Chapter 4 Socket Programming Preliminary
... • Different machines use different host bye orderings: • little-endian: least significant byte located at lower memory • E.g., Intel 80x86 • big-endian: least significant byte located at higher memory • E.g., Motorola 68000 • These machines may communicate with one another over the network, and they ...
... • Different machines use different host bye orderings: • little-endian: least significant byte located at lower memory • E.g., Intel 80x86 • big-endian: least significant byte located at higher memory • E.g., Motorola 68000 • These machines may communicate with one another over the network, and they ...
Chapter 5: Data Link Layer, MAC protocols, and Local Area Networks
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To | Introduction
... 802.1AB LLDP, adding mediaand IP telephony-specific messages that can be exchanged between the network and endpoint devices. 802.1x IEEE 802.1x is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is part of the IEEE 802.1 group of networking protocols. It provides an authentication ...
... 802.1AB LLDP, adding mediaand IP telephony-specific messages that can be exchanged between the network and endpoint devices. 802.1x IEEE 802.1x is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is part of the IEEE 802.1 group of networking protocols. It provides an authentication ...
Link-State Routing Protocols
... –This is the time that must transpire before the neighbor is considered down –Default time is 4 times the hello interval ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 ...
... –This is the time that must transpire before the neighbor is considered down –Default time is 4 times the hello interval ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 ...
Configuration
... The Internet routing architecture business and other customer networks that are connected to it has evolved over the years into a distributed system of . interconnected networks. The Internet is now so vast and involves so many networks that it is impossible for a single organization to manage all ...
... The Internet routing architecture business and other customer networks that are connected to it has evolved over the years into a distributed system of . interconnected networks. The Internet is now so vast and involves so many networks that it is impossible for a single organization to manage all ...
WHAT: A Big Data Approach for Accounting of Modern Web Services
... time to core domain flows. The intuition is that support flows are opened immediately after a visit to websites. We call the time interval in which flows are considered the observation window OW . Second, WHAT filters out unrelated domains by calculating a domain score, represented by frequency that ...
... time to core domain flows. The intuition is that support flows are opened immediately after a visit to websites. We call the time interval in which flows are considered the observation window OW . Second, WHAT filters out unrelated domains by calculating a domain score, represented by frequency that ...
M T ASTER’S HESIS
... Multicasting allows us to send a data packet to multiple sites at the same time. The key here is the ability to send one message to one or more nodes in a single operation. This provides a tremendous amount of savings in bandwidth when compared to traditional unicast transmission which sends message ...
... Multicasting allows us to send a data packet to multiple sites at the same time. The key here is the ability to send one message to one or more nodes in a single operation. This provides a tremendous amount of savings in bandwidth when compared to traditional unicast transmission which sends message ...
Tsunami 8000 Series (Point-to-point and Point-to
... Copyright (c) 1998-2002 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved. The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to refer to, endorse, or promote the products or for any other purpose related to the products without prior written permission. For written permission, please contact ...
... Copyright (c) 1998-2002 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved. The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to refer to, endorse, or promote the products or for any other purpose related to the products without prior written permission. For written permission, please contact ...
IPv6 based NGN
... – Broadband capabilities with end-to-end QoS and transparency – Interworking with legacy networks via open interfaces – Generalised mobility – Unfettered access by users to different service providers – A variety of identification schemes which can be resolved to IP addresses for the purposes of rou ...
... – Broadband capabilities with end-to-end QoS and transparency – Interworking with legacy networks via open interfaces – Generalised mobility – Unfettered access by users to different service providers – A variety of identification schemes which can be resolved to IP addresses for the purposes of rou ...
Technical University Berlin Telecommunication Networks Group Optimization of Handover Performance
... Looking at layer-3 handover triggers in detail, the underlying algorithm offers potential for improvement. Well-known algorithms for handover detection and triggering in Mobile IPv4 – applied in Mobile IPv6 as well – are Lazy Cell Switching (LCS) and Eager Cell Switching (ECS) [12], where ECS can be ...
... Looking at layer-3 handover triggers in detail, the underlying algorithm offers potential for improvement. Well-known algorithms for handover detection and triggering in Mobile IPv4 – applied in Mobile IPv6 as well – are Lazy Cell Switching (LCS) and Eager Cell Switching (ECS) [12], where ECS can be ...
Routing protocol Chapter 4 4.1 Introduction
... there is a large database and a topology change occurs or a change in a node's real time parameters occurs. This is because a change in the network results in a convergence period which might not be fast enough for the routing protocol to be usable. In distance-vector algorithms, each node keeps a ...
... there is a large database and a topology change occurs or a change in a node's real time parameters occurs. This is because a change in the network results in a convergence period which might not be fast enough for the routing protocol to be usable. In distance-vector algorithms, each node keeps a ...
oneM2M-TR-0009-Protocol_Analysis-V0_4_0
... This is a draft oneM2M document and should not be relied upon; the final version, if any, will be made available by oneM2M Partners Type 1. ...
... This is a draft oneM2M document and should not be relied upon; the final version, if any, will be made available by oneM2M Partners Type 1. ...
now
... status information about Frame Relay connections between the router (DTE) and the Frame Relay switch (DCE). • Every 10 seconds or so, the end device polls the network. • If the network does not respond with the requested information, the user device may consider the connection to be down. • When the ...
... status information about Frame Relay connections between the router (DTE) and the Frame Relay switch (DCE). • Every 10 seconds or so, the end device polls the network. • If the network does not respond with the requested information, the user device may consider the connection to be down. • When the ...
Understanding Network Failures in Data Centers: Measurement
... • NOC Tickets. To track the resolution of issues, the operators employ a ticketing system. Tickets contain information about when and how events were discovered as well as when they were resolved. Additional descriptive tags are applied to tickets describing the cause of the problem, if any specific ...
... • NOC Tickets. To track the resolution of issues, the operators employ a ticketing system. Tickets contain information about when and how events were discovered as well as when they were resolved. Additional descriptive tags are applied to tickets describing the cause of the problem, if any specific ...
Document
... • Two routers are service routers adding/dropping traffic from the network side and passing through transit traffic. • Other two routers are drop routers connected to client devices. • Two connections from the network port at the ingress service router to two drop ports, one in each of the drop rout ...
... • Two routers are service routers adding/dropping traffic from the network side and passing through transit traffic. • Other two routers are drop routers connected to client devices. • Two connections from the network port at the ingress service router to two drop ports, one in each of the drop rout ...
PPTX - gozips.uakron.edu
... • We first consider how to encode bits into the signal at the source and recover bits at the receiving node • Once it is possible to transmit bits, we need to figure out how to package these bits into FRAME • Assume each node is able to recognize the collections of bits making up a frame, the third ...
... • We first consider how to encode bits into the signal at the source and recover bits at the receiving node • Once it is possible to transmit bits, we need to figure out how to package these bits into FRAME • Assume each node is able to recognize the collections of bits making up a frame, the third ...
Understanding Network Failures in Data Centers: Measurement, Analysis, and Implications
... • NOC Tickets. To track the resolution of issues, the operators employ a ticketing system. Tickets contain information about when and how events were discovered as well as when they were resolved. Additional descriptive tags are applied to tickets describing the cause of the problem, if any specific ...
... • NOC Tickets. To track the resolution of issues, the operators employ a ticketing system. Tickets contain information about when and how events were discovered as well as when they were resolved. Additional descriptive tags are applied to tickets describing the cause of the problem, if any specific ...
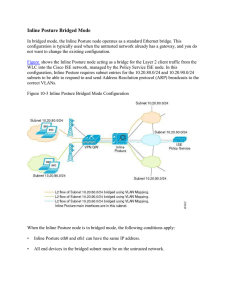
15360608-Inline Posture Bridged Mode
... traffic from entering the network by filtering source and destination IP addresses, transport protocols, and other variables, using the RADIUS protocol. After you create DACLs as named permission objects, add them to authorization profiles, which you then specify as the result of an authorization po ...
... traffic from entering the network by filtering source and destination IP addresses, transport protocols, and other variables, using the RADIUS protocol. After you create DACLs as named permission objects, add them to authorization profiles, which you then specify as the result of an authorization po ...
signaling transfer point
... signaling, carrying signaling data over the same voice trunks that would later carry the corresponding conversation. This method gave a reasonable assurance that trunks would be available and voice data would go through once the connection was established. The problem was the trunks that between swi ...
... signaling, carrying signaling data over the same voice trunks that would later carry the corresponding conversation. This method gave a reasonable assurance that trunks would be available and voice data would go through once the connection was established. The problem was the trunks that between swi ...