Cell Model
... HAVE FUN LEARNING ABOUT CELLS & BE CREATIVE!!! Cells are complex structures filled with many parts called organelles, which perform the functions organisms depend upon to live and develop. Each organelle in a cell is structurally adapted to perform Its important job so all the organelles can work to ...
... HAVE FUN LEARNING ABOUT CELLS & BE CREATIVE!!! Cells are complex structures filled with many parts called organelles, which perform the functions organisms depend upon to live and develop. Each organelle in a cell is structurally adapted to perform Its important job so all the organelles can work to ...
Vocabulary Assignment Unit 03
... o. Sacks of membranes that move material around the cell; the cell’s ‘highway’ p. One part of this says all cells came from other cells q. Diffusion in which the material is helped in or out of the cell by protein channels r. Cell transport that goes from low concentration to high by using energy s. ...
... o. Sacks of membranes that move material around the cell; the cell’s ‘highway’ p. One part of this says all cells came from other cells q. Diffusion in which the material is helped in or out of the cell by protein channels r. Cell transport that goes from low concentration to high by using energy s. ...
Make Vocabulary Flash Cards
... Chloroplast – A green structure found inside a plant cell. This structure changes ...
... Chloroplast – A green structure found inside a plant cell. This structure changes ...
6th Grade
... HOUR: CELL THEORY: Look at the cell theory on page 476 of your book and record each of the step of cell theory below. This is going to be on your final. ...
... HOUR: CELL THEORY: Look at the cell theory on page 476 of your book and record each of the step of cell theory below. This is going to be on your final. ...
image - Filament Games
... the information center of a cell that controls the chemical reactions that happen in cytoplasm; also stores DNA. a round structure that is inside the nucleus of a cell; this structure makes ribosomes. separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell; regulates substances that move in and out of the n ...
... the information center of a cell that controls the chemical reactions that happen in cytoplasm; also stores DNA. a round structure that is inside the nucleus of a cell; this structure makes ribosomes. separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell; regulates substances that move in and out of the n ...
Cells Alive Worksheet
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
Cel l and Tissue Injury
... • Pathology is "Scientific study of disease“ Study of structural and functional changes in disease. • Diseases is an expression of "discomfort" due to structural or functional abnormality. • "Pathology deals with knowledge of what causes disease, how disease starts, progresses & it explains the rea ...
... • Pathology is "Scientific study of disease“ Study of structural and functional changes in disease. • Diseases is an expression of "discomfort" due to structural or functional abnormality. • "Pathology deals with knowledge of what causes disease, how disease starts, progresses & it explains the rea ...
Mitochondria Biogenesis
... Interactions with chaperones in the cytosol keep the precursor in an unfolded conformation (“import-competent”) ...
... Interactions with chaperones in the cytosol keep the precursor in an unfolded conformation (“import-competent”) ...
Genomic instability - Roswell Park Cancer Institute
... High frequency of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT abnormalities in T-‐cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009 ...
... High frequency of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT abnormalities in T-‐cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009 ...
BIOL 107 A3 - Fall 2007 - Dr. Harrington Midterm Exam October 23
... A. inhibits the COX-1 enzyme B. inhibits the COX-2 enzyme C. activates the COX-1 enzyme D. activates the COX-2 enzyme 11) The existence of life does not violate the second law of thermodynamics because growth of an organism: A. increases the organism’s entropy B. does not create or destroy energy C. ...
... A. inhibits the COX-1 enzyme B. inhibits the COX-2 enzyme C. activates the COX-1 enzyme D. activates the COX-2 enzyme 11) The existence of life does not violate the second law of thermodynamics because growth of an organism: A. increases the organism’s entropy B. does not create or destroy energy C. ...
1. Robert Hook was famous for: 2. Matthias Schleiden: 3. Theodor
... activity. The nuclear envelope has many ____________________ for letting out genetic information. When the cell is making copies of itself, it contains DNA in the form of thick ropy strands called_____________________. When the cell is resting and making ____________ the DNA is thin and relaxed and ...
... activity. The nuclear envelope has many ____________________ for letting out genetic information. When the cell is making copies of itself, it contains DNA in the form of thick ropy strands called_____________________. When the cell is resting and making ____________ the DNA is thin and relaxed and ...
The Parts of a Cell
... materials others transport materials in the cell. • Examples are Lysosomes , Central vacuole, and other vacuoles. Central Vacuole – stores water and nutrients in plant cells. ...
... materials others transport materials in the cell. • Examples are Lysosomes , Central vacuole, and other vacuoles. Central Vacuole – stores water and nutrients in plant cells. ...
CELL CITY INTRODUCTION! Floating around in the cytoplasm are
... ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 8. The C is an oval, green structure found in the cytopla ...
... ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 8. The C is an oval, green structure found in the cytopla ...
Surprise! This eukaryote completely lacks mitochondria
... within cells that are often described as the cells' powerhouses. They've long been considered as essential components for life in eukaryotes, the group including plants, fungi, animals, and unicellular protists, if for no other reason than that every known eukaryote had them. But researchers reporti ...
... within cells that are often described as the cells' powerhouses. They've long been considered as essential components for life in eukaryotes, the group including plants, fungi, animals, and unicellular protists, if for no other reason than that every known eukaryote had them. But researchers reporti ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to the next in cell cycle ...
... CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to the next in cell cycle ...
The story inside the Cell
... with ribosomes that make its surface look rough The proteins are released from the ER for use elsewhere ...
... with ribosomes that make its surface look rough The proteins are released from the ER for use elsewhere ...
Cell Cycle Regulation
... Name__________________ Cell Cycle Regulation & Cancer Web Quest: Activity Introduction: Cells divide in order for an organism to grow, develop and repair itself. Cells grow and divide in a specific fashion. When cells do not divide the way they are supposed to cancer can develop. In this activity, y ...
... Name__________________ Cell Cycle Regulation & Cancer Web Quest: Activity Introduction: Cells divide in order for an organism to grow, develop and repair itself. Cells grow and divide in a specific fashion. When cells do not divide the way they are supposed to cancer can develop. In this activity, y ...
4-2 Cell Organelles - TJ
... a. allows substances to pass into and out of the cell. b. prevents all substances from passing in and out of the cell. c. is composed mainly of a protein bilayer. d. is composed mainly of a lipid bilayer. 5. Substances produced in a cell and exported outside of the cell would pass through the a. end ...
... a. allows substances to pass into and out of the cell. b. prevents all substances from passing in and out of the cell. c. is composed mainly of a protein bilayer. d. is composed mainly of a lipid bilayer. 5. Substances produced in a cell and exported outside of the cell would pass through the a. end ...
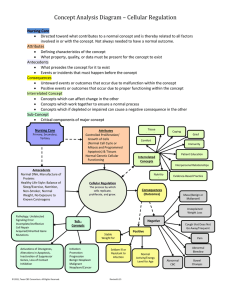
Concept Analysis Diagram * Cellular Regulation
... Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, healthy life-style: balance of sleep/exercise/nut ...
... Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, healthy life-style: balance of sleep/exercise/nut ...
Cell City - CAC
... UFOs!! UFOs!! I see them: Unidentified Floating Objects! They’re taking over your cells, and it’s up to you to figure out what they are!! Just like the first scientists studying cells, you need to identify the names and functions of each of the “UFO’s” (a.k.a. organelles) that are found in your ce ...
... UFOs!! UFOs!! I see them: Unidentified Floating Objects! They’re taking over your cells, and it’s up to you to figure out what they are!! Just like the first scientists studying cells, you need to identify the names and functions of each of the “UFO’s” (a.k.a. organelles) that are found in your ce ...
Anti-Cytochrome c Mouse mAb (7H8.2C12) Cat. No. AP1029
... protein. Holocytochrome c is a soluble protein located in the intermembrane space of mitochondria, loosely attached to the inner membrane and is an essential component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Early studies showed that during the course of an apoptotic response there was a rapid loss ...
... protein. Holocytochrome c is a soluble protein located in the intermembrane space of mitochondria, loosely attached to the inner membrane and is an essential component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Early studies showed that during the course of an apoptotic response there was a rapid loss ...
Parts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
... made of DNA, found in the NUCLEOID REGION. Like all cells, bacteria are surrounded by a cell membrane which contains the gel-like cytosol of the cell. ...
... made of DNA, found in the NUCLEOID REGION. Like all cells, bacteria are surrounded by a cell membrane which contains the gel-like cytosol of the cell. ...
Apoptosis

Apoptosis (/ˌæpəˈtoʊsɪs/; from Ancient Greek ἀπό apo, ""by, from, of, since, than"" and πτῶσις ptōsis, ""fall"") is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay.In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bodies that phagocytic cells are able to engulf and quickly remove before the contents of the cell can spill out onto surrounding cells and cause damage.Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. For an average child between the ages of 8 and 14, approximately 20 billion to 30 billion cells die a day.Research in and around apoptosis has increased substantially since the early 1990s. In addition to its importance as a biological phenomenon, defective apoptotic processes have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases. Excessive apoptosis causes atrophy, whereas an insufficient amount results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, such as cancer.Some factors like Fas receptor, caspases (C-cysteine rich, asp- aspartic acid moiety containing, ase – proteases) etc. promote apoptosis, while members of Bcl-2 inhibit apoptosis.