In Depth Analysis of Protein Amino Acid Sequence and PTMs with
... • Peptides from the set of confident proteins are “modified” in-silico by trying all possible modifications in UNIMOD. • Speed up by de novo tags PeaksPTM: Mass spectrometry-based identification of peptides with unspecified modifications. Journal of Proteome Research 10.7 (2011) : 2930-2936 ...
... • Peptides from the set of confident proteins are “modified” in-silico by trying all possible modifications in UNIMOD. • Speed up by de novo tags PeaksPTM: Mass spectrometry-based identification of peptides with unspecified modifications. Journal of Proteome Research 10.7 (2011) : 2930-2936 ...
PDF - School of Chemistry
... “stripped-down” sequences; i.e., only the residues important for structural specification and stabilization are defined, leaving the remainder as agnostic side chains (e.g., alanine (Ala, A) or glutamine (Gln, Q)) and free for substitution later in the design process. The basis-set peptides are fully ...
... “stripped-down” sequences; i.e., only the residues important for structural specification and stabilization are defined, leaving the remainder as agnostic side chains (e.g., alanine (Ala, A) or glutamine (Gln, Q)) and free for substitution later in the design process. The basis-set peptides are fully ...
ppt - Central Web Server 2
... Consider a protein of 600 amino acids. Assume that for every position there could be any of the twenty possible amino acid. Then the total number of possibilities is 20 choices for the first position times 20 for the second position times 20 to the third .... = 20 to the 600 = 4*10780 different prot ...
... Consider a protein of 600 amino acids. Assume that for every position there could be any of the twenty possible amino acid. Then the total number of possibilities is 20 choices for the first position times 20 for the second position times 20 to the third .... = 20 to the 600 = 4*10780 different prot ...
TD11 Identification of in vivo substrates of GroEL Nature 1999, 402
... by co-running w/ cold crude bacterial lysate->there is more of the same, unlabeled protein at that spot for analysis) 2) extract protein from gel 3) complete digest with trypsin protease (cleaves C-terminal to Lys and Arg) 4) MALDI mass spec on fragments ->match collected mass to sequence and ID pro ...
... by co-running w/ cold crude bacterial lysate->there is more of the same, unlabeled protein at that spot for analysis) 2) extract protein from gel 3) complete digest with trypsin protease (cleaves C-terminal to Lys and Arg) 4) MALDI mass spec on fragments ->match collected mass to sequence and ID pro ...
Protein Structure Prediction: On the cusp between Futility and
... • Low resolution scoring functions – knowledge based • from database of known protein structures • only meaningful when database is big • data mining? ...
... • Low resolution scoring functions – knowledge based • from database of known protein structures • only meaningful when database is big • data mining? ...
analyzing gene and protein sequences
... resources, students can perform many types of analyses on the sequences. Students may search various databases, investigate taxonomy, and perform a number of analyses. For example students can compare human gene/protein sequences to other species’ sequences, simulate restriction analysis, predict se ...
... resources, students can perform many types of analyses on the sequences. Students may search various databases, investigate taxonomy, and perform a number of analyses. For example students can compare human gene/protein sequences to other species’ sequences, simulate restriction analysis, predict se ...
Atomic model of human Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane
... pdb 1r0z; at left), for which only six amino acids at the centre of the loop (dotted line) are not seen and which thus directly allows to completely model this long insertion. The regulatory insertion starts with a typical amphipatic helix, which is centered on the hydrophobic cluster 10011001 (mous ...
... pdb 1r0z; at left), for which only six amino acids at the centre of the loop (dotted line) are not seen and which thus directly allows to completely model this long insertion. The regulatory insertion starts with a typical amphipatic helix, which is centered on the hydrophobic cluster 10011001 (mous ...
Assignments 3 Problem 1 Below is the protein melting data for a pair
... wild-type protein. b) Determine your signal for the fully folded and the fully unfolded form (both mutant and WT). c) Plot the melting curves as the fraction of folded protein vs. temp. d) What are the melting temperatures for the two proteins? e) Pick the appropriate plots to determine ΔH and ΔS of ...
... wild-type protein. b) Determine your signal for the fully folded and the fully unfolded form (both mutant and WT). c) Plot the melting curves as the fraction of folded protein vs. temp. d) What are the melting temperatures for the two proteins? e) Pick the appropriate plots to determine ΔH and ΔS of ...
a server for analyzing and predicting RNA
... residues. KYG is a structure-based server and relies on estimating the interface propensity for single amino acids and pairs of amino acids. KYG also utilizes evolutionary information in the form of a multiple sequence alignment profile, which must be supplied by the user. Users are allowed to choose ...
... residues. KYG is a structure-based server and relies on estimating the interface propensity for single amino acids and pairs of amino acids. KYG also utilizes evolutionary information in the form of a multiple sequence alignment profile, which must be supplied by the user. Users are allowed to choose ...
NIH Public Access - The Scripps Research Institute
... (55/68, percent identity/similarity) and TlmI (55/70) from the zorbamycin and tallysomycin biosynthetic pathways, respectively. The conservation of these genes suggests that they have a function in these related biosynthetic pathways, although that function remains to be elucidated. BlmI sequence co ...
... (55/68, percent identity/similarity) and TlmI (55/70) from the zorbamycin and tallysomycin biosynthetic pathways, respectively. The conservation of these genes suggests that they have a function in these related biosynthetic pathways, although that function remains to be elucidated. BlmI sequence co ...
Protein synthesis I Biochemistry 302 February 17, 2006
... among related 16S rRNA sequences but primary sequences are not. Additional folding of rRNA and contribution of ribosomal proteins generate a more realistic 3D structure. ...
... among related 16S rRNA sequences but primary sequences are not. Additional folding of rRNA and contribution of ribosomal proteins generate a more realistic 3D structure. ...
tRNA aminoacylation by arginyltRNA synthetase: induced
... side chains that are involved in direct or water-mediated interactions with the nucleic acid. Cyt35, which has been shown to be the strongest identity determinant for tRNAArg (Giege et al., 1998), is recognized mainly by main chain atoms of the protein belonging to the loop between helices H22 and ...
... side chains that are involved in direct or water-mediated interactions with the nucleic acid. Cyt35, which has been shown to be the strongest identity determinant for tRNAArg (Giege et al., 1998), is recognized mainly by main chain atoms of the protein belonging to the loop between helices H22 and ...
Prokaryotic Translation
... Non-coding RNA Repression: Unpaired regions (in blue) of ncRNAs bind to complementary nucleotides of target mRNAs (forming perfect or imperfect duplexes) and regulate gene expression at multiple levels: transcriptional attenuation, translation initiation, mRNA decay and mRNA processing. Many ncRNAs ...
... Non-coding RNA Repression: Unpaired regions (in blue) of ncRNAs bind to complementary nucleotides of target mRNAs (forming perfect or imperfect duplexes) and regulate gene expression at multiple levels: transcriptional attenuation, translation initiation, mRNA decay and mRNA processing. Many ncRNAs ...
Interaction interfaces of protein domains are not topologically
... when compared with their orthologues from Caenorhabditis elegans, evolve at similar rates. Recent studies, however, have shown that the interacting proteins in closely related genomes have a slight influence on the rate at which these proteins diverge.13 Additionally, Jordan et al.14 have shown that ...
... when compared with their orthologues from Caenorhabditis elegans, evolve at similar rates. Recent studies, however, have shown that the interacting proteins in closely related genomes have a slight influence on the rate at which these proteins diverge.13 Additionally, Jordan et al.14 have shown that ...
Definition of Protein Superfamily
... separate evolutionary histories, has made this approach no longer effective. Moreover, the term superfamily has come into common usage and its meaning is no longer well defined. Although originally defined as a group of evolutionarily related proteins, it also has been used in the published literatu ...
... separate evolutionary histories, has made this approach no longer effective. Moreover, the term superfamily has come into common usage and its meaning is no longer well defined. Although originally defined as a group of evolutionarily related proteins, it also has been used in the published literatu ...
Infrared spectroscopy: a tool for protein characterization Chenge Li
... Proteins are relatively large, compact, structurally complex molecules that are made from small molecules called amino acids. Amino acids share a common structure, which contains an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), along with a side chain that is specific for each amino acid. The side c ...
... Proteins are relatively large, compact, structurally complex molecules that are made from small molecules called amino acids. Amino acids share a common structure, which contains an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), along with a side chain that is specific for each amino acid. The side c ...
Shine – Dalgarno sequence
... factors IF2-GTP, IF1, IF3, as well as the initiator tRNA fMet-tRNA (fMet) are recruited to the ribosome. In Gram-negative bacteria, however, Shine-Dalgarno sequence presence is not obligatory for ribosome to locate initiator codon, since deletion of Anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence from 16S rRNA doesn't ...
... factors IF2-GTP, IF1, IF3, as well as the initiator tRNA fMet-tRNA (fMet) are recruited to the ribosome. In Gram-negative bacteria, however, Shine-Dalgarno sequence presence is not obligatory for ribosome to locate initiator codon, since deletion of Anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence from 16S rRNA doesn't ...
Using PEPscreen to Study Protein Phosphorylation - Sigma
... between specific PKs and particular sites is crucial to elucidate related biological pathways. On a more technical level, highthroughput assays are needed to establish these valid kinase-client interactions. Past methods have used low-throughput methods such as radiolabeling or 2D-gel electrophoresi ...
... between specific PKs and particular sites is crucial to elucidate related biological pathways. On a more technical level, highthroughput assays are needed to establish these valid kinase-client interactions. Past methods have used low-throughput methods such as radiolabeling or 2D-gel electrophoresi ...
Divergence and Convergence in Enzyme Evolution
... Cupins—The cupin superfamily, together with the 2-ketoglutarate- and iron-dependent dioxygenase superfamily, belongs to the double-stranded -helix fold, and members of both superfamilies have been occasionally referred to as cupins (41, 42). However, even cupins sensu stricto are extremely diverse, ...
... Cupins—The cupin superfamily, together with the 2-ketoglutarate- and iron-dependent dioxygenase superfamily, belongs to the double-stranded -helix fold, and members of both superfamilies have been occasionally referred to as cupins (41, 42). However, even cupins sensu stricto are extremely diverse, ...
Document
... have a common ancestor. This is not a measure of conservation and there is no percentage of homology! (It's either yes or no). Homologous sequences do not necessarily serve the same function, nor are they always highly similar: structure may be conserved while sequence is not. ...
... have a common ancestor. This is not a measure of conservation and there is no percentage of homology! (It's either yes or no). Homologous sequences do not necessarily serve the same function, nor are they always highly similar: structure may be conserved while sequence is not. ...
Protein domains as units of genetic transfer
... We implemented a two-phase strategy [10] for the detection of recombination events among these data. To remove potential complication from paralogous history in the sequences and to ensure a confident inference of genetic transfer event rather subsequent evolution of duplicated genes, we selected 14 ...
... We implemented a two-phase strategy [10] for the detection of recombination events among these data. To remove potential complication from paralogous history in the sequences and to ensure a confident inference of genetic transfer event rather subsequent evolution of duplicated genes, we selected 14 ...
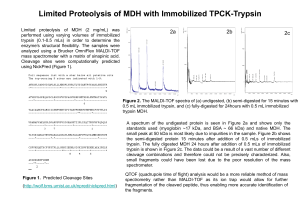
Limited Proteolysis
... 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin, and (c) fully-digested for 24hours with 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin MDH. A spectrum of the undigested protein is seen in Figure 2a and shows only the standards used (myoglobin ~17 kDa, and BSA ~ 66 kDa) and native MDH. The small peak at 50 kDa is most likely due to impurit ...
... 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin, and (c) fully-digested for 24hours with 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin MDH. A spectrum of the undigested protein is seen in Figure 2a and shows only the standards used (myoglobin ~17 kDa, and BSA ~ 66 kDa) and native MDH. The small peak at 50 kDa is most likely due to impurit ...
Effective Scoring Function for Protein Sequence Design
... the ASPs in such a way that the modeled loop structure with the global minimum resembled the X-ray structure. We previously developed a side-chain modeling program by optimizing the weights of the energy terms.22 In the course of optimization, for every residue, its side-chain was replaced by varyin ...
... the ASPs in such a way that the modeled loop structure with the global minimum resembled the X-ray structure. We previously developed a side-chain modeling program by optimizing the weights of the energy terms.22 In the course of optimization, for every residue, its side-chain was replaced by varyin ...
A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites
... compares favourably with that obtained with a recently published signal-sequence detecting algorithm (9). DISCUSSION U3ing a standard weight-matrix approach easily implemented even on a micro-ccmputer, it is possible to set up a prediction method that (i) provides a clean discrimination between sign ...
... compares favourably with that obtained with a recently published signal-sequence detecting algorithm (9). DISCUSSION U3ing a standard weight-matrix approach easily implemented even on a micro-ccmputer, it is possible to set up a prediction method that (i) provides a clean discrimination between sign ...
Structural alignment

Structural alignment attempts to establish homology between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures but can also be used for large RNA molecules. In contrast to simple structural superposition, where at least some equivalent residues of the two structures are known, structural alignment requires no a priori knowledge of equivalent positions. Structural alignment is a valuable tool for the comparison of proteins with low sequence similarity, where evolutionary relationships between proteins cannot be easily detected by standard sequence alignment techniques. Structural alignment can therefore be used to imply evolutionary relationships between proteins that share very little common sequence. However, caution should be used in using the results as evidence for shared evolutionary ancestry because of the possible confounding effects of convergent evolution by which multiple unrelated amino acid sequences converge on a common tertiary structure.Structural alignments can compare two sequences or multiple sequences. Because these alignments rely on information about all the query sequences' three-dimensional conformations, the method can only be used on sequences where these structures are known. These are usually found by X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy. It is possible to perform a structural alignment on structures produced by structure prediction methods. Indeed, evaluating such predictions often requires a structural alignment between the model and the true known structure to assess the model's quality. Structural alignments are especially useful in analyzing data from structural genomics and proteomics efforts, and they can be used as comparison points to evaluate alignments produced by purely sequence-based bioinformatics methods.The outputs of a structural alignment are a superposition of the atomic coordinate sets and a minimal root mean square deviation (RMSD) between the structures. The RMSD of two aligned structures indicates their divergence from one another. Structural alignment can be complicated by the existence of multiple protein domains within one or more of the input structures, because changes in relative orientation of the domains between two structures to be aligned can artificially inflate the RMSD.