Mathematical Analysis of Problems in the Natural Sciences
... An abstract number, for example, 1 or 2 23 , and the arithmetic of abstract numbers, for example, that 2 + 3 = 5 irrespective of whether one is adding apples or elephants, is a great achievement of civilization comparable with the invention of writing. We have become so used to this that we are no l ...
... An abstract number, for example, 1 or 2 23 , and the arithmetic of abstract numbers, for example, that 2 + 3 = 5 irrespective of whether one is adding apples or elephants, is a great achievement of civilization comparable with the invention of writing. We have become so used to this that we are no l ...
D23Lc - damtp - University of Cambridge
... We assume that at every point x of the fluid and at all times t we can define, by averaging over a small volume, “continuum” properties like density ρ(x, t), velocity u(x, t) and pressure p(x, t). Here x refers to a position in the laboratory frame (Eulerian description). We thus do not deal with th ...
... We assume that at every point x of the fluid and at all times t we can define, by averaging over a small volume, “continuum” properties like density ρ(x, t), velocity u(x, t) and pressure p(x, t). Here x refers to a position in the laboratory frame (Eulerian description). We thus do not deal with th ...
Turbulent Horizontal Convection and the Global Thermohaline
... thermohaline circulation) carries warm subtropical surface waters to high latitudes, where it cools and sinks. In the present pattern of circulation the dense cold (and sufficiently saline) water sinks in confined regions at high latitudes to form `Deep' and `Bottom' waters. There must be a slow, po ...
... thermohaline circulation) carries warm subtropical surface waters to high latitudes, where it cools and sinks. In the present pattern of circulation the dense cold (and sufficiently saline) water sinks in confined regions at high latitudes to form `Deep' and `Bottom' waters. There must be a slow, po ...
Lecture 23 - MSU Physics
... about 1/3 that at sea level, so the lift is also reduced by this amount. Note that high velocity implies low pressure, IN the fluid. This is counterintuitive as we know that if a high velocity fluid hits us (e.g. a water canon), then the pressure on us is large. We have to carefully distinguish betw ...
... about 1/3 that at sea level, so the lift is also reduced by this amount. Note that high velocity implies low pressure, IN the fluid. This is counterintuitive as we know that if a high velocity fluid hits us (e.g. a water canon), then the pressure on us is large. We have to carefully distinguish betw ...
Lecture 14c - TTU Physics
... Section 14.5: Fluid Dynamics • We’ve done fluid statics. Now, Fluid Dynamics (fluid flow), which is much more interesting! ...
... Section 14.5: Fluid Dynamics • We’ve done fluid statics. Now, Fluid Dynamics (fluid flow), which is much more interesting! ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... This force is result of pressure differences in the fluid; the pressure is greater at the bottom than at the top. This is why objects can ‘float’: the magnitude of the buoyant force equals that of the force of gravity: ...
... This force is result of pressure differences in the fluid; the pressure is greater at the bottom than at the top. This is why objects can ‘float’: the magnitude of the buoyant force equals that of the force of gravity: ...
Analogous physical systems
... – Pressure must be measured across two points – Temperature difference is relevant in heat transfer – Velocity is relative – Newtonian frame of reference ...
... – Pressure must be measured across two points – Temperature difference is relevant in heat transfer – Velocity is relative – Newtonian frame of reference ...
02_Basic biorheology and gemodynamics
... The knowledge of viscosity is needed for proper design of required temperatures for storage, pumping or injection of fluids. There are two related measures of fluid viscosity - known as dynamic (or absolute) and kinematic viscosity. ...
... The knowledge of viscosity is needed for proper design of required temperatures for storage, pumping or injection of fluids. There are two related measures of fluid viscosity - known as dynamic (or absolute) and kinematic viscosity. ...
Template for the Design Expo Poster (PowerPoint)
... The overarching goal of this research is to develop a miniaturized, on-line, and low-cost technology to rapidly detect and quantify bacteria and fungus populations in environmental applications. This poster outlines the first of two phases of research that will achieve a novel integration of microfl ...
... The overarching goal of this research is to develop a miniaturized, on-line, and low-cost technology to rapidly detect and quantify bacteria and fungus populations in environmental applications. This poster outlines the first of two phases of research that will achieve a novel integration of microfl ...
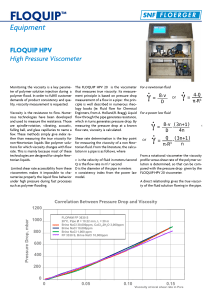
The Problems of Using USMs at Low Reynolds Numbers (High
... influenced by Reynolds number. • In general the major effects of Reynolds number are at the low values. • This takes us into the TRANSITION and LAMINAR regions of fluid operation. • It is the “heavy” oils, the higher viscosity oils that pull us into this region. ...
... influenced by Reynolds number. • In general the major effects of Reynolds number are at the low values. • This takes us into the TRANSITION and LAMINAR regions of fluid operation. • It is the “heavy” oils, the higher viscosity oils that pull us into this region. ...
Throttling Valves Versus The RadMax Expander
... kinetic energy - the energy of motion potential energy - the energy associated with altitude flow work - the energy associated with pressure, evaluated as pressure divided by density internal energy - the energy associated with molecular motion, plus that related to the bonds between molecul ...
... kinetic energy - the energy of motion potential energy - the energy associated with altitude flow work - the energy associated with pressure, evaluated as pressure divided by density internal energy - the energy associated with molecular motion, plus that related to the bonds between molecul ...
Kinematics of fluid motion
... [2] B. R. Munson, D.F Young and T. H. Okiisshi, 1998. Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. . [3] J.M. McDonough, 2004. Lectures in Elementary Fluid Dynamics: Physics, Mathematics and Applications, University of Kentucky, Lexington. ...
... [2] B. R. Munson, D.F Young and T. H. Okiisshi, 1998. Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. . [3] J.M. McDonough, 2004. Lectures in Elementary Fluid Dynamics: Physics, Mathematics and Applications, University of Kentucky, Lexington. ...
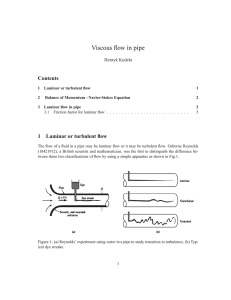
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""