repeats of a 6base DNA sequence added by telomerase ...
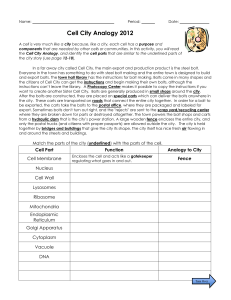
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Human Protein Factories in 3D - Max-Planck
... Martinsried near Munich, Germany, succeeded in mapping the inner life of an intact human cell three-dimensionally via cryo-electron tomography. In this way they were able to show where the ribosomes are located in the cell and how they are arranged. In the past, this was only possible with bacterial ...
... Martinsried near Munich, Germany, succeeded in mapping the inner life of an intact human cell three-dimensionally via cryo-electron tomography. In this way they were able to show where the ribosomes are located in the cell and how they are arranged. In the past, this was only possible with bacterial ...
Apoptosis

Apoptosis (/ˌæpəˈtoʊsɪs/; from Ancient Greek ἀπό apo, ""by, from, of, since, than"" and πτῶσις ptōsis, ""fall"") is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay.In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bodies that phagocytic cells are able to engulf and quickly remove before the contents of the cell can spill out onto surrounding cells and cause damage.Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. For an average child between the ages of 8 and 14, approximately 20 billion to 30 billion cells die a day.Research in and around apoptosis has increased substantially since the early 1990s. In addition to its importance as a biological phenomenon, defective apoptotic processes have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases. Excessive apoptosis causes atrophy, whereas an insufficient amount results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, such as cancer.Some factors like Fas receptor, caspases (C-cysteine rich, asp- aspartic acid moiety containing, ase – proteases) etc. promote apoptosis, while members of Bcl-2 inhibit apoptosis.