5.07 Wind - 94 Newmarket Air Cadet Squadron
... –A sudden increase in wind strength –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
... –A sudden increase in wind strength –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
5.07 Wind
... –A sudden increase in wind strength –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
... –A sudden increase in wind strength –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
Difficult Quiz on Meteorology
... The air flowing around the low pressure center of a large storm rotates a) cyclonically in both hemispheres. b) anti-cyclonically in both hemispheres. c) cyclonically in the northern hemispheres and anti-cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. d) anti-cyclonically in the northern hemisphere and cyc ...
... The air flowing around the low pressure center of a large storm rotates a) cyclonically in both hemispheres. b) anti-cyclonically in both hemispheres. c) cyclonically in the northern hemispheres and anti-cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. d) anti-cyclonically in the northern hemisphere and cyc ...
File
... forward by winds. The result is a current or a stream of water that flows like a river through the ocean. ...
... forward by winds. The result is a current or a stream of water that flows like a river through the ocean. ...
Foehn winds and effect on fire weather: Victorian Case Study File
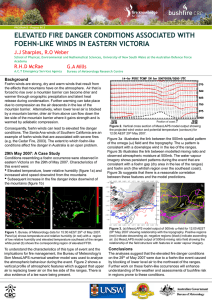
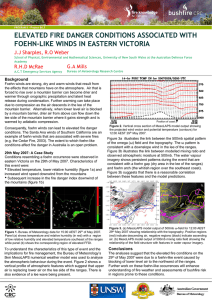
... implications for fire management, the Bureau of Meteorology’s 5km MesoLAPS numerical weather model was used to analyse the atmospheric behaviour during the event. Figure 2 shows a vertical profile of atmospheric features which suggest that upper air is replacing lower air on the lee side of the rang ...
... implications for fire management, the Bureau of Meteorology’s 5km MesoLAPS numerical weather model was used to analyse the atmospheric behaviour during the event. Figure 2 shows a vertical profile of atmospheric features which suggest that upper air is replacing lower air on the lee side of the rang ...
Content Benchmark E
... Planetary wind belts on Earth are a result of unequal heating of Earth, with the largest difference in heating occurring between the equator and the poles. Maximum insolation, also known as incoming solar radiation, occurs where the sun heats Earth’s surface at the equatorial belts causes warm air t ...
... Planetary wind belts on Earth are a result of unequal heating of Earth, with the largest difference in heating occurring between the equator and the poles. Maximum insolation, also known as incoming solar radiation, occurs where the sun heats Earth’s surface at the equatorial belts causes warm air t ...
Content Benchmark E
... Planetary wind belts on Earth are a result of unequal heating of Earth, with the largest difference in heating occurring between the equator and the poles. Maximum insolation, also known as incoming solar radiation, occurs where the sun heats Earth’s surface at the equatorial belts causes warm air t ...
... Planetary wind belts on Earth are a result of unequal heating of Earth, with the largest difference in heating occurring between the equator and the poles. Maximum insolation, also known as incoming solar radiation, occurs where the sun heats Earth’s surface at the equatorial belts causes warm air t ...
Foehn Winds in Eastern Victoria
... implications for fire management, the Bureau of Meteorology’s 5km MesoLAPS numerical weather model was used to analyse the atmospheric behaviour during the event. Figure 2 shows a vertical profile of atmospheric features which suggest that upper air is replacing lower air on the lee side of the rang ...
... implications for fire management, the Bureau of Meteorology’s 5km MesoLAPS numerical weather model was used to analyse the atmospheric behaviour during the event. Figure 2 shows a vertical profile of atmospheric features which suggest that upper air is replacing lower air on the lee side of the rang ...
weather-conduction-convection
... – Where does solar radiation come from? – What happens to solar radiation when it enters Earth’s atmosphere? – How does the Earth naturally keep from overheating? ...
... – Where does solar radiation come from? – What happens to solar radiation when it enters Earth’s atmosphere? – How does the Earth naturally keep from overheating? ...
Document
... Landbreezes and Seabreezes During the day, the land heats up faster than the water. The air over the land has a lower density than the air over the water. Because of this, the air over the land rises. There is now an empty spot over the land, so the air over the water fills it in. That is why the b ...
... Landbreezes and Seabreezes During the day, the land heats up faster than the water. The air over the land has a lower density than the air over the water. Because of this, the air over the land rises. There is now an empty spot over the land, so the air over the water fills it in. That is why the b ...
Chapter 1 - U.S. Coast Guard Auxiliary
... Solar radiation, heat and temperature: The relationship between solar energy and weather. Energy balance in the atmosphere. Temperature and temperature scales. Specific Heat—its definition and importance. Types of energy transfer within and between objects. Global winds and the Corioli ...
... Solar radiation, heat and temperature: The relationship between solar energy and weather. Energy balance in the atmosphere. Temperature and temperature scales. Specific Heat—its definition and importance. Types of energy transfer within and between objects. Global winds and the Corioli ...
TEACHER RESOURCE NETWORK/TEACHER CHANNEL®
... a. The student will know that weather is the effect of the conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. b. The students will know unequal heating of land and water forms wind systems and weather events. Wind is caused by the differences in air pressure, going from an area of high pre ...
... a. The student will know that weather is the effect of the conditions of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. b. The students will know unequal heating of land and water forms wind systems and weather events. Wind is caused by the differences in air pressure, going from an area of high pre ...
Wind-speed maps - Red Lodge Public Schools
... Air pressure depends on the density of the air, or how close together its molecules are. You know that a hard rubber ball is more dense than a Styrofoam ball and that ice cream is more dense that whipped cream. Air lower in the atmosphere is more dense than air above, so air pressure down low is gre ...
... Air pressure depends on the density of the air, or how close together its molecules are. You know that a hard rubber ball is more dense than a Styrofoam ball and that ice cream is more dense that whipped cream. Air lower in the atmosphere is more dense than air above, so air pressure down low is gre ...
Climate
... The angle of _____________________________________________________________ in the course of one day/seasons; ____________________________ intensity occurs at __________________/summer. Angle of ...
... The angle of _____________________________________________________________ in the course of one day/seasons; ____________________________ intensity occurs at __________________/summer. Angle of ...
Thermosphere
... temperature in the mesophere as height increases? decreases 7. Which layer is 70km high? Mesosphere 8. In what layer can the temperature rise to 200C? thermosphere ...
... temperature in the mesophere as height increases? decreases 7. Which layer is 70km high? Mesosphere 8. In what layer can the temperature rise to 200C? thermosphere ...
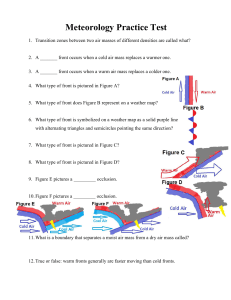
Meteorology Practice Test
... 27. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 28. Name the pressure belt. 29. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 30. Name the pressure belt. 31. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 32. Name the pressure belt. 33. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 34. Name the pressure belt. 35. Name the prevailing wind pattern ...
... 27. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 28. Name the pressure belt. 29. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 30. Name the pressure belt. 31. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 32. Name the pressure belt. 33. Name the prevailing wind pattern. 34. Name the pressure belt. 35. Name the prevailing wind pattern ...
Intro to the Atmosphere
... an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather occurs. The boundary that divides the troposphere from the stratosphere is called the "tropo ...
... an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather occurs. The boundary that divides the troposphere from the stratosphere is called the "tropo ...
File
... so the number of collisions between particles falls. In the atmosphere, however, air pressure approaches a state of equilibrium, so air density drops when the temperature rises. ...
... so the number of collisions between particles falls. In the atmosphere, however, air pressure approaches a state of equilibrium, so air density drops when the temperature rises. ...
Interpret weather conditions in the field - Canoeing WA
... Land generally heats (and cools) faster than the ocean. On a summer day air above the land will become warmer than land over the sea. It therefore expands, and being less dense, will be buoyed upwards by cooler air from the sea: that cooler air flowing in is the sea breeze. Aloft, there will be move ...
... Land generally heats (and cools) faster than the ocean. On a summer day air above the land will become warmer than land over the sea. It therefore expands, and being less dense, will be buoyed upwards by cooler air from the sea: that cooler air flowing in is the sea breeze. Aloft, there will be move ...
Study Guide for Weather Test :(gases, air pressure, layers of
... Terms: Know how to use the vocabulary words. Look at each word on the list. If you would be stumped by it, ask! ...
... Terms: Know how to use the vocabulary words. Look at each word on the list. If you would be stumped by it, ask! ...
1. What are the two most abundant permanent gasses, and roughly
... strongly affected by the greenhouse effect? 27.Do greenhouse gases warm the earth by absorbing sunlight? 28.What are the two most important greenhouse gases on Earth? 29.Why do we expect increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide should lead to "global warming"? 30.Explain why clouds tend to keep t ...
... strongly affected by the greenhouse effect? 27.Do greenhouse gases warm the earth by absorbing sunlight? 28.What are the two most important greenhouse gases on Earth? 29.Why do we expect increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide should lead to "global warming"? 30.Explain why clouds tend to keep t ...
Atmospheric
... What methods are used by meteorologists to measure the change in temperature with height in our atmosphere? ...
... What methods are used by meteorologists to measure the change in temperature with height in our atmosphere? ...
Meteorology Unit Study Guide
... 32. Meteorologists classify air masses according to the general temperature and moisture of the region where they form. The terms ‘maritime’ and ‘continental’ refer to the amount of moisture in the region while the terms ‘arctic’ and ‘tropical’ refer to the general temperature of the region. The map ...
... 32. Meteorologists classify air masses according to the general temperature and moisture of the region where they form. The terms ‘maritime’ and ‘continental’ refer to the amount of moisture in the region while the terms ‘arctic’ and ‘tropical’ refer to the general temperature of the region. The map ...
Atmospheric circulation

Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air, and the means (together with the smaller ocean circulation) by which thermal energy is distributed on the surface of the Earth.The large-scale structure of the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic climatological structure remains fairly constant. Individual weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur ""randomly"", and it is accepted that weather cannot be predicted beyond a fairly short limit: perhaps a month in theory, or (currently) about ten days in practice (see Chaos theory and Butterfly effect). Nonetheless, as the climate is the average of these systems and patterns – where and when they tend to occur again and again – it is stable over longer periods of time.As a rule, the ""cells"" of Earth's atmosphere shift polewards in warmer climates (e.g. interglacials compared to glacials), but remain largely constant even due to continental drift; they are, fundamentally, a property of the Earth's size, rotation rate, heating and atmospheric depth, all of which change little. However, a tectonic uplift can significantly alter their major elements, for example, the jet stream, and plate tectonics may shift ocean currents. In the extremely hot climates of the Mesozoic, indications of a third desert belt at the Equator has been found; it was perhaps caused by convection. But even then, the overall latitudinal pattern of Earth's climate was not much different from the one today.