1. Electrostatics
... fields and therefore two forces; one from each of the other two charges. • The net field (and force) will be the vector sum of those two fields (and ...
... fields and therefore two forces; one from each of the other two charges. • The net field (and force) will be the vector sum of those two fields (and ...
Zero-Temperature Susceptibility of a Localized Spin Exchange
... performed in parallel to the case of J = 0 and the details are omitted. Eliminating rt_k~l,;:l from the equations, we obtain as the first approximation the following equations which correspond to Eqs. (19) and (20) of I : ...
... performed in parallel to the case of J = 0 and the details are omitted. Eliminating rt_k~l,;:l from the equations, we obtain as the first approximation the following equations which correspond to Eqs. (19) and (20) of I : ...
H - JMap
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
B - s3.amazonaws.com
... Charges and fields of a conductor • In electrostatic equilibrium, charges inside a conductor do not move. Thus, E = 0 everywhere in the interior of a conductor. • Since E = 0 inside, there are no net charges anywhere in the interior. Net charges can only be on the surface(s). ...
... Charges and fields of a conductor • In electrostatic equilibrium, charges inside a conductor do not move. Thus, E = 0 everywhere in the interior of a conductor. • Since E = 0 inside, there are no net charges anywhere in the interior. Net charges can only be on the surface(s). ...
Chapter 25 Study Guide
... This section also discusses the potential created by continuous charge distributions (starting after example 5), but you do not need to worry about this material. Problems: 5, 6, 7 3. Potential in Conductors Because the electric field is zero inside a conductor, the potential difference between two ...
... This section also discusses the potential created by continuous charge distributions (starting after example 5), but you do not need to worry about this material. Problems: 5, 6, 7 3. Potential in Conductors Because the electric field is zero inside a conductor, the potential difference between two ...
anomalous diffusion of a low-density current-carrying plasma
... greater than the number of electrons falling behind the wave. In other words, in the region in which n' > 0 there is a retarding field Ez while in the region characterized by n' < 0 there is an accelerating field; hence, on the average the electrons are retarded by the wave. In an oblique wave, howe ...
... greater than the number of electrons falling behind the wave. In other words, in the region in which n' > 0 there is a retarding field Ez while in the region characterized by n' < 0 there is an accelerating field; hence, on the average the electrons are retarded by the wave. In an oblique wave, howe ...
On the formulation of balance laws for electromagnetic continua
... manner that appeals strongly to those trained in modern continuum mechanics. While contact with earlier work is largely absent, some may find the latter to be somewhat disjointed, and so will appreciate Kovetz’ text for the organization it brings to the field. Even so, Kovetz’ basic postulates conce ...
... manner that appeals strongly to those trained in modern continuum mechanics. While contact with earlier work is largely absent, some may find the latter to be somewhat disjointed, and so will appreciate Kovetz’ text for the organization it brings to the field. Even so, Kovetz’ basic postulates conce ...
AP Physics 2: Algebra-Based 2015 Free
... 1. (10 points - suggested time 20 minutes) The figure above shows a cross section of a drinking glass (index of refraction 1.52) filled with a thin layer of liquid (index of refraction 1.33). The bottom corners of the glass are circular arcs, with the bottom right arc centered at point O. A monochro ...
... 1. (10 points - suggested time 20 minutes) The figure above shows a cross section of a drinking glass (index of refraction 1.52) filled with a thin layer of liquid (index of refraction 1.33). The bottom corners of the glass are circular arcs, with the bottom right arc centered at point O. A monochro ...
Phase-separation transition in liquid mixtures near curved charged
... Landau1 and later Onuki2 showed that the critical temperature can change by a small amount, proportional to E2. Experiment by Debye and Kleboth3 partially confirmed the theory. However, here we show that the situation in spatially nonuniform electric fields, occurring when liquid mixtures are found ...
... Landau1 and later Onuki2 showed that the critical temperature can change by a small amount, proportional to E2. Experiment by Debye and Kleboth3 partially confirmed the theory. However, here we show that the situation in spatially nonuniform electric fields, occurring when liquid mixtures are found ...
Capacitance - University of Kentucky
... A capacitor is a device used in a variety of electric circuits The capacitance, C, of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of the charge on either conductor (plate) to the magnitude of the potential difference between the conductors (plates) ...
... A capacitor is a device used in a variety of electric circuits The capacitance, C, of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of the charge on either conductor (plate) to the magnitude of the potential difference between the conductors (plates) ...
Properties of Electric Charges
... • Like gravitational force, electric force acts through space. Physical contact is unnecessary. An electric field exists in space around a charged object. This field exerts a force on any charged object in its field. • Consider a large charge Q exerting an electrical force F on a small charge qo, th ...
... • Like gravitational force, electric force acts through space. Physical contact is unnecessary. An electric field exists in space around a charged object. This field exerts a force on any charged object in its field. • Consider a large charge Q exerting an electrical force F on a small charge qo, th ...
Following are some practice problems
... cross section) that are uniformly charged. The center of the larger sphere is at < 0, 0, 0 >; it has a radius of 12 cm and a uniform positive charge of 4 x10-9 C. The center of the smaller sphere is at < 25, 0, 0 > cm; it has a radius of 3 cm and a uniform negative charge of -2 x10-9 C. What is the ...
... cross section) that are uniformly charged. The center of the larger sphere is at < 0, 0, 0 >; it has a radius of 12 cm and a uniform positive charge of 4 x10-9 C. The center of the smaller sphere is at < 25, 0, 0 > cm; it has a radius of 3 cm and a uniform negative charge of -2 x10-9 C. What is the ...
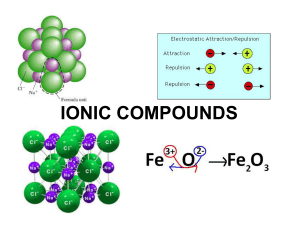
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... 12. the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions • 13. Ions form from electron transfer. Oppositely charge electrons attract. • 14. exist as crystals, high BP and MP, hard, rigid, conductive when dissolved or molten but not solid. • 15. Each ion is surrounded by oppositely charged ...
... 12. the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions • 13. Ions form from electron transfer. Oppositely charge electrons attract. • 14. exist as crystals, high BP and MP, hard, rigid, conductive when dissolved or molten but not solid. • 15. Each ion is surrounded by oppositely charged ...
Periodic_Chemical_Properties
... an initial guess of the radius of a single ion, e.g. O2G, one can estimate the size of other ions bonded to it. These estimated values can be used to determine the size of additional ions. The initial guess can then be revised to give consistent results. effective nuclear charge: The number of proto ...
... an initial guess of the radius of a single ion, e.g. O2G, one can estimate the size of other ions bonded to it. These estimated values can be used to determine the size of additional ions. The initial guess can then be revised to give consistent results. effective nuclear charge: The number of proto ...
Rules for drawing electric field lines
... Charging by contact 1. Friction - by rubbing two different neutral materials together, you can transfer some electrons from one surface to another. Ex: shoes on carpet – electrons move from the carpet to the shoes. The two objects receive an opposite charge. 2. Conduction - an already charged objec ...
... Charging by contact 1. Friction - by rubbing two different neutral materials together, you can transfer some electrons from one surface to another. Ex: shoes on carpet – electrons move from the carpet to the shoes. The two objects receive an opposite charge. 2. Conduction - an already charged objec ...