Document
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
Physics 2B Sample Midterm Exam #1 by Todd Sauke
... direction.) We want to find the speed of the electron as it approaches infinity (far away). The force on the electron changes as it moves away, so we can't use constant ...
... direction.) We want to find the speed of the electron as it approaches infinity (far away). The force on the electron changes as it moves away, so we can't use constant ...
Electricity - DarringtonScience
... electrons that are loosely bound. These electrons are able to move throughout the conductor. As these electrons flow through the conductor, they form an electric current. When you turn on a light switch, are the charges coming from the power station to the lightbulb? ...
... electrons that are loosely bound. These electrons are able to move throughout the conductor. As these electrons flow through the conductor, they form an electric current. When you turn on a light switch, are the charges coming from the power station to the lightbulb? ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in the body. – These include structural, enzymatic, and homeostatic balance. • Com ...
... – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in the body. – These include structural, enzymatic, and homeostatic balance. • Com ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in the body. – These include structural, enzymatic, and homeostatic balance. • Com ...
... – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in the body. – These include structural, enzymatic, and homeostatic balance. • Com ...
ICP Plasma
... Inductively Coupled Plasma Energy supplied by electric currents Time varying electric current passes through coil Creates time-varying mag. field Induces oscillating electric currents in gas Ionizes atoms ...
... Inductively Coupled Plasma Energy supplied by electric currents Time varying electric current passes through coil Creates time-varying mag. field Induces oscillating electric currents in gas Ionizes atoms ...
Electric Fields
... Electric Charge *All solids, liquids, and gasses are made up of tiny particles called atoms. • Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. * Strong Nuclear Force holds protons and neutrons inside the nucleus. • Protons and electrons have an electric charge and neutrons do NOT have an ele ...
... Electric Charge *All solids, liquids, and gasses are made up of tiny particles called atoms. • Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. * Strong Nuclear Force holds protons and neutrons inside the nucleus. • Protons and electrons have an electric charge and neutrons do NOT have an ele ...
lect7_conductivity_meter
... Law, is the same as the field around an infinitely long line of charge with uniform line charge density. Next we will try to find an expression for the electric field in terms of the potential difference between the two cylinders. ...
... Law, is the same as the field around an infinitely long line of charge with uniform line charge density. Next we will try to find an expression for the electric field in terms of the potential difference between the two cylinders. ...
AP Physics Chapter 17 Electric Potential and
... • W=qVba • W=Fd=qEd where d is the distance ll to field lines from point a to b… • qV=qEd …so V=Ed and E=V/d • See Example 17-2 p 506 ...
... • W=qVba • W=Fd=qEd where d is the distance ll to field lines from point a to b… • qV=qEd …so V=Ed and E=V/d • See Example 17-2 p 506 ...
Electric Potential Difference Or Voltage
... •To increase electric Ep between two like charges, move them closer together d ...
... •To increase electric Ep between two like charges, move them closer together d ...
Problem Set 02
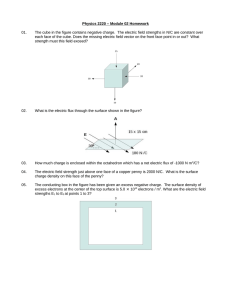
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
Chapter 5
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
Review for second exam:
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...