The Universe - HMXEarthScience
... sizes of nearby galaxies relative motions of distant galaxies densities of the planets rotation periods of the planets ...
... sizes of nearby galaxies relative motions of distant galaxies densities of the planets rotation periods of the planets ...
ch 7 prob B
... 7. The two Echo satellites, which were launched in 1960 and 1964, were early examples of communications satellites. Suppose the gas pressure inside Echo 1 was the same as the atmospheric pressure at Earth’s surface. If the total force exerted on the inner surface of Echo 1 was 2.86 x 108 N, what was ...
... 7. The two Echo satellites, which were launched in 1960 and 1964, were early examples of communications satellites. Suppose the gas pressure inside Echo 1 was the same as the atmospheric pressure at Earth’s surface. If the total force exerted on the inner surface of Echo 1 was 2.86 x 108 N, what was ...
Lab 4
... “The hotter the bulb, the ___________________________ the B–V color index.” 7. a. Generalize to stars: Given a red star and a blue star of equal magnitude (apparent brightness) and given a yellow filter, which would appear brighter? ...
... “The hotter the bulb, the ___________________________ the B–V color index.” 7. a. Generalize to stars: Given a red star and a blue star of equal magnitude (apparent brightness) and given a yellow filter, which would appear brighter? ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
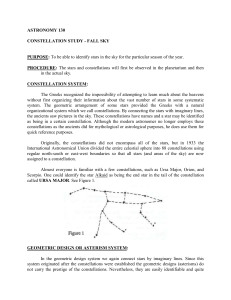
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
f - 廖寶珊紀念書院Liu Po Shan Memorial College
... Shift to short wavelengths. (blue end of visible light spectrum) Spectrum is blueshifted ...
... Shift to short wavelengths. (blue end of visible light spectrum) Spectrum is blueshifted ...
Astronomy
... True (A) or False (B) 1. ______ The constellation Ursa Major is visible to observers near Pittsburgh year-round. 2. ______ The celestial equator always crosses the horizon at the north point and south point. 3. ______ The celestial equator always passes directly overhead to those that live on the eq ...
... True (A) or False (B) 1. ______ The constellation Ursa Major is visible to observers near Pittsburgh year-round. 2. ______ The celestial equator always crosses the horizon at the north point and south point. 3. ______ The celestial equator always passes directly overhead to those that live on the eq ...
ppt
... This depends on the number density of electrons, ne. This is because as the number of free electrons increases, it is more likely that they can recombine with an atom and lower the ionization state. The Boltzmann factor exp(-ci/kT) means it is more difficult to ionize ...
... This depends on the number density of electrons, ne. This is because as the number of free electrons increases, it is more likely that they can recombine with an atom and lower the ionization state. The Boltzmann factor exp(-ci/kT) means it is more difficult to ionize ...
ph709-15-testrevision
... of planetary radii. SELECTION: Of course, while planets close to their parent stars will preferentially be found, due to their shorter orbital periods and greater likelihood to transit, planetary transits will be detected at all orbital separations. CONFIRMATION: In general, the detection of three s ...
... of planetary radii. SELECTION: Of course, while planets close to their parent stars will preferentially be found, due to their shorter orbital periods and greater likelihood to transit, planetary transits will be detected at all orbital separations. CONFIRMATION: In general, the detection of three s ...
Transcript of lecture I
... In the written word one does not have a specific audience unless one is writing a letter or something like that. The audience for writing is abstract and the writer is writing to the world at large. In such a situation the writer must anticipate a general audience instead intuitively sensing a real ...
... In the written word one does not have a specific audience unless one is writing a letter or something like that. The audience for writing is abstract and the writer is writing to the world at large. In such a situation the writer must anticipate a general audience instead intuitively sensing a real ...
18._Sun_student
... Provided energy that heated core as Sun was forming. Intense heat eventually forced fusion. Contraction stopped when fusion began ...
... Provided energy that heated core as Sun was forming. Intense heat eventually forced fusion. Contraction stopped when fusion began ...
The Peculiar Physics of Line-Driving
... * Line-force requires nonlocal solution of radiation transfer, in principle in hundreds of spectral lines of varying strength ...
... * Line-force requires nonlocal solution of radiation transfer, in principle in hundreds of spectral lines of varying strength ...
Starspots (AIP – Klaus G
... Doppler imaging is an inversion technique to recover a 2-D image of a rapidly rotating star from a series of high-resolution spectral line profiles. The inverse problem for stars with cool spots amounts to solving the integral equation relating the surface temperature distribution to the observed li ...
... Doppler imaging is an inversion technique to recover a 2-D image of a rapidly rotating star from a series of high-resolution spectral line profiles. The inverse problem for stars with cool spots amounts to solving the integral equation relating the surface temperature distribution to the observed li ...
What Makes a Planet Habitable?
... The youngest stages of planets Planets form and grow in so-called protoplanetary disks, which are huge gas and dust disks orbiting the youngest stars at ages of only one to a few million years, with sizes larger than the entire solar system. Dust particles coagulate in disks to ever larger grains an ...
... The youngest stages of planets Planets form and grow in so-called protoplanetary disks, which are huge gas and dust disks orbiting the youngest stars at ages of only one to a few million years, with sizes larger than the entire solar system. Dust particles coagulate in disks to ever larger grains an ...
every star in the cluster.
... giants, continually forming from evolving stars near the turnoff. But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
... giants, continually forming from evolving stars near the turnoff. But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
Click Here To
... 1) Name the 8 planets in order of their proximity to the sun. 2) How are the first 4 planets similar? 3) How are the 4 gas giants similar? Why do they have gas surrounding them while the inner planets do not? 4) What is the cause of Jupiter’s Great Red spot? 5) What type of star is our Sun? What is ...
... 1) Name the 8 planets in order of their proximity to the sun. 2) How are the first 4 planets similar? 3) How are the 4 gas giants similar? Why do they have gas surrounding them while the inner planets do not? 4) What is the cause of Jupiter’s Great Red spot? 5) What type of star is our Sun? What is ...
Atoms and Starlight Generating light
... (same overall area, i.e. same total power output) — ~6000 K (most similar shape) note that this is only its surface temperature ...
... (same overall area, i.e. same total power output) — ~6000 K (most similar shape) note that this is only its surface temperature ...
– 1 – 1. Star Formation At Low Metallicity 1.1.
... Molecules normally form on the surface of dust grains. Since there is no dust at 0Z, the molecules must form in the gas, which is much harder to do. A detailed consideration of the various reactions involved is required to evaluate the ratio of n(H)/n(H2 ). The relevant reactions require free electr ...
... Molecules normally form on the surface of dust grains. Since there is no dust at 0Z, the molecules must form in the gas, which is much harder to do. A detailed consideration of the various reactions involved is required to evaluate the ratio of n(H)/n(H2 ). The relevant reactions require free electr ...
Nebulae - Innovative Teachers BG
... Planetary Nebulae Planetary nebulae in their Photography by Emil Ivanov physical nature are different from nebulae discussed above and being essentially gas-dust clouds. Planetary nebula is an evolution phase of stars with masses 7-8 solar masses and greater. When a star forward in its evolution, l ...
... Planetary Nebulae Planetary nebulae in their Photography by Emil Ivanov physical nature are different from nebulae discussed above and being essentially gas-dust clouds. Planetary nebula is an evolution phase of stars with masses 7-8 solar masses and greater. When a star forward in its evolution, l ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.