Comparison and Contrast between the OSI and TCP/IP Model
... • Transport protocols can also mark packets with sequencing information so that the destination system can properly order the packets if they’re received outof-sequence • In addition, Transport protocols provide facilities for insuring the integrity of packets and requesting retransmission should th ...
... • Transport protocols can also mark packets with sequencing information so that the destination system can properly order the packets if they’re received outof-sequence • In addition, Transport protocols provide facilities for insuring the integrity of packets and requesting retransmission should th ...
DKTCOMEGA 797xx FTU/CPE series presentation
... => higher OPEX costs • All CPE vendors define their ”one-fits-all” box as defacto ...
... => higher OPEX costs • All CPE vendors define their ”one-fits-all” box as defacto ...
2 - MUET Scholars
... Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks: Theory and Practice Waltenegus Dargie and Christian Poellabauer © 2010 ...
... Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks: Theory and Practice Waltenegus Dargie and Christian Poellabauer © 2010 ...
Operating Systems
... Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks: Theory and Practice Waltenegus Dargie and Christian Poellabauer © 2010 ...
... Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks: Theory and Practice Waltenegus Dargie and Christian Poellabauer © 2010 ...
Tree-based IP lookup
... It seems any number between 8-16 is reasonable. But, N=9 gives a better search time, memory size. Assuming 9 branching factors in the internal node, %50 node utilization and 128K prefixes, we need max. 128K/4.5= 28.5K address. Then, 15 bit address for left and right pointers are more than enough. Bu ...
... It seems any number between 8-16 is reasonable. But, N=9 gives a better search time, memory size. Assuming 9 branching factors in the internal node, %50 node utilization and 128K prefixes, we need max. 128K/4.5= 28.5K address. Then, 15 bit address for left and right pointers are more than enough. Bu ...
The Changing Structure of the Internet
... Technology Trends for Cable Systems Part of the changing nature of the Internet is an outcome of the rapidly decreasing cost of ...
... Technology Trends for Cable Systems Part of the changing nature of the Internet is an outcome of the rapidly decreasing cost of ...
Chapter 1. Introduction to Data Communications
... • More complex than switches or routers • Connect two or more networks that use the same or different data link and network protocols • Some work at the application layer ...
... • More complex than switches or routers • Connect two or more networks that use the same or different data link and network protocols • Some work at the application layer ...
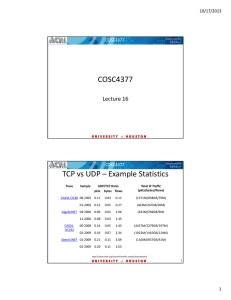
COSC4377 TCP vs UDP – Example Statistics
... routers. Routers advertise prefixes that identify the subnet(s) associated with a link, while hosts generate an "interface identifier" that uniquely identifies an interface on a subnet. An address is formed by combining the two. In the absence of routers, a host can only generate link‐local addre ...
... routers. Routers advertise prefixes that identify the subnet(s) associated with a link, while hosts generate an "interface identifier" that uniquely identifies an interface on a subnet. An address is formed by combining the two. In the absence of routers, a host can only generate link‐local addre ...
Chapter 2 - Slide DataComm file - Elearning-KL
... Logical addresses are necessary for universal communications that are independent of underlying physical networks. Physical addresses are not adequate in an internetwork environment where different networks can have different address formats. A universal addressing system is needed in which each ...
... Logical addresses are necessary for universal communications that are independent of underlying physical networks. Physical addresses are not adequate in an internetwork environment where different networks can have different address formats. A universal addressing system is needed in which each ...
Internet Design Principles (Cont.) and Link Layer
... (shared air, acoustical) 5: DataLink Layer ...
... (shared air, acoustical) 5: DataLink Layer ...
Week 8 lesson06
... • iSNS server — Receives and processes registration requests and queries from clients on the SAN, using the iSNS database as an information store. • iSNS database — Information store on an iSNS server that contains data supplied by client registrations. The server retrieves the data to respond to cl ...
... • iSNS server — Receives and processes registration requests and queries from clients on the SAN, using the iSNS database as an information store. • iSNS database — Information store on an iSNS server that contains data supplied by client registrations. The server retrieves the data to respond to cl ...
Network - PTT.br
... of Cisco's product and technology portfolio Cisco will in the near term engage with specific customers on OpenFlow as a prototype technology © 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ...
... of Cisco's product and technology portfolio Cisco will in the near term engage with specific customers on OpenFlow as a prototype technology © 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ...
On the Validation of Traffic Classification Algorithms
... [2] M. Perenyi and S. Molnar: Enhanced Skype Traffic Identification ...
... [2] M. Perenyi and S. Molnar: Enhanced Skype Traffic Identification ...
Quantenna develops first 802.11ac 10G Wave 3 Wi-Fi product
... Figure 2: 8×8 Downlink to Four 2×2 Mu-MIMO Clients for User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Traffic. (Image courtesy of Quantenna) ...
... Figure 2: 8×8 Downlink to Four 2×2 Mu-MIMO Clients for User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Traffic. (Image courtesy of Quantenna) ...
Slides - TERENA> Events> tnc2006
... assignment to the school router, the Frame-Interface-ID* should also be provided. – Internal LAN interfaces are automatically configured using DHCP-PD (prefix delegation). This process takes place in IP layer, aka independent of the PPP session. – Automatically, a static route towards the CPE is set ...
... assignment to the school router, the Frame-Interface-ID* should also be provided. – Internal LAN interfaces are automatically configured using DHCP-PD (prefix delegation). This process takes place in IP layer, aka independent of the PPP session. – Automatically, a static route towards the CPE is set ...
XAPP941 - 参考系统:PLB 三态以太网 MAC
... low and the target received nearly all UDP packets sent from the host, then the target is waiting on the PC. Setting up the TCP/IP Address of the Host: Typically the host computer will have two network cards: one for the normal work related connection, and another for a dedicated test network. The t ...
... low and the target received nearly all UDP packets sent from the host, then the target is waiting on the PC. Setting up the TCP/IP Address of the Host: Typically the host computer will have two network cards: one for the normal work related connection, and another for a dedicated test network. The t ...
Why networks?
... designing/implementing networks. • Each layer responsible for a set of functions. • Top layer relies on services provided by bottom layer. • Layer makes it service available to higher layer through an interface. ...
... designing/implementing networks. • Each layer responsible for a set of functions. • Top layer relies on services provided by bottom layer. • Layer makes it service available to higher layer through an interface. ...
12 things effective Page title appears here
... and client side attacks Fundamentally, your IPS must include comprehensive signature coverage for attacks directed at both servers and clients. All intrusion prevention systems should include application vulnerability protection, buffer overflow protection and protocol anomaly detection for a wide v ...
... and client side attacks Fundamentally, your IPS must include comprehensive signature coverage for attacks directed at both servers and clients. All intrusion prevention systems should include application vulnerability protection, buffer overflow protection and protocol anomaly detection for a wide v ...
LANdesign
... process? Can all ports work simultaneously at maximum speed? Link aggregation (EtherChannel) – up to 8 ports bound together, acting as one, with combined bandwidth – can it do this? 25-May-17 ...
... process? Can all ports work simultaneously at maximum speed? Link aggregation (EtherChannel) – up to 8 ports bound together, acting as one, with combined bandwidth – can it do this? 25-May-17 ...
in router
... network, it may also be referred to as a port. In IP routing. • Each interface must have a separate, unique network address. ...
... network, it may also be referred to as a port. In IP routing. • Each interface must have a separate, unique network address. ...
Packet and Circuit Switching - California State University, Los Angeles
... • Continuity assured in the order of transmission • Audio can be transmitted without streaming provided adequate bandwidth is available – Otherwise streaming is necessary ...
... • Continuity assured in the order of transmission • Audio can be transmitted without streaming provided adequate bandwidth is available – Otherwise streaming is necessary ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Metropolitan Area Networks and Wide
... to multiple companies as though they were all part of a large local area network. The former connection is the same as having a private connection between two points. A common example of this type of Metro Ethernet connection is found when a company is connected to an Internet service provider. All ...
... to multiple companies as though they were all part of a large local area network. The former connection is the same as having a private connection between two points. A common example of this type of Metro Ethernet connection is found when a company is connected to an Internet service provider. All ...