Lecture 4
... Spectral Classification – Harvard Classification scheme Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spe ...
... Spectral Classification – Harvard Classification scheme Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spe ...
Lecture 34: Habitable Zones around Stars
... Region around the Sun where liquid water is stable on the surface of a planet at a pressure of 1 atmosphere. ...
... Region around the Sun where liquid water is stable on the surface of a planet at a pressure of 1 atmosphere. ...
The star Betelgeuse is about 500 light years away from us. If this star
... From the spectrum of a starts light we can learn about a. the CBR b. Planck's constant c. the elements in the star d. its look back time An electron in an atom can go to a higher, more energetic orbit by a. absorbing a photon b. emitting a photon c. changing to a proton d. emitting neutrinos From H ...
... From the spectrum of a starts light we can learn about a. the CBR b. Planck's constant c. the elements in the star d. its look back time An electron in an atom can go to a higher, more energetic orbit by a. absorbing a photon b. emitting a photon c. changing to a proton d. emitting neutrinos From H ...
Part 2 of Our Lecture
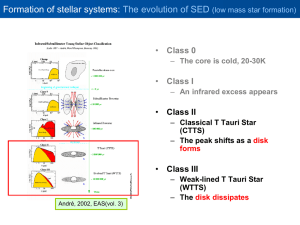
... Formation of stellar systems: CTTS (Class II) • Classical T Tauri Star T Tauri Star with strong Hα emission line - much brighter than other stars of similar T in IR – Dust in disk absorb light from central star and reradiate @ IR – ‘reprocessing’ or ‘irradiated’( or ‘passive’) disk – Disk accretion ...
... Formation of stellar systems: CTTS (Class II) • Classical T Tauri Star T Tauri Star with strong Hα emission line - much brighter than other stars of similar T in IR – Dust in disk absorb light from central star and reradiate @ IR – ‘reprocessing’ or ‘irradiated’( or ‘passive’) disk – Disk accretion ...
Measuring Our Universe
... is obtained by measuring positions of objects when the Earth is at opposite points in its orbit around the Sun. That is, if the Sun is at D and C is observed at two times, A, B, that are six months apart, then the baseline for parallax measurements would be AU. Of course, this requires an accurate d ...
... is obtained by measuring positions of objects when the Earth is at opposite points in its orbit around the Sun. That is, if the Sun is at D and C is observed at two times, A, B, that are six months apart, then the baseline for parallax measurements would be AU. Of course, this requires an accurate d ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Section 1
... • Stars vary in size and mass. • Stars such as the sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. • Most of the stars you can see in the night sky are medium-sized stars. • Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less mas ...
... • Stars vary in size and mass. • Stars such as the sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. • Most of the stars you can see in the night sky are medium-sized stars. • Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less mas ...
mslien~1
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
Visual Double Star Measurements with Equatorial - Alt
... the pair proves to be binary in nature. Conversely, if the two stars are an optical pair, meaning they do not orbit around a common center of mass, there will be a linear change in separation or position angle over time. Today’s astronomers continue to observe these changes with fairly simple equipm ...
... the pair proves to be binary in nature. Conversely, if the two stars are an optical pair, meaning they do not orbit around a common center of mass, there will be a linear change in separation or position angle over time. Today’s astronomers continue to observe these changes with fairly simple equipm ...
The Early Evolution of Protostars
... Not consistent with fast, early infall (Andre et al.) Except Oph: 0.04 Myr, Oph was basis of low t(0) Oph has faster evolution or not continuous ...
... Not consistent with fast, early infall (Andre et al.) Except Oph: 0.04 Myr, Oph was basis of low t(0) Oph has faster evolution or not continuous ...
AST4930 Star and Planet Formation
... Spectroscopic analysis can identify if an early type star is in main-sequence or already leaving the main sequence. In the first case, it follows a given temperature-luminosity relation, which can be exploited to determine their distance (but reddening must be corrected for). ...
... Spectroscopic analysis can identify if an early type star is in main-sequence or already leaving the main sequence. In the first case, it follows a given temperature-luminosity relation, which can be exploited to determine their distance (but reddening must be corrected for). ...
It`s cosmic! - NSW Department of Education
... Each galaxy is a very large spinning structure. It contains billions of stars. It also contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Some of the stars, like our Sun, have planets. All these things are held together in each galaxy by gravitational forces. (You feel a gravitational force on Earth. I ...
... Each galaxy is a very large spinning structure. It contains billions of stars. It also contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Some of the stars, like our Sun, have planets. All these things are held together in each galaxy by gravitational forces. (You feel a gravitational force on Earth. I ...
Brightness and Distance
... the term luminosity to describe the amount of energy the star radiates in all directions per unit time. Visual luminosity means the luminosity at visual wavelengths, that is wavelengths that humans can see. Bolometric luminosity is the luminosity at all wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. T ...
... the term luminosity to describe the amount of energy the star radiates in all directions per unit time. Visual luminosity means the luminosity at visual wavelengths, that is wavelengths that humans can see. Bolometric luminosity is the luminosity at all wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. T ...
Luminosities and magnitudes of stars
... The solid angle, , that an object subtends at a point is a measure of how big that object appears to an observer at that point. For instance, a small object nearby could subtend the same solid angle as a large object far away. The solid angle is proportional to the surface area, S, of a projection ...
... The solid angle, , that an object subtends at a point is a measure of how big that object appears to an observer at that point. For instance, a small object nearby could subtend the same solid angle as a large object far away. The solid angle is proportional to the surface area, S, of a projection ...
Grossmugl Star Walk Installation
... 600 and 500 BC. This was the time when Babylon experienced one of its wealthiest periods under king Nebuchadnezzar II, democracy was invented in Athens and the city of Rome was still a small kingdom, far from the great empire it would later become. When stargazing at this historic site one can almos ...
... 600 and 500 BC. This was the time when Babylon experienced one of its wealthiest periods under king Nebuchadnezzar II, democracy was invented in Athens and the city of Rome was still a small kingdom, far from the great empire it would later become. When stargazing at this historic site one can almos ...
02.03 Distances in Space Assignment To prepare for this visit you
... 02.03 Distances in Space Assignment ...
... 02.03 Distances in Space Assignment ...
poster
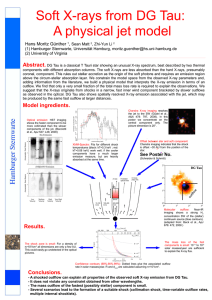
... adding information from the literature, we build a physical model that interprets the X-ray emission in terms of an outflow. We find that only a very small fraction of the total mass loss rate is required to explain the observations. We suggest that the X-rays originate from shocks in a narrow, fast ...
... adding information from the literature, we build a physical model that interprets the X-ray emission in terms of an outflow. We find that only a very small fraction of the total mass loss rate is required to explain the observations. We suggest that the X-rays originate from shocks in a narrow, fast ...
Dear Leif - LEIF.org
... indeed, as it has the current authors. Much better, in my opinion, is to teach the students the fundamentals of the subject, leaving them with the ability to teach themselves the rest in later life. The obvious way to approach the matter in hand, in my opinion, is to work in the accelerating frame o ...
... indeed, as it has the current authors. Much better, in my opinion, is to teach the students the fundamentals of the subject, leaving them with the ability to teach themselves the rest in later life. The obvious way to approach the matter in hand, in my opinion, is to work in the accelerating frame o ...
Astronomy Exam - domenicoscience
... change location at a much greater rate. How do you explain this weird truth? What causes a star to radiate heat and light? What makes a Neutron star so dense? What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? What element is the main ingredient of most stars? Some stars in the sky t ...
... change location at a much greater rate. How do you explain this weird truth? What causes a star to radiate heat and light? What makes a Neutron star so dense? What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? What element is the main ingredient of most stars? Some stars in the sky t ...
dtu7ech10sun - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... If the temperature at the core of the protosun rises above 10 million Kelvin, then fusion of hydrogen into helium nuclei occurs. The Sun becomes a star at this time. ...
... If the temperature at the core of the protosun rises above 10 million Kelvin, then fusion of hydrogen into helium nuclei occurs. The Sun becomes a star at this time. ...
Falling Stars
... In a meteor storm, over 1,000 meteors blaze across the sky every hour. In 1833, people all over America woke up to see hundreds of stars falling every minute! All night, the sky was brightened by meteors that rocketed through the night by the thousands! Since no telescopes or fancy equipment were ne ...
... In a meteor storm, over 1,000 meteors blaze across the sky every hour. In 1833, people all over America woke up to see hundreds of stars falling every minute! All night, the sky was brightened by meteors that rocketed through the night by the thousands! Since no telescopes or fancy equipment were ne ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.