* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
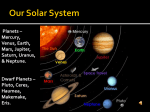
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
The Sun: Our Most Important Star If the Sun did not exist, there would be no life on Earth. The Sun plays vital roles in most of the processes on Earth, as well as in every life on Earth. The Sun provides plants with energy for photosynthesis. It is also the basis for birds’ migration schedules. Sunlight is even the essential ingredient that helps human beings make vitamins that are necessary for healthy bodies. An Interesting Star The Sun is not a planet like Earth; it is a star. At an The Sun is much bigger than the other average distance of 93,000,000 miles away, the objects in the Solar System. Compared to other stars, however, the Sun is merely Sun is Earth’s closest star. This is why the Sun is bigger than other stars in the sky. Studying the Sun average in size. helps people to learn about other stars that are farther away from Earth. The Sun is made up of several layers of gas. The innermost portion of the Sun is the core. The core is approximately 27,000,000 degrees Fahrenheit or 15,000,000 degrees Celsius. This extreme heat causes regular nuclear reactions to take place inside its core. The radiation zone surrounds the core and is a dense layer of gases. This layer is surrounded by a less-dense layer known as the convective zone. The convective zone takes its name from the fact that the gases in this layer constantly move in convection currents. Warm gases move in towards The Sun is composed of several layers of gases. the core and cooler gases move outward. The part of the Sun usually seen from Earth is the photosphere. The two outermost layers of the Sun, the chromosphere and the corona, are such thin layers of gas that they can only be seen during a total solar eclipse. The Sun is almost a perfect sphere, which means it has nearly the same radius when measured in any direction from its center. Much like Earth, the Sun rotates on an axis. The Earth rotates once per day, but the Sun rotates once every 25 days. This slow Discovery Education Science © Discovery Communications, LLC The Sun: Our Most Important Star rotation allows this big ball of gas to maintain its perfect spherical shape. The Mass of the Sun The Sun is by far the biggest object in the Solar System. It measures 875,000 miles wide. The Sun is responsible for 99.8% of the entire mass of the Solar System; it could contain approximately 1.3 million Earths. The Sun may seem big to people, but compared to red giants and other massive stars, the Sun is small. Unraveling the Mystery of the Sun The Sun is much smaller than a red giant, which is what it will eventually become. Up until the 16th century, humans believed that all of the stars, including the Sun, revolved around the Earth. In 1543, Nicolaus Copernicus was the first to theorize that the Sun was the center of the Solar System. His research was based on the movement of the stars in the sky. He was also the first to theorize that the Earth was not stationary. Instead, Copernicus argued that Earth revolves around the Sun. Later astronomers, observing the sky through telescopes, proved Copernicus correct. The Sun: Keeper of Life on Earth The Sun is responsible for many important processes on Earth that are necessary for our survival. Modern telescopes have provided humans with incredible images of the Sun and the processes that happen on its surface and in its atmosphere. Gravity Due to its great mass, the Sun has a strong gravitational pull that keeps Earth in orbit. Without the Sun’s strong pull, Earth would float out into space. Food Plants rely on the Sun for the energy necessary for photosynthesis, a process that allows plants to make their own food. If the Sun didn’t exist, plants could not survive. If plants Discovery Education Science © Discovery Communications, LLC The Sun: Our Most Important Star did not exists, the animals that depend on them for food— including humans—could not survive. Energy Sunlight is the primary source of energy on the planet. The Sun produces solar energy that we use in our daily lives. Fossil fuels, such as natural gas and coal, are made from natural matter whose existence depended on the light and heat from the Sun. Climate Without the heat from the Sun, the Earth would freeze. Heat from the Sun causes differences in air pressure on Earth, which in turn cause the wind and weather to change. Health Sunlight absorbed through the skin is used by humans to make vitamin D, an important vitamin for bone health. The Changing Sun Much like everything else in the Solar System, the Sun is constantly changing. Every eleven years, the Sun goes through a solar cycle, which causes an increase in its magnetic activity. Scientists can see this activity by observing dark spots on the Sun’s surface known as sun spots. Solar flares are explosions on the Sun’s surface. These flares usually occur around active areas, such as sun spots. These explosions can be strong enough to affect certain electronic processes on Earth such as long-range radio communication and radar. The Future of the Sun The Sun has existed for four billion years. Scientists predict that it will continue to burn for approximately another five billion years. The Sun will then begin to die. The first step in this process is to transform into a red giant star. The Sun will swell in size and absorb Mercury, Venus, and Earth. After the red giant phase, the Sun will lose much of its mass and become a nebula. Once the core of the nebula cools, all that will remain of the Sun will be a slowly fading white dwarf star. Since the death of the Sun, and therefore of Earth, is inevitable, scientists have already started to look to the future. Several solar Discovery Education Science © Discovery Communications, LLC The Sun: Our Most Important Star systems have been identified that may have planets similar to Earth which revolve around stars much like our own Sun. Perhaps billions of years from now future humans will look up at the sky from a different planet and observe a different Sun. Discovery Education Science © Discovery Communications, LLC