File
... systemic expression of defense genes and is a long-lasting response • Salicylic acid is synthesized around the infection site and is likely the signal that triggers systemic acquired resistance ...
... systemic expression of defense genes and is a long-lasting response • Salicylic acid is synthesized around the infection site and is likely the signal that triggers systemic acquired resistance ...
Teaching metabolic pathways
... potential electrons can readily be converted into ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The pathway of reducing equivalents can usually be described as the involvement of electron carriers, such as N A D H and FADH2. In glycolysis, all the intermediates between glucose and pyruvate have at least one pho ...
... potential electrons can readily be converted into ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The pathway of reducing equivalents can usually be described as the involvement of electron carriers, such as N A D H and FADH2. In glycolysis, all the intermediates between glucose and pyruvate have at least one pho ...
New Product Highlights Monoclonal Anti
... and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is released by autoproteolysis and functions through interactions with a multicomponent receptor complex containing the transmembrane proteins, Patched and Smoothened. Shh protein is expressed in key embryonic tissues such as the Hensen’s node, zone of polariz ...
... and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is released by autoproteolysis and functions through interactions with a multicomponent receptor complex containing the transmembrane proteins, Patched and Smoothened. Shh protein is expressed in key embryonic tissues such as the Hensen’s node, zone of polariz ...
Regulation of Metabolism
... • Cells in the pancreas sense [glucose] and release the peptide hormone insulin • Insulin circulates in the blood and attaches to receptors on target cells • Receptors translate insulin binding into an appropriate cellular response (lower blood glucose) via a second messenger signaling pathway. • In ...
... • Cells in the pancreas sense [glucose] and release the peptide hormone insulin • Insulin circulates in the blood and attaches to receptors on target cells • Receptors translate insulin binding into an appropriate cellular response (lower blood glucose) via a second messenger signaling pathway. • In ...
p-IRS-1/2 (Tyr 612)-R: sc-17195-R
... to induce IRS-1 Ser 312 phosphorylation. Insulin resistance in the aorta of hypertensive rats is associated with elevated IRS-1 phosphorylation at Ser 307 and increased SAPK/JNK activation. IRS-1 contains three putative binding sites for 14-3-3 protein at Ser 270, Ser 374 and Ser 641 that are capabl ...
... to induce IRS-1 Ser 312 phosphorylation. Insulin resistance in the aorta of hypertensive rats is associated with elevated IRS-1 phosphorylation at Ser 307 and increased SAPK/JNK activation. IRS-1 contains three putative binding sites for 14-3-3 protein at Ser 270, Ser 374 and Ser 641 that are capabl ...
1. Metabolic pathways 2. Basic enzyme kinetics 3. Metabolic
... » ATP binding decreases affinity for F6P (substrate) » F-2,6-P binding causes large increase in F6P affinity » Glycolytic flux stimulated by F-2,6-P & inhibited by ATP ...
... » ATP binding decreases affinity for F6P (substrate) » F-2,6-P binding causes large increase in F6P affinity » Glycolytic flux stimulated by F-2,6-P & inhibited by ATP ...
Presentation
... We attempted to place negatively charged regions in this pocket to ensure tight binding We also looked for other potential binding sites in nearby amino acids ...
... We attempted to place negatively charged regions in this pocket to ensure tight binding We also looked for other potential binding sites in nearby amino acids ...
Proteins and Enzymes (p
... End product inhibition prevents the cell from wasting chemical resources and energy by making more of a substance than it needs. Many metabolic reactions occur in an assembly line type of process so that a specific end product can be achieved. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme. When the en ...
... End product inhibition prevents the cell from wasting chemical resources and energy by making more of a substance than it needs. Many metabolic reactions occur in an assembly line type of process so that a specific end product can be achieved. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme. When the en ...
The Role of Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems in
... (Fig. lA). Receipt of an input signal by the histidine kinase stimulates its autophosphorylation whereby the gamma-phosphoryl group of an ATP molecule is transferred to a conserved histidine residue. Histidine kinases are often integral membrane proteins with a periplasmic domain that receives a sig ...
... (Fig. lA). Receipt of an input signal by the histidine kinase stimulates its autophosphorylation whereby the gamma-phosphoryl group of an ATP molecule is transferred to a conserved histidine residue. Histidine kinases are often integral membrane proteins with a periplasmic domain that receives a sig ...
Max ARM (Anabolic Recovery Matrix) from Max Muscle Sports
... with the BCAAs and arginine is mediated through signaling pathways controlling protein synthesis involving phosphorylation of the target enzymes Akt/mTOR (rapamycin), a protein kinase and the sequential stimulation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70 S6K) through enhanced translation of specific mRNAs. ...
... with the BCAAs and arginine is mediated through signaling pathways controlling protein synthesis involving phosphorylation of the target enzymes Akt/mTOR (rapamycin), a protein kinase and the sequential stimulation of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70 S6K) through enhanced translation of specific mRNAs. ...
Domain fusion between SNF1-related kinase subunits during plant
... polypeptide in another organism. Here, we report the identification of such a mosaic protein during evolution of the SNF1/AMPactivated protein kinase (AMPK) family. The yeast SNF1 kinase is a prototype of AMPKs that regulate cellular responses to a variety of nutritional and environmental stresses ( ...
... polypeptide in another organism. Here, we report the identification of such a mosaic protein during evolution of the SNF1/AMPactivated protein kinase (AMPK) family. The yeast SNF1 kinase is a prototype of AMPKs that regulate cellular responses to a variety of nutritional and environmental stresses ( ...
Reading GuideChapter6_Tues
... Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another key concept for ...
... Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another key concept for ...
Ubiquitin-proteosome protein degradation ppt
... Half lives of proteins vary from minutes to infinity “Normal” proteins – 100-200 hrs Short-lived proteins regulatory proteins enzymes that catalyze committed steps ...
... Half lives of proteins vary from minutes to infinity “Normal” proteins – 100-200 hrs Short-lived proteins regulatory proteins enzymes that catalyze committed steps ...
file1
... - Given a large, diverse superfamily - protein may evolve different function or subtype - different substrate specificity or activity - proteins with similar fold but different function ...
... - Given a large, diverse superfamily - protein may evolve different function or subtype - different substrate specificity or activity - proteins with similar fold but different function ...
Heart, Vascular Smooth Muscle, Excitation
... compliance, and cardiac contractility. We now turn to specific functionalities for cardiac contractility based on Ca2+ signaling in excitation-contraction coupling. The modifications discussed apply specifically to cardiac muscle and not to skeletal muscle. The observations described might raise que ...
... compliance, and cardiac contractility. We now turn to specific functionalities for cardiac contractility based on Ca2+ signaling in excitation-contraction coupling. The modifications discussed apply specifically to cardiac muscle and not to skeletal muscle. The observations described might raise que ...
Biology of Cancer - Tunghai University
... 6.4 SH2 groups explain how growth factors activate Ras and acquire signaling ...
... 6.4 SH2 groups explain how growth factors activate Ras and acquire signaling ...
Protein Structure & Function
... each one had multiple shapes Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
... each one had multiple shapes Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
Protein Structure & Function - Lectures For UG-5
... multiple shapes Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
... multiple shapes Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
Bio102 Problems
... 15. Why can your cells produce more usable cellular energy per carbon atom from a lipid molecule than from a carbohydrate molecule? Both are ultimately expelled from the body as CO2. To get there, each carbon atom from a lipid must be more oxidized more times than each carbon atom from a carbohydrat ...
... 15. Why can your cells produce more usable cellular energy per carbon atom from a lipid molecule than from a carbohydrate molecule? Both are ultimately expelled from the body as CO2. To get there, each carbon atom from a lipid must be more oxidized more times than each carbon atom from a carbohydrat ...
Selective kinase inhibitors as tools for neuroscience research
... Keywords: Kinase inhibitor Small molecule Signaling ...
... Keywords: Kinase inhibitor Small molecule Signaling ...
Questions
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
Lecture 3section7
... bridge between glycolysis and the TCA cycle is the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Mitochondrial enzyme complex Consists of multiple copies of 3 enzymes pyruvate decarboxlyase dihydrolipoyl transacetylase dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase ...
... bridge between glycolysis and the TCA cycle is the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Mitochondrial enzyme complex Consists of multiple copies of 3 enzymes pyruvate decarboxlyase dihydrolipoyl transacetylase dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase ...
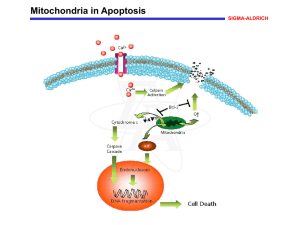
No Slide Title
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
Isoforms of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
... exclusively in the plastids of plants (which is also the site of expression of the ‘prokaryotic’ form of ACC when it is present). Two major isoforms of multifunctional animal ACC have so far been detected, and each may exist in one of two possible forms based on the presence or absence of a distinct ...
... exclusively in the plastids of plants (which is also the site of expression of the ‘prokaryotic’ form of ACC when it is present). Two major isoforms of multifunctional animal ACC have so far been detected, and each may exist in one of two possible forms based on the presence or absence of a distinct ...