Compare Star Catalogues - Asteroid Occultation Predictions
... PPMX An expanded and updated version of the PPM catalogue. Referenced to Hipparcos system, but is based on positions from a range of catalogues. It appears to have a high dependency on UCAC2 positions. CMC14. Linked to Hipparcos system. Epoch generally more recent that UCAC. Formal uncertainty in po ...
... PPMX An expanded and updated version of the PPM catalogue. Referenced to Hipparcos system, but is based on positions from a range of catalogues. It appears to have a high dependency on UCAC2 positions. CMC14. Linked to Hipparcos system. Epoch generally more recent that UCAC. Formal uncertainty in po ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... (with contributions of Denis Mourard, Margarida Cunha, Nicolas Nardetto) ...
... (with contributions of Denis Mourard, Margarida Cunha, Nicolas Nardetto) ...
Spinar Paradigm
... event. A spinar can be viewed as an intermediate state of a collapsing object whose lifetime is determined by the time scale of dissipation of the angular momentum. As Lipunova & Lipunov (1998) pointed out, the centrifugal barrier could explain the long (from several seconds to several hours) durati ...
... event. A spinar can be viewed as an intermediate state of a collapsing object whose lifetime is determined by the time scale of dissipation of the angular momentum. As Lipunova & Lipunov (1998) pointed out, the centrifugal barrier could explain the long (from several seconds to several hours) durati ...
Night Photography
... Problem: Capturing star trails in urban areas is impossible with conventional photography because lights and light pollution makes it impossible to take a long enough exposure to capture the motion of the stars Solution: “Image Stacking” ...
... Problem: Capturing star trails in urban areas is impossible with conventional photography because lights and light pollution makes it impossible to take a long enough exposure to capture the motion of the stars Solution: “Image Stacking” ...
Document
... 1.11 & 1.12: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and Review Questions 2, 3, 6, 7, 8 on page 10. 3.1 through 3.3: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and the six Review Questions on page 35. 3.4 through 3.6.2: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and the Review Questions ...
... 1.11 & 1.12: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and Review Questions 2, 3, 6, 7, 8 on page 10. 3.1 through 3.3: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and the six Review Questions on page 35. 3.4 through 3.6.2: Be prepared to discuss the Vocabulary terms and the Review Questions ...
Binary Star Formation Part 2
... producing a binary or a small multiple system 2. Fragmentation of a higher-mass core, leading to formation of a small cluster 3. Fragmentation of a gravitationally unstable disk 4. Fragmentation induced by a cloud–cloud collision ...
... producing a binary or a small multiple system 2. Fragmentation of a higher-mass core, leading to formation of a small cluster 3. Fragmentation of a gravitationally unstable disk 4. Fragmentation induced by a cloud–cloud collision ...
There are 88 constellations in the sky around the Earth. 12 are the
... Noteable doubles are: Zeta Cancri, magnitudes 5.6 & 6.0 (A binary with separation 1 second of arc & a period of 60 years. Larger telescopes reveal it to be a multiple star.) and Iota Cancri, magnitudes 4.3 & 6.3 (Separation 31 seconds of arc) ...
... Noteable doubles are: Zeta Cancri, magnitudes 5.6 & 6.0 (A binary with separation 1 second of arc & a period of 60 years. Larger telescopes reveal it to be a multiple star.) and Iota Cancri, magnitudes 4.3 & 6.3 (Separation 31 seconds of arc) ...
11 - Visual Magnitudes Project
... 11 - Visual Magnitudes Project - Charts, Stars & Magnitudes Perception & the Magnitude Scale The capabilities of the eye far surpass those of the best camera. Your eye is so sensitive it can sense a single photon (packet of light energy) or accommodate the glare of the noonday Sun, some 100 billion ...
... 11 - Visual Magnitudes Project - Charts, Stars & Magnitudes Perception & the Magnitude Scale The capabilities of the eye far surpass those of the best camera. Your eye is so sensitive it can sense a single photon (packet of light energy) or accommodate the glare of the noonday Sun, some 100 billion ...
The Next Great Exoplanet Hunt Please share
... around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones in any given region of the sky, a practical strategy is to monitor a rich field of relatively faint stars. This is precisely what the K ...
... around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones in any given region of the sky, a practical strategy is to monitor a rich field of relatively faint stars. This is precisely what the K ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... an improved fix from two or more LOPs. You can select from amongst the previously acquired observations by checking the associated checkbox. The results are shown in red text in the lower left corner. These include: ...
... an improved fix from two or more LOPs. You can select from amongst the previously acquired observations by checking the associated checkbox. The results are shown in red text in the lower left corner. These include: ...
Module1: Scale of the Universe
... A(100(watt(light(bulb(right(next(to(you(will(appear(very(bright,(whereas(a(100(watt( light(bulb(in(the(next(room(to(you(will(appear(much(fainter.(If(you(know(the(distance(to( the(bulb(and(measure(its(apparent(brightness,(we(can(calculate(is(wattage.(Likewise,(if( you(know(the(wattage(of(the(bulb(and ...
... A(100(watt(light(bulb(right(next(to(you(will(appear(very(bright,(whereas(a(100(watt( light(bulb(in(the(next(room(to(you(will(appear(much(fainter.(If(you(know(the(distance(to( the(bulb(and(measure(its(apparent(brightness,(we(can(calculate(is(wattage.(Likewise,(if( you(know(the(wattage(of(the(bulb(and ...
Star Clusters in Mergers
... which is ~ 30 % closer than our previous estimate (we believe unlikely since peculiar velocity would have to be ~ 500 km/s). ...
... which is ~ 30 % closer than our previous estimate (we believe unlikely since peculiar velocity would have to be ~ 500 km/s). ...
The Young Stars
... Why a disk? The puzzle was to fit a large amount of circumstellar material around a CTTS without obscuring it. If distributed spherically, the young star would not be visible in the optical. It was therefore suggested that it is distributed in a geometrically thin disk. A disk was, in any case, expe ...
... Why a disk? The puzzle was to fit a large amount of circumstellar material around a CTTS without obscuring it. If distributed spherically, the young star would not be visible in the optical. It was therefore suggested that it is distributed in a geometrically thin disk. A disk was, in any case, expe ...
talk
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
Entropy
... because, according to the modern concepts, stars of the same cluster are formed from the same molecular cloud and therefore have the same age (which is relatively easy to determine) and the same composition (e.g., metallicity [Fe/H]). Furthermore, cluster stars are located at the same distance from ...
... because, according to the modern concepts, stars of the same cluster are formed from the same molecular cloud and therefore have the same age (which is relatively easy to determine) and the same composition (e.g., metallicity [Fe/H]). Furthermore, cluster stars are located at the same distance from ...
Chapter 2 | The Vastness of Space
... every 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 04.09074 s. The sun passes the meridian at noon, essentially once every 24-hour day. Stars circle the celestial pole, which is presently near but on exactly at the star Polaris (Figure 1). As discussed later in Chapter 3, the position of the celestial pole changes slo ...
... every 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 04.09074 s. The sun passes the meridian at noon, essentially once every 24-hour day. Stars circle the celestial pole, which is presently near but on exactly at the star Polaris (Figure 1). As discussed later in Chapter 3, the position of the celestial pole changes slo ...
NAS biographical memoir of Martin Schwarzschild
... the progress of a typical star after it contracts out of the interstellar medium and begins to burn its nuclear fuel through a sequence of phases: main sequence (like the sun) to red giant (like our neighbor Arcturus) to degenerate dwarf (like another neighbor, Sirius B). By now there have been innu ...
... the progress of a typical star after it contracts out of the interstellar medium and begins to burn its nuclear fuel through a sequence of phases: main sequence (like the sun) to red giant (like our neighbor Arcturus) to degenerate dwarf (like another neighbor, Sirius B). By now there have been innu ...
Orion – The Hunter - Guild of Students
... The ancient Egyptians are thought to have identified the constellation of Orion with Osiris, their god of the underworld. It is believed that the three pyramids at Giza were built to mirror the three stars of Orion's belt. Osiris was born in Thebes in Upper Egypt, the heavenly mirror-world that the ...
... The ancient Egyptians are thought to have identified the constellation of Orion with Osiris, their god of the underworld. It is believed that the three pyramids at Giza were built to mirror the three stars of Orion's belt. Osiris was born in Thebes in Upper Egypt, the heavenly mirror-world that the ...
PPT presentation
... In addition, some 20 objects of different kinds were found, namely: • Many extended sources, presumably star formation regions at low redshift. Those pose no confusion problem because of their extended nature. • Two point sources bright in the on-band and fainter but visible in the offband. Could be ...
... In addition, some 20 objects of different kinds were found, namely: • Many extended sources, presumably star formation regions at low redshift. Those pose no confusion problem because of their extended nature. • Two point sources bright in the on-band and fainter but visible in the offband. Could be ...
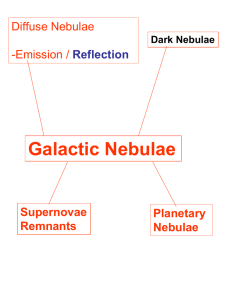
Galactic Nebulae
... Layers of gas expelled from star at end of star`s life Core of star – hot/ bright – uv radiation ionizes ejected layers Ejected layers – radiate at visible wavelengths Planetary nebulae – return elements to interstellar medium ...
... Layers of gas expelled from star at end of star`s life Core of star – hot/ bright – uv radiation ionizes ejected layers Ejected layers – radiate at visible wavelengths Planetary nebulae – return elements to interstellar medium ...
Lithium abundances along the red giant branch: FLAMES
... were rejected. Before averaging the good spectra, small wavelength shifts caused by splitting the individual observations in some cases over a few weeks were corrected. The applied shift agreed with the expected value for the difference in heliocentric correction, and the same shift was found for all ...
... were rejected. Before averaging the good spectra, small wavelength shifts caused by splitting the individual observations in some cases over a few weeks were corrected. The applied shift agreed with the expected value for the difference in heliocentric correction, and the same shift was found for all ...
ABSTRACT XMM-Newton X-Ray Spectroscopy of the B2 Bright Giant
... to thousands of kilometers per second, within a few stellar radii of the surface. The wind of a lORe,) star can be accelerated to its terminal velocity of 2000 km s-l in 10 4 seconds, with about 10 7 photons scattering off each ion per second (Lamers & Cassinelli 1999). It is possible for the wind t ...
... to thousands of kilometers per second, within a few stellar radii of the surface. The wind of a lORe,) star can be accelerated to its terminal velocity of 2000 km s-l in 10 4 seconds, with about 10 7 photons scattering off each ion per second (Lamers & Cassinelli 1999). It is possible for the wind t ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.