December - Rose City Astronomers
... The left image is an annotated DSS image showing NGC 4319, NGC 4291 and Markarian 205 in relation to each other. On the right is my processed sketch from the Oregon Star Party showing the same field. Research is unsure exactly what this star-like object is – it’s either a compact companion galaxy or ...
... The left image is an annotated DSS image showing NGC 4319, NGC 4291 and Markarian 205 in relation to each other. On the right is my processed sketch from the Oregon Star Party showing the same field. Research is unsure exactly what this star-like object is – it’s either a compact companion galaxy or ...
File
... Not all electromagnetic radiation coming from space reaches the Earth's surface. The diagram shows how far radiation from each part of the electromagnetic spectrum travels down through the atmosphere. ...
... Not all electromagnetic radiation coming from space reaches the Earth's surface. The diagram shows how far radiation from each part of the electromagnetic spectrum travels down through the atmosphere. ...
Apparent Brightness, Parallax and the Distance to Sirius
... Before people had discovered the phenomenon of parallax they had no idea how far away Sirius is. But suppose they had guessed that Sirius is just like our Sun. They would then have explored the ...
... Before people had discovered the phenomenon of parallax they had no idea how far away Sirius is. But suppose they had guessed that Sirius is just like our Sun. They would then have explored the ...
... the 2001 season, we could not resolve the pair. In 2000, the sky conditions were better and the star could be separated from the blend in all our images. Although noisy, the light curve phased with a period of about 1.15 days is shown in Figure 3. As seen, the star is indeed variable and brighter th ...
12 The Milky Way - Journigan-wiki
... than open clusters. Their populations can range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clus ...
... than open clusters. Their populations can range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clus ...
Apparent Motion of the Stars Worksheet
... State and draw the slant path of rising/setting stars along the eastern/western horizon as seen from any location. [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equato ...
... State and draw the slant path of rising/setting stars along the eastern/western horizon as seen from any location. [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equato ...
Document
... • A protostar forms with a surrounding disk of material (b) • Stellar wind breaks out along the poles of the star (c) • The solar wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of more material and a newly formed star is visible surrounded by a disk (d) ...
... • A protostar forms with a surrounding disk of material (b) • Stellar wind breaks out along the poles of the star (c) • The solar wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of more material and a newly formed star is visible surrounded by a disk (d) ...
sections 7-8 instructor notes
... information equivalent to spectroscopic data in a smaller amount of observing time. It is also a highly efficient method of studying variable stars. Stellar continua vary with spectral type, and different photometric systems are designed to sample selected portions of such continua either for the eq ...
... information equivalent to spectroscopic data in a smaller amount of observing time. It is also a highly efficient method of studying variable stars. Stellar continua vary with spectral type, and different photometric systems are designed to sample selected portions of such continua either for the eq ...
Nebula
... explosions, the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The material thrown off from the supernova explosion is ionised by the supernova remnant. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. It is the result of a recorded supernova in the year 1054 and at the centre of the neb ...
... explosions, the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The material thrown off from the supernova explosion is ionised by the supernova remnant. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula, in Taurus. It is the result of a recorded supernova in the year 1054 and at the centre of the neb ...
dark matter - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... the center and less on the outskirts. Based on this information, where do you expect most of the mass to be located in a galaxy? 2. At right is a picture of a spiral galaxy similar to the Milky Way. The orbits of three stars are labeled. Star A is on the edge of the bulge. The Sun’s orbit is marked ...
... the center and less on the outskirts. Based on this information, where do you expect most of the mass to be located in a galaxy? 2. At right is a picture of a spiral galaxy similar to the Milky Way. The orbits of three stars are labeled. Star A is on the edge of the bulge. The Sun’s orbit is marked ...
Studying the Stars
... Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers for those stars that are brighter than 1st order. ...
... Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers for those stars that are brighter than 1st order. ...
Autoguiding - Thrush Observatory
... no more difficult or complicated than using an off-axis guider if one follows a few simple rules. • The most fundamental mistake is to attempt to mount the guide scope directly to the primary tube. A guide scope is just too heavy and will bend the main tube in all sorts of random ways when in use. • ...
... no more difficult or complicated than using an off-axis guider if one follows a few simple rules. • The most fundamental mistake is to attempt to mount the guide scope directly to the primary tube. A guide scope is just too heavy and will bend the main tube in all sorts of random ways when in use. • ...
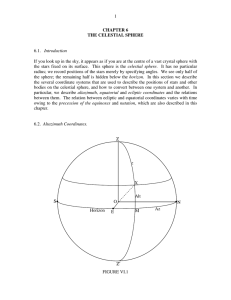
CHAPTER 6 THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... night. Thus we can describe the position of a star on the celestial sphere by the two coordinates δ, its declination, and α, its right ascension, and since its right ascension does not change (at least not very much), we can list the right ascensions as well as the declinations of the stars in our c ...
... night. Thus we can describe the position of a star on the celestial sphere by the two coordinates δ, its declination, and α, its right ascension, and since its right ascension does not change (at least not very much), we can list the right ascensions as well as the declinations of the stars in our c ...
Radiation feedback in star formation simulations
... ● How do supernovae interact with HII regions and clouds? ● How do supernovae interact with HII regions and clouds? ● Can we explain self-regulation of star formation? ● Can we explain self-regulation of star formation? ● Interaction between observational techniques and simulations ● Interaction bet ...
... ● How do supernovae interact with HII regions and clouds? ● How do supernovae interact with HII regions and clouds? ● Can we explain self-regulation of star formation? ● Can we explain self-regulation of star formation? ● Interaction between observational techniques and simulations ● Interaction bet ...
Aspects of Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics - Wiley-VCH
... 1951 that a small equilibrium concentration of unstable 8 Be could capture another α-particle to form stable 12 C and that this “triple-α reaction” could be the main energy source in red giant stars (Salpeter 1952). Hoyle pointed out that the capture probability would be far too small unless an exci ...
... 1951 that a small equilibrium concentration of unstable 8 Be could capture another α-particle to form stable 12 C and that this “triple-α reaction” could be the main energy source in red giant stars (Salpeter 1952). Hoyle pointed out that the capture probability would be far too small unless an exci ...
Chapter16.2
... • Gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser. • Gravity can therefore overcome pressure in smaller pieces of the cloud, causing it to break apart into multiple fragments, each of which may go on to form a star. ...
... • Gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser. • Gravity can therefore overcome pressure in smaller pieces of the cloud, causing it to break apart into multiple fragments, each of which may go on to form a star. ...
KINEMATIC DISCOVERY OF A STELLAR STREAM LOCATED IN
... RGB stars shown in Figure 1, we selected a smaller velocity range of 75 km s−1 < vgsr < 115 km s−1 . We plotted the positions of stars in Galactic coordinates, and noted that many of these velocity-selected giant stars with metallicities between −2.8 < [Fe/H] < −1.8 are concentrated in a small fract ...
... RGB stars shown in Figure 1, we selected a smaller velocity range of 75 km s−1 < vgsr < 115 km s−1 . We plotted the positions of stars in Galactic coordinates, and noted that many of these velocity-selected giant stars with metallicities between −2.8 < [Fe/H] < −1.8 are concentrated in a small fract ...
Exploring the Variable Sky with the Catalina Real-Time
... – Benefits the entire community and maximizes the follow-up and the resulting science – A new “open data” sociology – the shifting focus from the ownership of data to the ownership of expertise ...
... – Benefits the entire community and maximizes the follow-up and the resulting science – A new “open data” sociology – the shifting focus from the ownership of data to the ownership of expertise ...
an Educator`s GuidE
... These exoplanets are very far away, so how do we actually “see” them? Exoplanets are nearly impossible to photograph in the traditional sense, so we have to find them by observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as ei ...
... These exoplanets are very far away, so how do we actually “see” them? Exoplanets are nearly impossible to photograph in the traditional sense, so we have to find them by observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as ei ...
Drawing Constellations
... First star seen as a sphere instead of a point of light by the Hubble Space Telescope on March 3, 1995. 12th brightest star in the sky . Possibly will be the very next supernova in our galaxy. ...
... First star seen as a sphere instead of a point of light by the Hubble Space Telescope on March 3, 1995. 12th brightest star in the sky . Possibly will be the very next supernova in our galaxy. ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.