Stars and Constellations
... other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise. • The object switches to become a “true star” and it is then able to make its own heat and light. • The life of the star then depends on its mass. ...
... other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise. • The object switches to become a “true star” and it is then able to make its own heat and light. • The life of the star then depends on its mass. ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main sequence. In the ain sequence, the hotter the star, the brighter it is. Not all star’s, however, follow that pattern. While some star’s are very hot, ...
... It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main sequence. In the ain sequence, the hotter the star, the brighter it is. Not all star’s, however, follow that pattern. While some star’s are very hot, ...
Document
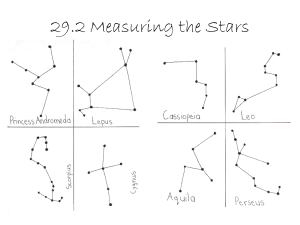
... • People in years past used the constellations to know when to prepare for planting, harvest and ritual celebrations ...
... • People in years past used the constellations to know when to prepare for planting, harvest and ritual celebrations ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Fusion of hydrogen occurs in star cores releasing huge amounts of energy Evolution of stars A nebula contracts and breaks apart from the instability caused by gravity Temperatures in each nebula chunk increase as particles move closer together At 10 million K fusion begins and energy from a n ...
... Fusion of hydrogen occurs in star cores releasing huge amounts of energy Evolution of stars A nebula contracts and breaks apart from the instability caused by gravity Temperatures in each nebula chunk increase as particles move closer together At 10 million K fusion begins and energy from a n ...
The Lifecycle of Stars
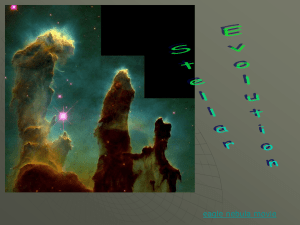
... - Sculpted by stellar winds and radiation, these fantastic, undulating shapes lie within the stellar nursery known as M17, - Omega Nebula, some 5,500 light-years away in the nebula-rich constellation Sagittarius. - Colors in the fog of surrounding hotter material indicate M17's chemical make up. The ...
... - Sculpted by stellar winds and radiation, these fantastic, undulating shapes lie within the stellar nursery known as M17, - Omega Nebula, some 5,500 light-years away in the nebula-rich constellation Sagittarius. - Colors in the fog of surrounding hotter material indicate M17's chemical make up. The ...
hw4
... Stellar spectra provide astronomers with information that enables temperature, composition, radial motion, magnetic properties, rotation, and color to be determined. An indication (but not direct measurement) of stellar radius, mass, and absolute magnitude can also be obtained from spectral informat ...
... Stellar spectra provide astronomers with information that enables temperature, composition, radial motion, magnetic properties, rotation, and color to be determined. An indication (but not direct measurement) of stellar radius, mass, and absolute magnitude can also be obtained from spectral informat ...
Stellar Classification Worksheet 2
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
Stars and Sun
... Only part of the Milky Way is visible due to our being in the galaxy Galileo saw the Milky Way in 1609 using a telescope Bigger and brighter than most galaxies in the universe ...
... Only part of the Milky Way is visible due to our being in the galaxy Galileo saw the Milky Way in 1609 using a telescope Bigger and brighter than most galaxies in the universe ...
AST 443
... 8. Calculate the average density of a red-giant core of 0.25 solar-mass and radius 15,000 km. Compare this with the average density of the giant’s envelope, if it has a 0.5 solar-mass and its radius is 0.5 A.U. Compare each with the central density of the Sun. ...
... 8. Calculate the average density of a red-giant core of 0.25 solar-mass and radius 15,000 km. Compare this with the average density of the giant’s envelope, if it has a 0.5 solar-mass and its radius is 0.5 A.U. Compare each with the central density of the Sun. ...
Document
... d) As a main sequence star. 25. What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age? a) The number of red giants. b) The faintest stars seen in the cluster. c) The main sequence turnoff. d) The total number of stars in the cluster. 26. Astronomers talk about "low-mass" and "high-mass" ...
... d) As a main sequence star. 25. What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age? a) The number of red giants. b) The faintest stars seen in the cluster. c) The main sequence turnoff. d) The total number of stars in the cluster. 26. Astronomers talk about "low-mass" and "high-mass" ...
What is a Star
... What is a Star? A star is a luminous globe of glowing gas producing its own heat and light by nuclear reactions in the star's core. Stars vary in size, mass, brightness, temperature and colour. The smallest mass possible for a star is about 1/10 that of the Sun, while the brightest stars have masses ...
... What is a Star? A star is a luminous globe of glowing gas producing its own heat and light by nuclear reactions in the star's core. Stars vary in size, mass, brightness, temperature and colour. The smallest mass possible for a star is about 1/10 that of the Sun, while the brightest stars have masses ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
Star Game Cards
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
... Before being engulfed, matter that is pulled into a black hole should become very hot and emit ____. ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 6. What two star characteristics does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram compare? 7. What is a star’s spectrum? ...
... 6. What two star characteristics does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram compare? 7. What is a star’s spectrum? ...
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... balanced by outward gas pressure. • Inward gas pressure trying to escape, causing internal temp. & press. to rise ...
... balanced by outward gas pressure. • Inward gas pressure trying to escape, causing internal temp. & press. to rise ...
Star

A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names. Extensive catalogues of stars have been assembled by astronomers, which provide standardized star designations.For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Once the hydrogen in the core of a star is nearly exhausted, almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime and, for some stars, by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the principal determinant of its evolution and eventual fate. Other characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement. A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Once the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily converted into helium through nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity. Once the hydrogen fuel at the core is exhausted, a star with at least 0.4 times the mass of the Sun expands to become a red giant, in some cases fusing heavier elements at the core or in shells around the core. The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of its matter into the interstellar environment, where it will contribute to the formation of a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements. Meanwhile, the core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or (if it is sufficiently massive) a black hole.Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.