Sky Watching Talk
... direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
... direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... larger star would be more luminous If the same size, hotter one would be brighter Types of magnitude Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky ...
... larger star would be more luminous If the same size, hotter one would be brighter Types of magnitude Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky ...
Orion - CSIC
... looking for patterns in the stars that appeal to them. Students can then be asked to make up stories to go with their new constellations. Older students can research the constellation patterns and stories that other cultures saw in the night sky and compare them to the more familiar Greek ones. This ...
... looking for patterns in the stars that appeal to them. Students can then be asked to make up stories to go with their new constellations. Older students can research the constellation patterns and stories that other cultures saw in the night sky and compare them to the more familiar Greek ones. This ...
Folie 1 - univie.ac.at
... Canadian Space Agency (CSA). Each will fly a CCD camera to perform high-precision two-color photometry continuously for two years or more, primarily of stars brighter than 4th magnitude (V), and with reduced accuracy also of fainter stars. ...
... Canadian Space Agency (CSA). Each will fly a CCD camera to perform high-precision two-color photometry continuously for two years or more, primarily of stars brighter than 4th magnitude (V), and with reduced accuracy also of fainter stars. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
Document
... In the early part of this century, astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung studied the luminosities and types of stars. Soon, he and American astronomer, Henry Russell, developed a graphical representation comparing a star’s temperature against its luminosity (also called absolute magnitude) and types of stars ...
... In the early part of this century, astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung studied the luminosities and types of stars. Soon, he and American astronomer, Henry Russell, developed a graphical representation comparing a star’s temperature against its luminosity (also called absolute magnitude) and types of stars ...
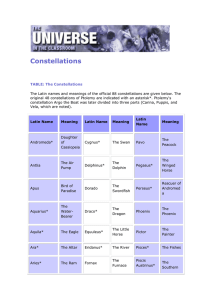
Star Maps and Constellations
... names are often related to the part of the "picture". •Alhena in Gemini means "mark", pertaining to a mark on the foot of Gemini twin Pollux. ...
... names are often related to the part of the "picture". •Alhena in Gemini means "mark", pertaining to a mark on the foot of Gemini twin Pollux. ...
- Stevenson High School
... 2. How many constellations are there? 3. Constellations are made up by the apparent arrangement of stars. Are those stars in a constellations physically connected/bound to one another? Tell me about those stars. 4. Are there any stars that are not part of a constellation? Explain. 5. How is astrolog ...
... 2. How many constellations are there? 3. Constellations are made up by the apparent arrangement of stars. Are those stars in a constellations physically connected/bound to one another? Tell me about those stars. 4. Are there any stars that are not part of a constellation? Explain. 5. How is astrolog ...
Ast 405, Pulsating Stars The following is based Chapter 14 of the
... The following is based Chapter 14 of the book. • 1. Stars whose brightness varies regularly due to some internal mechanism. • 2. Examples are Miras, Cepheids, RR Lyraes, W Virginis, BL Her stars. You shouyld be familiar with Table 14.1 in the book. • 3. The Cepheid Period-Luminosity relation, or PL ...
... The following is based Chapter 14 of the book. • 1. Stars whose brightness varies regularly due to some internal mechanism. • 2. Examples are Miras, Cepheids, RR Lyraes, W Virginis, BL Her stars. You shouyld be familiar with Table 14.1 in the book. • 3. The Cepheid Period-Luminosity relation, or PL ...
Star Properties and Stellar Evolution
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
... 1. Pulsating stars – expand and contract 2. Cepheid Variables – used to find distances to galaxies that contain them 3. Eclipsing Binaries – 2 stars revolve around each other ...
The Stars
... • What is the difference between apparent and absolute magnitude? • What two factors cause luminosity to increase? • What are the spectral classes? • Why is a blue star more luminous than a yellow star of the same size? • What does the H-R diagram show us about most stars (main sequence stars)? • Wh ...
... • What is the difference between apparent and absolute magnitude? • What two factors cause luminosity to increase? • What are the spectral classes? • Why is a blue star more luminous than a yellow star of the same size? • What does the H-R diagram show us about most stars (main sequence stars)? • Wh ...
chapter-30-pp
... Most stars are made of the same elements as Earth except the most common element is different. On Earth it is oxygen and for stars it is hydrogen. ...
... Most stars are made of the same elements as Earth except the most common element is different. On Earth it is oxygen and for stars it is hydrogen. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... be thought of as “warm” colors and blue may be thought of as a “cool” color, scientists consider red and yellow to be cool colors and blue to be a warm color. ...
... be thought of as “warm” colors and blue may be thought of as a “cool” color, scientists consider red and yellow to be cool colors and blue to be a warm color. ...
May - RASC St. John`s Centre
... Venus (magnitude –3.9) the bright Evening Star shining in the west-northwest during and after twilight. Mars (magnitude +0.5) high in the west during evening in the constellation Cancer. Jupiter (magnitude –2.2) is low in the dawn. Look for it above the eastern horizon. Saturn (magnitude +0.7) is hi ...
... Venus (magnitude –3.9) the bright Evening Star shining in the west-northwest during and after twilight. Mars (magnitude +0.5) high in the west during evening in the constellation Cancer. Jupiter (magnitude –2.2) is low in the dawn. Look for it above the eastern horizon. Saturn (magnitude +0.7) is hi ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky H. Variable Stars 1. Some st ...
... 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky H. Variable Stars 1. Some st ...
Astronomy Day 2006: A short presentation on eclipsing binary stars
... Just what are they? Why do we care? It is recognized as fact by astronomers that well over half of the stars in the universe belong to multiple systems. You might think of our Sun as being an exceptional system that involves only one star and you would be right. ...
... Just what are they? Why do we care? It is recognized as fact by astronomers that well over half of the stars in the universe belong to multiple systems. You might think of our Sun as being an exceptional system that involves only one star and you would be right. ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
AST121 Introduction to Astronomy
... • Most stars in the Milky Way are in multiple systems but far from other stars. • Some stars group together to form clusters • Types of clusters: open and globular ...
... • Most stars in the Milky Way are in multiple systems but far from other stars. • Some stars group together to form clusters • Types of clusters: open and globular ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest
... 18. If you were in a spaceship would you be able to see a star twinkling? ____________ Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 18. If you were in a spaceship would you be able to see a star twinkling? ____________ Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Document
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
Stars
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.