Where Does Helium Come from?
... immediately after the Big Bang. It was these gamma ray photons with unfathomable energy which created the matter we see around us. As mentioned in the previous paragraphs, it takes an enormous amount of energy to create matter and it was these high-energy gamma ray photons which allowed this to happ ...
... immediately after the Big Bang. It was these gamma ray photons with unfathomable energy which created the matter we see around us. As mentioned in the previous paragraphs, it takes an enormous amount of energy to create matter and it was these high-energy gamma ray photons which allowed this to happ ...
The Sun and the Stars
... Spectral Classification – Harvard Classification scheme Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spe ...
... Spectral Classification – Harvard Classification scheme Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spe ...
HERE - Montana State University Extended University
... in this activity explore the orbital characteristics a planetary home needs to support Earth-like life forms. The “Goldilocks Phenomenon” loosely defines the major characteristics a planet needs to potentially support life: having just the right temperature and type of star, orbiting at just the rig ...
... in this activity explore the orbital characteristics a planetary home needs to support Earth-like life forms. The “Goldilocks Phenomenon” loosely defines the major characteristics a planet needs to potentially support life: having just the right temperature and type of star, orbiting at just the rig ...
The Milky Way and Its Neighbors
... Approximately 10% of known galaxies are elliptical Stars orbit the galaxy center in all different planes Circular orbital velocity measurements do not work very well Sometimes a preferred direction of very slow rotation Luminosity decreases quickly from center so measurements are always ma ...
... Approximately 10% of known galaxies are elliptical Stars orbit the galaxy center in all different planes Circular orbital velocity measurements do not work very well Sometimes a preferred direction of very slow rotation Luminosity decreases quickly from center so measurements are always ma ...
Planisphere
... for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfortable with the planisphere is simply to take it outside and use it. Like most things, your ability with it will improve with practice. Using the Planisphere: Use your planisphere to a ...
... for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfortable with the planisphere is simply to take it outside and use it. Like most things, your ability with it will improve with practice. Using the Planisphere: Use your planisphere to a ...
Coronal Mass Ejection
... • The Sun continues to shine, while it radiates away as its luminosity, by generating energy by thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. • Gravitational and thermal equilibrium determine the Sun’s internal structure and its rate of energy generation. • The Sun’s atmosphere displays its own vers ...
... • The Sun continues to shine, while it radiates away as its luminosity, by generating energy by thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. • Gravitational and thermal equilibrium determine the Sun’s internal structure and its rate of energy generation. • The Sun’s atmosphere displays its own vers ...
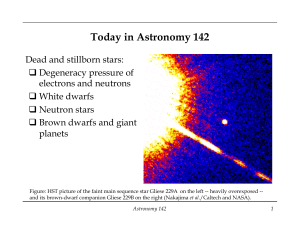
Today in Astronomy 142
... and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conservation of flux) and rotate rapidly (conservation of angular momentum), and are observed as pulsars: appar ...
... and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conservation of flux) and rotate rapidly (conservation of angular momentum), and are observed as pulsars: appar ...
Name: pd: ______ Date: Constellation Scavenger Hunt! Google Sky
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
Test - Scioly.org
... potential sources of error in the collected data? i. Imperfections in the telescopes’ lenses/mirrors and general construction distort data ii. The diffraction of light blurs the observed image iii. Earth’s atmosphere has turbulence and uneven pressures that blur images iv. Photons arrive randoml ...
... potential sources of error in the collected data? i. Imperfections in the telescopes’ lenses/mirrors and general construction distort data ii. The diffraction of light blurs the observed image iii. Earth’s atmosphere has turbulence and uneven pressures that blur images iv. Photons arrive randoml ...
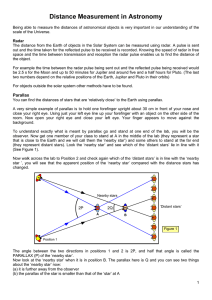
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
Document
... Only 10-40% of the gas goes into stars. Stellar winds, jets and supernova explosions blow away the gas from the cluster and stop any further star ...
... Only 10-40% of the gas goes into stars. Stellar winds, jets and supernova explosions blow away the gas from the cluster and stop any further star ...
30 Doradus - HubbleSOURCE
... Only 10-40% of the gas goes into stars. Stellar winds, jets and supernova explosions blow away the gas from the cluster and stop any further star ...
... Only 10-40% of the gas goes into stars. Stellar winds, jets and supernova explosions blow away the gas from the cluster and stop any further star ...
View the presentation slides
... Fortunately, optical techniques are capable of exquisite accuracy. Let’s look at some data. This is a “Jupiter” (M ~ 0.96 MJ) orbiting a “Sol” (M = 0.88 MS). The orbital period is 9 years (Jupiter’s is 12), because the orbit is a bit smaller (4.2 AU instead of 5.2). This is how astronomers 60 light- ...
... Fortunately, optical techniques are capable of exquisite accuracy. Let’s look at some data. This is a “Jupiter” (M ~ 0.96 MJ) orbiting a “Sol” (M = 0.88 MS). The orbital period is 9 years (Jupiter’s is 12), because the orbit is a bit smaller (4.2 AU instead of 5.2). This is how astronomers 60 light- ...
Is Protostellar Jet Spinning? Chin
... is estimated to be ~ 30 yrs. This periodic variation may be due to a solar-type magnetic cycle or a periodic disturbance of an unseen stellar companion orbiting the protostar at ~ 4 AU away with a period of 30 yrs. The averaged two-sided mass-loss rate of the jet is estimated to be (1-3) x10-6 M⊙ yr ...
... is estimated to be ~ 30 yrs. This periodic variation may be due to a solar-type magnetic cycle or a periodic disturbance of an unseen stellar companion orbiting the protostar at ~ 4 AU away with a period of 30 yrs. The averaged two-sided mass-loss rate of the jet is estimated to be (1-3) x10-6 M⊙ yr ...
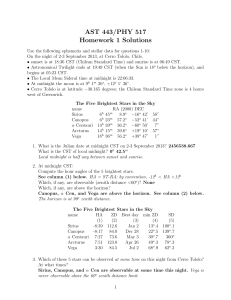
Sample Problems - Princeton University Press
... 1. (**) If we want to communicate with aliens on a timescale commensurate with a typical human lifespan, then the nearest aliens should be no more than about 20 to 30 light years away from us. Under this assumption, estimate the total number of alien races in the galaxy. 2. (**) The mathematician Jo ...
... 1. (**) If we want to communicate with aliens on a timescale commensurate with a typical human lifespan, then the nearest aliens should be no more than about 20 to 30 light years away from us. Under this assumption, estimate the total number of alien races in the galaxy. 2. (**) The mathematician Jo ...
- Europhysics News
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
Secrets of the Sun
... The joining of two or more atoms to form a heavier atom. In the nucleus of the Sun, fusion of hydrogen into helium releases energy. ...
... The joining of two or more atoms to form a heavier atom. In the nucleus of the Sun, fusion of hydrogen into helium releases energy. ...
Photometric analysis of the globular cluster NGC5466
... the lowest known values of metallicity. We took a couple of images from the free software “WhereIsM13?” (http://www.thinkastronomy.com/M13) in order to show clearly the position of NGC5466 (Fig. 2). NGC5466 is also one of the least dense known glob- ...
... the lowest known values of metallicity. We took a couple of images from the free software “WhereIsM13?” (http://www.thinkastronomy.com/M13) in order to show clearly the position of NGC5466 (Fig. 2). NGC5466 is also one of the least dense known glob- ...
Testing
... because Earth’s orbit is slightly elliptical. • Mean solar time is based on the average length of a day. • Noon is average time at which Sun crosses meridian • It is a local definition of time ...
... because Earth’s orbit is slightly elliptical. • Mean solar time is based on the average length of a day. • Noon is average time at which Sun crosses meridian • It is a local definition of time ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.