iaf2001_paper (doc - 1.8 MB)
... The satellite will be operated from the COROT Control Center, located in Toulouse and sharing the facilities of the PROTEUS satellites family. The preparation of the observation sequences and the pre-processing of the scientific data will be done by the COROT Mission Center, located in Toulouse and ...
... The satellite will be operated from the COROT Control Center, located in Toulouse and sharing the facilities of the PROTEUS satellites family. The preparation of the observation sequences and the pre-processing of the scientific data will be done by the COROT Mission Center, located in Toulouse and ...
Physics 306
... Very hot stars can excite clouds of gas and dust to emit light and this reveals that the clouds contain mostly hydrogen gas at very low densities. 3 kinds of nebulae: o Emission nebulae – produced when a star with temperature higher than 25,000K excites the gas near to produce an emission spectr ...
... Very hot stars can excite clouds of gas and dust to emit light and this reveals that the clouds contain mostly hydrogen gas at very low densities. 3 kinds of nebulae: o Emission nebulae – produced when a star with temperature higher than 25,000K excites the gas near to produce an emission spectr ...
First Light Sources at the End of the Dark Ages: Direct
... and when massive galaxies containing Population II stars formed. There is an apparent chemical enrichment “floor” of [Fe/H]~-4 in the solar neighborhood indicating a rapid, prompt enrichment of the IGM at high redshift. Constraining the initial mass function (IMF) of primordial stars is the key to u ...
... and when massive galaxies containing Population II stars formed. There is an apparent chemical enrichment “floor” of [Fe/H]~-4 in the solar neighborhood indicating a rapid, prompt enrichment of the IGM at high redshift. Constraining the initial mass function (IMF) of primordial stars is the key to u ...
The Sky Tonight - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Alpha Centauri, which is 4.3 light years away or 25,278,000,000,000 miles away! Meteor: A small rock, pebble or piece of dust that falls to Earth and burns or vaporizes due to friction with Earth's atmosphere. Floating around in space, its called a meteoroid; in the atmosphere, its called a meteor; ...
... Alpha Centauri, which is 4.3 light years away or 25,278,000,000,000 miles away! Meteor: A small rock, pebble or piece of dust that falls to Earth and burns or vaporizes due to friction with Earth's atmosphere. Floating around in space, its called a meteoroid; in the atmosphere, its called a meteor; ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
Document
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
... D • A is incorrect because star A has a negative apparent magnitude, which means it is a brighter star. • B is incorrect because even though star B has a big apparent magnitude, it does not have the biggest apparent magnitude of the stars listed. • C is incorrect because stars that have smaller appa ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... (ghosts!) form a fascinating and complex part of the ongoing process of stellar evolution, energizing and enriching the interstellar medium. Individual objects show a variety of characteristics that do not always track the “standard model.” Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic e ...
... (ghosts!) form a fascinating and complex part of the ongoing process of stellar evolution, energizing and enriching the interstellar medium. Individual objects show a variety of characteristics that do not always track the “standard model.” Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic e ...
Astronomy Activity: The Life-Line of the Stars
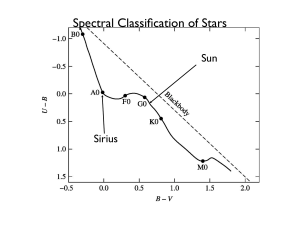
... Just like a fire flame (like a burning match) has different colors, so do the stars. This is because stars have different temperatures. Really hot stars are blue or white-hot. Cool stars are red or redish-orange in color. Astronomers classify stars based on what they are made of (in addition to hydr ...
... Just like a fire flame (like a burning match) has different colors, so do the stars. This is because stars have different temperatures. Really hot stars are blue or white-hot. Cool stars are red or redish-orange in color. Astronomers classify stars based on what they are made of (in addition to hydr ...
Size of the Earth
... This is an easily measurable effect and depends solely on the sharpness of the curvature of the Earth's surface, which is related to the radius of the Earth. This effect, therefore, can be used to measure the size of the Earth. This was realized by an Egyptian astronomer named Eratosthenes about 200 ...
... This is an easily measurable effect and depends solely on the sharpness of the curvature of the Earth's surface, which is related to the radius of the Earth. This effect, therefore, can be used to measure the size of the Earth. This was realized by an Egyptian astronomer named Eratosthenes about 200 ...
ASTR 1010 Homework Solutions
... 34. (a) For an observer at the north pole, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s north pole and the north celestial pole at the top of the diagram. (b) For an observer at the equator, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s poles and the celestial poles at the sides of the diagram, 90° away from the top. (c ...
... 34. (a) For an observer at the north pole, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s north pole and the north celestial pole at the top of the diagram. (b) For an observer at the equator, Figure 2-10 would have the Earth’s poles and the celestial poles at the sides of the diagram, 90° away from the top. (c ...
The Sun
... The Sun is composed of several layers of gases. the core and cooler gases move outward. The part of the Sun usually seen from Earth is the photosphere. The two outermost layers of the Sun, the chromosphere and the corona, are such thin layers of gas that they can only be seen during a total solar ec ...
... The Sun is composed of several layers of gases. the core and cooler gases move outward. The part of the Sun usually seen from Earth is the photosphere. The two outermost layers of the Sun, the chromosphere and the corona, are such thin layers of gas that they can only be seen during a total solar ec ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... from the gravitational collapse of a massive star after a supernova. Neutron star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles ...
... from the gravitational collapse of a massive star after a supernova. Neutron star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles ...
Milky Way inner halo reveals its age | COSMOS magazine
... halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain a ...
... halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain a ...
5-E Galaxy T - McDonald Observatory
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
Lecture 1 - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... These are ultraviolet lines and can only be seen from space by satellite observatories. ...
... These are ultraviolet lines and can only be seen from space by satellite observatories. ...
lecture_1_mbu - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... These are ultraviolet lines and can only be seen from space by satellite observatories. ...
... These are ultraviolet lines and can only be seen from space by satellite observatories. ...
MS 1512–CB58 - Columbia University Department of Astronomy
... 2. Element Abundances As can be seen from Figure 2, the ambient interstellar medium of cB58 is highly enriched in the elements released by Type II supernovae (SN); O, Mg, Si, P and S all have abundances of ∼ 2/5 solar. Thus, even at this relatively early epoch (corresponding to a look-back time of 8 ...
... 2. Element Abundances As can be seen from Figure 2, the ambient interstellar medium of cB58 is highly enriched in the elements released by Type II supernovae (SN); O, Mg, Si, P and S all have abundances of ∼ 2/5 solar. Thus, even at this relatively early epoch (corresponding to a look-back time of 8 ...
Chapter 15
... structure about 1000 light-years across • Some energetic event, perhaps a supernova explosion, violently disturbed the center in the not-to-distant past • Deep within the core lies an incredibly small (10 AU diameter) radio source known as Sgr A* • A 106 M black hole may occupy the very center of t ...
... structure about 1000 light-years across • Some energetic event, perhaps a supernova explosion, violently disturbed the center in the not-to-distant past • Deep within the core lies an incredibly small (10 AU diameter) radio source known as Sgr A* • A 106 M black hole may occupy the very center of t ...
Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... The mass of a neutron star cannot exceed about 3 solar masses. If a core remnant is more massive than that, nothing will stop its collapse, and it will become smaller and smaller and denser and denser. Eventually the gravitational force is so intense that even light cannot escape. The remnant has be ...
... The mass of a neutron star cannot exceed about 3 solar masses. If a core remnant is more massive than that, nothing will stop its collapse, and it will become smaller and smaller and denser and denser. Eventually the gravitational force is so intense that even light cannot escape. The remnant has be ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.