tissues - Perkins Science
... • Some tissues are non-vascular and will repair very slowly • If excitable tissue is replaced by scar tissue – function is lost! ...
... • Some tissues are non-vascular and will repair very slowly • If excitable tissue is replaced by scar tissue – function is lost! ...
- Institute of Education
... Wh~t did you do before placing the slide with the stained cells ori the microscope platform? ...
... Wh~t did you do before placing the slide with the stained cells ori the microscope platform? ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
Word - New Haven Science
... 6. Atoms can combine chemically to make a molecule of a new substance with new properties called a compound. A molecule is the smallest part of a compound and is made of atoms of different elements in specific amounts. Unlike mixtures, compounds cannot be separated using the physical properties of t ...
... 6. Atoms can combine chemically to make a molecule of a new substance with new properties called a compound. A molecule is the smallest part of a compound and is made of atoms of different elements in specific amounts. Unlike mixtures, compounds cannot be separated using the physical properties of t ...
1 • The ear ( vestibulo-acoustic organs ) consists of vestibular
... inner tunnel (T). This space is continuous throughout the length of the cochlea and is bounded below by thin lateral extensions of the base of the pillar cells that rest on the basilar lamina. It is bounded above by the converging cylindrical bodies of the inner and outer pillar cells. The most dist ...
... inner tunnel (T). This space is continuous throughout the length of the cochlea and is bounded below by thin lateral extensions of the base of the pillar cells that rest on the basilar lamina. It is bounded above by the converging cylindrical bodies of the inner and outer pillar cells. The most dist ...
TISSUES AND OTHER LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... Matrix is composed of ossein. Matrix also contains salts of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Matrix in mammalian long bones (such as thigh bone) is arranged in concentric rings. The osteocytes (bone cells) lie on the lamellae (concentric rings in the matrix.) Osteocytes give out branched processes ...
... Matrix is composed of ossein. Matrix also contains salts of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Matrix in mammalian long bones (such as thigh bone) is arranged in concentric rings. The osteocytes (bone cells) lie on the lamellae (concentric rings in the matrix.) Osteocytes give out branched processes ...
Chapter 4: Tissues
... form branching networks around fat cells, nerve fibers, and skeletal and smooth muscle cells. ...
... form branching networks around fat cells, nerve fibers, and skeletal and smooth muscle cells. ...
Histology
... secretory acini that drain into numerous efferent ducts. These ducts typically merge into a smaller number of main ducts. The parotid salivary glands and the pancreas are examples of this type of gland. h) Compound alveolar glands (Compound acinar ) are compound glands because they have numerous dra ...
... secretory acini that drain into numerous efferent ducts. These ducts typically merge into a smaller number of main ducts. The parotid salivary glands and the pancreas are examples of this type of gland. h) Compound alveolar glands (Compound acinar ) are compound glands because they have numerous dra ...
Question paper - Unit B731/02 - Modules B1, B2, B3 - Higher
... Answer all the questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and question ...
... Answer all the questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and question ...
TISSUES AND OTHER LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... Organs such as stem, and roots in plants, and stomach, heart and lungs in animals are made up of different kinds of tissues. A tissue is a group of cells with a common origin, structure and function. Their common origin means they are derived from the same layer (details in lesson No. 20) of cells i ...
... Organs such as stem, and roots in plants, and stomach, heart and lungs in animals are made up of different kinds of tissues. A tissue is a group of cells with a common origin, structure and function. Their common origin means they are derived from the same layer (details in lesson No. 20) of cells i ...
Chapter 17: Cellular Mechanisms of Development
... At the most basic level, the developmental paths of plants and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose wall ...
... At the most basic level, the developmental paths of plants and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose wall ...
Fertilization & Development
... fertilized. After fertilization, the fertilized egg (zygote) undergoes a series of rapid mitotic cell divisions. This is called cleavage. Stage 1: Cleavage During cleavage there is no increase in cell size, just an increase in cell numbers. First the many new cells forms a mass called the morula. Th ...
... fertilized. After fertilization, the fertilized egg (zygote) undergoes a series of rapid mitotic cell divisions. This is called cleavage. Stage 1: Cleavage During cleavage there is no increase in cell size, just an increase in cell numbers. First the many new cells forms a mass called the morula. Th ...
1 Chapter 4: The Tissue Level of Organization What are the four
... The Process of Inflammation • Dilation of blood vessels: – increases blood circulation in the area – causes warmth and redness – brings more nutrients and oxygen to the ...
... The Process of Inflammation • Dilation of blood vessels: – increases blood circulation in the area – causes warmth and redness – brings more nutrients and oxygen to the ...
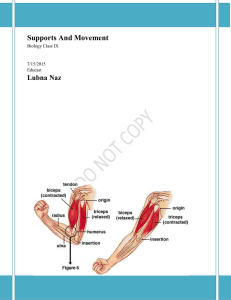
Supports And Movement
... producing pseudopodia, which are cytoplasmic projections. This involves change in the shape of the cell body and streaming movement of cytoplasm into the pseudopodium. The movement due to pseudopodia in amoeba is termed as amoeboid movement. Amoeboid movement is characteristic of certain cells in ot ...
... producing pseudopodia, which are cytoplasmic projections. This involves change in the shape of the cell body and streaming movement of cytoplasm into the pseudopodium. The movement due to pseudopodia in amoeba is termed as amoeboid movement. Amoeboid movement is characteristic of certain cells in ot ...
32 Cell Division
... Cells reproduce. That is, one cell divides into two through a process known as cell division. When a parent cell divides, the two daughter cells are genetically identical (or nearly so) to the parent cell. In multicellular organisms like humans, cell division enables growth and the replacement of wo ...
... Cells reproduce. That is, one cell divides into two through a process known as cell division. When a parent cell divides, the two daughter cells are genetically identical (or nearly so) to the parent cell. In multicellular organisms like humans, cell division enables growth and the replacement of wo ...
Sample - 101 Biology
... 1. Every living organism is made up of one or more cells. 2. The smallest living organisms are single cells, and cells are the functional units of multicellular organism. 3. All cells arise by division of pre-existing cells. 4. All cell have the following in common: plasma membrane, nucleous, ...
... 1. Every living organism is made up of one or more cells. 2. The smallest living organisms are single cells, and cells are the functional units of multicellular organism. 3. All cells arise by division of pre-existing cells. 4. All cell have the following in common: plasma membrane, nucleous, ...
Chapter 1
... A group of similar cells that do the same job in an organism is a called a tissue (TISH•ew). Both plants and animals have tissues. Muscle cells in your legs make up muscle tissue, which allows you to move your legs. Other kinds of tissues in an animal’s body include blood, nerves, bone, and skin. On ...
... A group of similar cells that do the same job in an organism is a called a tissue (TISH•ew). Both plants and animals have tissues. Muscle cells in your legs make up muscle tissue, which allows you to move your legs. Other kinds of tissues in an animal’s body include blood, nerves, bone, and skin. On ...
Connective and Muscle Tissues
... Major Cell Types of C.T. _____________ - connective tissue proper Chondroblasts - cartilage Osteoblasts - bone Hematopoietic stem cells - ___________ White blood cells, plasma cells, macrophages, and mast cells Fibers Collagen - tough; provides high tensile strength Elastic - long, thin fibers that ...
... Major Cell Types of C.T. _____________ - connective tissue proper Chondroblasts - cartilage Osteoblasts - bone Hematopoietic stem cells - ___________ White blood cells, plasma cells, macrophages, and mast cells Fibers Collagen - tough; provides high tensile strength Elastic - long, thin fibers that ...
Embryology (Animal
... dependent upon milk from its mothers breast for food. The juvenile condition is very important in humans because juveniles tend to have a large head relative to the body of the embryo. By emphasis and extension of the juvenile stage, a process known as neoteny, humans have developed a large brain an ...
... dependent upon milk from its mothers breast for food. The juvenile condition is very important in humans because juveniles tend to have a large head relative to the body of the embryo. By emphasis and extension of the juvenile stage, a process known as neoteny, humans have developed a large brain an ...
cell growth, division, and reproduction
... a. Stem cell research may lead to new ways to repair the cellular damage that results from heart attack, stroke, and spinal cord injuries. One example is the approach to reversing heart attack damage illustrated below. ...
... a. Stem cell research may lead to new ways to repair the cellular damage that results from heart attack, stroke, and spinal cord injuries. One example is the approach to reversing heart attack damage illustrated below. ...
Chapter 40 Animal Form and Function: Organ Systems, Tissues and
... because the columnar cells are not all the same height, and not all penetrate to the surface or lumen which they are facing. (Example: Trachea.) In Pathology (the study of disease), there are many example of columnar or cuboidal epithelium flattening out and turning into squamous cells as a result o ...
... because the columnar cells are not all the same height, and not all penetrate to the surface or lumen which they are facing. (Example: Trachea.) In Pathology (the study of disease), there are many example of columnar or cuboidal epithelium flattening out and turning into squamous cells as a result o ...
Chapter 4: The Tissue Level of Organization
... – Fills internal spaces – Provides structure and strength to support other tissues – Transports materials – Stores energy ...
... – Fills internal spaces – Provides structure and strength to support other tissues – Transports materials – Stores energy ...
Cells and Tissues
... – Products travel in transport vesicles from the ER to the Golgi apparatus – One side of the Golgi apparatus functions as a receiving dock for the product and the other as a shipping dock – Products are modified as they go from one side of the Golgi apparatus to the other and travel in vesicles to o ...
... – Products travel in transport vesicles from the ER to the Golgi apparatus – One side of the Golgi apparatus functions as a receiving dock for the product and the other as a shipping dock – Products are modified as they go from one side of the Golgi apparatus to the other and travel in vesicles to o ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.