Starfarer
... the eastern horizon at its own special point and makes an arc across the sky. It does not rise straight up the horizon but at an angle, thus if a star rises at north-east, it will change its bearing while moving across the sky and set at its precise westerly bearing—the north west. Thus a horizon st ...
... the eastern horizon at its own special point and makes an arc across the sky. It does not rise straight up the horizon but at an angle, thus if a star rises at north-east, it will change its bearing while moving across the sky and set at its precise westerly bearing—the north west. Thus a horizon st ...
June 2015 - Bristol Astronomical Society
... changing in brightness as it does so from 3rd to 4th magnitude (see p 25). The Globular Cluster M13 is easily found on the western side of the Hercules "Keystone" asterism, 2.5 degrees south of Eta Herculis (η Her) along a line connecting Eta Herculis (η Her) with Zeta Herculis (ζ Her). When viewed ...
... changing in brightness as it does so from 3rd to 4th magnitude (see p 25). The Globular Cluster M13 is easily found on the western side of the Hercules "Keystone" asterism, 2.5 degrees south of Eta Herculis (η Her) along a line connecting Eta Herculis (η Her) with Zeta Herculis (ζ Her). When viewed ...
Curiosities of the Sky
... vast eddy, or system of eddies, whose vortices appear as dark holes. Only a maelstrom-like motion could keep such a funnel open, for without regard to the impulse derived from the projectile, the proper motions of the stars themselves would tend to fill it. Perhaps some other cause of the whirling m ...
... vast eddy, or system of eddies, whose vortices appear as dark holes. Only a maelstrom-like motion could keep such a funnel open, for without regard to the impulse derived from the projectile, the proper motions of the stars themselves would tend to fill it. Perhaps some other cause of the whirling m ...
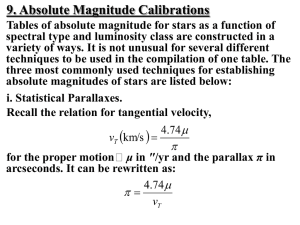
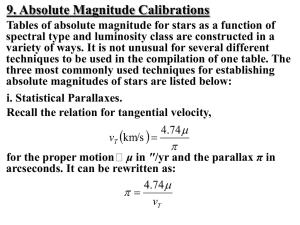
Using Parallax to Measure the Distance of Stars
... distances, with radar being useful nearby (for example, the Moon), and the Hubble Law being useful at the farthest distances. In this exercise, we investigate the use of the trigonometric or measured parallax method to determine distances. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are st ...
... distances, with radar being useful nearby (for example, the Moon), and the Hubble Law being useful at the farthest distances. In this exercise, we investigate the use of the trigonometric or measured parallax method to determine distances. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are st ...
norfolk skies - Norfolk Astronomical Society
... for his gentle, warm manner and for always having a good cup of fresh brewed coffee and snacks available at all the AST events. Scott Justis describes him as one of the nicest amateurs he's ever known. The following article is reprinted from his January 1981 issue of "Between The Stars". On a cold n ...
... for his gentle, warm manner and for always having a good cup of fresh brewed coffee and snacks available at all the AST events. Scott Justis describes him as one of the nicest amateurs he's ever known. The following article is reprinted from his January 1981 issue of "Between The Stars". On a cold n ...
Chap1-Introduction - Groupe d`astrophysique de UdeM
... The frequency of gas giants is strongly correlated with the host star metallicity. • No such correlation for low-mass (< 15 ME) planets. The mass distribution of Super-Earths and Neptune-mass planets (SEN) is strongly increasing between 30 and 15 ME. • Low-mass planets appear to be very common. ...
... The frequency of gas giants is strongly correlated with the host star metallicity. • No such correlation for low-mass (< 15 ME) planets. The mass distribution of Super-Earths and Neptune-mass planets (SEN) is strongly increasing between 30 and 15 ME. • Low-mass planets appear to be very common. ...
astro-ph/9410035 PDF
... parts of the star.2 Both regimes may occur in a real neutron star, depending on its history and on the uncertain properties of neutron star matter. The rst is more likely if a super uid is present (which inhibits reactions by reducing the available phase space, and probably also facilitates relativ ...
... parts of the star.2 Both regimes may occur in a real neutron star, depending on its history and on the uncertain properties of neutron star matter. The rst is more likely if a super uid is present (which inhibits reactions by reducing the available phase space, and probably also facilitates relativ ...
9/28/16 Wednesday Parallax Lab
... The parallax of the pencil depends on the distance the pencil is from you -- the closer the object, the larger the parallax. Thus, although it may have been hard to tell precisely, when the pencil was half the original distance from you, it had twice the parallax; when it was double the original dis ...
... The parallax of the pencil depends on the distance the pencil is from you -- the closer the object, the larger the parallax. Thus, although it may have been hard to tell precisely, when the pencil was half the original distance from you, it had twice the parallax; when it was double the original dis ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... individual evolutionary tracks for stars of different mass change slope as the dominant method of energy escape for the star changes. The evolutionary tracks for massive stars quickly become radiative, following which they trace out tracks of rapidly increasing stellar temperature in the H-R diagram ...
... individual evolutionary tracks for stars of different mass change slope as the dominant method of energy escape for the star changes. The evolutionary tracks for massive stars quickly become radiative, following which they trace out tracks of rapidly increasing stellar temperature in the H-R diagram ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... individual evolutionary tracks for stars of different mass change slope as the dominant method of energy escape for the star changes. The evolutionary tracks for massive stars quickly become radiative, following which they trace out tracks of rapidly increasing stellar temperature in the H-R diagram ...
... individual evolutionary tracks for stars of different mass change slope as the dominant method of energy escape for the star changes. The evolutionary tracks for massive stars quickly become radiative, following which they trace out tracks of rapidly increasing stellar temperature in the H-R diagram ...
CH12.AST1001.F16.EDS
... Mass measurements of main-sequence stars show that the hot, blue stars are much more massive than the cool, red ones. ...
... Mass measurements of main-sequence stars show that the hot, blue stars are much more massive than the cool, red ones. ...
- Cosmotography
... comparing observed star-counts to predicted numbers from a stellar populations model. For the stream, we use the I-band stellar luminosity function near the TRGB, and normalize it to Monte Carlo simulations drawn assuming Z =0.001–0.004, and ages 2–10 Gyr. We obtain M⋆ ∼ (2–5.5)×107 M⊙ for the strea ...
... comparing observed star-counts to predicted numbers from a stellar populations model. For the stream, we use the I-band stellar luminosity function near the TRGB, and normalize it to Monte Carlo simulations drawn assuming Z =0.001–0.004, and ages 2–10 Gyr. We obtain M⋆ ∼ (2–5.5)×107 M⊙ for the strea ...
Chapter 12: Surveying the Stars 12.1 Properties of Stars How do we
... are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores, like the Sun. ...
... are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores, like the Sun. ...
Interpolation of Magnitude.
... Use your feelings Maybe you think it is just a little brighter than midway. Your estimate would be 6.2! A little fainter, your estimate would be 6.3. Don’t try to think what it should be, just go with the ...
... Use your feelings Maybe you think it is just a little brighter than midway. Your estimate would be 6.2! A little fainter, your estimate would be 6.3. Don’t try to think what it should be, just go with the ...
LET THE STARS GET IN YOUR EYES SKY MOTIONS
... constellations requires a constellation chart, a red flashlight and your willingness to explore the sky. A red flashlight is a basic tool of astronomers because it won't ruin your night vision. You can paint your light red, or cover your light with a red filter. Red flashlights can also be purchased ...
... constellations requires a constellation chart, a red flashlight and your willingness to explore the sky. A red flashlight is a basic tool of astronomers because it won't ruin your night vision. You can paint your light red, or cover your light with a red filter. Red flashlights can also be purchased ...
13 – Synthesis of heavier elements
... - Its core shrinks, and the outer layers expand and cool. Its luminosity increases. - Later, its core starts 4He burning called helium flash. - The core expands due to the huge temperature in the core. - The luminosity decreases. - The slower rate of energy production makes the outer layers con ...
... - Its core shrinks, and the outer layers expand and cool. Its luminosity increases. - Later, its core starts 4He burning called helium flash. - The core expands due to the huge temperature in the core. - The luminosity decreases. - The slower rate of energy production makes the outer layers con ...
... Parallax to Barnard’s Star - If we take photographs or images of nearby stars at different times of the year, then the motion of the Earth about the Sun causes our observing location to be different and the nearby stars will show parallax motions. Barnard’s star is one such nearby star. But, in addi ...
Dust and molecular gas in the most distant quasars
... Discussion – star formation in the z~6 quasars • About 30% of the optically selected quasars at z~6 have been detected, and most of the detections show FIR excesses in their SEDs. • The MAMBO undetected quasars at z~6: – The average FIR-to-radio SED is consistent with the templates of local optical ...
... Discussion – star formation in the z~6 quasars • About 30% of the optically selected quasars at z~6 have been detected, and most of the detections show FIR excesses in their SEDs. • The MAMBO undetected quasars at z~6: – The average FIR-to-radio SED is consistent with the templates of local optical ...
November - Hawaiian Astronomical Society
... with access to the Herschel data. But in January, all the data these teams are working on will suddenly be released to the public. So they are all under pressure to finish their work by then. The team whose meeting I was sitting in on would like to publish a paper about the new disks by then. But it ...
... with access to the Herschel data. But in January, all the data these teams are working on will suddenly be released to the public. So they are all under pressure to finish their work by then. The team whose meeting I was sitting in on would like to publish a paper about the new disks by then. But it ...
starwalk2 manual en - Vito Technology Inc.
... Search allows you to find any star, constellation, Solar system body (the planets, the Sun, the Moon), Deep Space object or satellite, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. Information icon appears in middle of the bottom part of the screen when you select any celestial body on the sc ...
... Search allows you to find any star, constellation, Solar system body (the planets, the Sun, the Moon), Deep Space object or satellite, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. Information icon appears in middle of the bottom part of the screen when you select any celestial body on the sc ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... f) The faintest galaxies observed by the Hubble Space Telescope have apparent magnitudes around 30. Suppose these galaxies are ≈ 3 gigaparsecs away (3 × 109 parsecs). Assuming every star in these galaxies emits about the same amount of light as the Sun (a false assumption, but let’s make it just the ...
... f) The faintest galaxies observed by the Hubble Space Telescope have apparent magnitudes around 30. Suppose these galaxies are ≈ 3 gigaparsecs away (3 × 109 parsecs). Assuming every star in these galaxies emits about the same amount of light as the Sun (a false assumption, but let’s make it just the ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.