Chapter 12-Meteorology
... 3. The second wind system, the prevailing westerly, flows between 30 degrees and 60 degrees north and south latitude in a circulation pattern opposite that of the trade winds. ...
... 3. The second wind system, the prevailing westerly, flows between 30 degrees and 60 degrees north and south latitude in a circulation pattern opposite that of the trade winds. ...
ES17-Meteorology and Weather Mapping
... Earth Science 12: Water Cycle - This module presents a game that explains how water cycles through different forms and storage types on Earth and in Earth’s atmosphere. Students act as water molecules and move around the room to the different places water is found on Earth. Earth Science 16: Weather ...
... Earth Science 12: Water Cycle - This module presents a game that explains how water cycles through different forms and storage types on Earth and in Earth’s atmosphere. Students act as water molecules and move around the room to the different places water is found on Earth. Earth Science 16: Weather ...
Meteorologist_applicationassignment
... scientific principles to explain, understand, observe or forecast the earth's atmospheric phenomena. ...
... scientific principles to explain, understand, observe or forecast the earth's atmospheric phenomena. ...
Worksheet 2
... northeast to southwest in the northern hemisphere and from southeast to northwest in the southern hemisphere. When the air reaches the equator, it rises, then moves back toward 30O to start the cycle again. These winds from both hemispheres converge at the equator. They are forced upward, creating a ...
... northeast to southwest in the northern hemisphere and from southeast to northwest in the southern hemisphere. When the air reaches the equator, it rises, then moves back toward 30O to start the cycle again. These winds from both hemispheres converge at the equator. They are forced upward, creating a ...
Understanding Weather Maps - University of Alaska Fairbanks
... • Sea level pressure (SLP) can range from 925mb for a deep low to 1050mb for a big high • World records are even more extreme • SLP values are more extreme at higher laLtudes than at ...
... • Sea level pressure (SLP) can range from 925mb for a deep low to 1050mb for a big high • World records are even more extreme • SLP values are more extreme at higher laLtudes than at ...
Historical Survey - Atmospheric Sciences
... • During the first half of the nineteenth century several competing theories of the origin and development of midlatitude storms were proposed: – the linear two-current theory of Heinrich Dove – the centrifugal theory of William Redfield – the thermal or convective hypothesis of James Espy. ...
... • During the first half of the nineteenth century several competing theories of the origin and development of midlatitude storms were proposed: – the linear two-current theory of Heinrich Dove – the centrifugal theory of William Redfield – the thermal or convective hypothesis of James Espy. ...
AMOSSG/2 — SN No. 3 - 1 - AMOSSG/2 — SN No.3 23/01/01
... included in Annex 3. Particular attention should be paid to two specific issues listed under a) and b) above. ...
... included in Annex 3. Particular attention should be paid to two specific issues listed under a) and b) above. ...
US Air Force
... comptroller, inquiries and investigation, history office, information management, personnel, manpower and organization, and process improvement all fall in their functional area. Air Force global weather central (AFGWC), located at Offutt AFB, NE, maintains the world's most comprehensive weather dat ...
... comptroller, inquiries and investigation, history office, information management, personnel, manpower and organization, and process improvement all fall in their functional area. Air Force global weather central (AFGWC), located at Offutt AFB, NE, maintains the world's most comprehensive weather dat ...
Climate and Meteorology 03: Meteorology
... Why is predicting the weather important? Why is accuracy in predicting the weather important? Are weather predictions ...
... Why is predicting the weather important? Why is accuracy in predicting the weather important? Are weather predictions ...
A Mesoscale Tour of the Pacific Northwest
... • During the first half of the nineteenth century several competing theories of the origin and development of midlatitude storms were proposed: – the linear two-current theory of Heinrich Dove – the centrifugal theory of William Redfield – the thermal or convective hypothesis of James Espy. ...
... • During the first half of the nineteenth century several competing theories of the origin and development of midlatitude storms were proposed: – the linear two-current theory of Heinrich Dove – the centrifugal theory of William Redfield – the thermal or convective hypothesis of James Espy. ...
Weather Forecasting
... same direction and at approximately the same speed as they have been moving. • Analogue Forecast: The future will be like weather that historically occurred when similar conditions were present. • Statistical Forecast: Made routinely of weather elements based on the past performance of computer mo ...
... same direction and at approximately the same speed as they have been moving. • Analogue Forecast: The future will be like weather that historically occurred when similar conditions were present. • Statistical Forecast: Made routinely of weather elements based on the past performance of computer mo ...
TRIP PREPERATION
... Individually you will be required to record observations and reflections. The processing of this experience is a powerful way to accelerate learning. You will be required to make daily recordings in your trip journals. ...
... Individually you will be required to record observations and reflections. The processing of this experience is a powerful way to accelerate learning. You will be required to make daily recordings in your trip journals. ...
Outgassing from Volcanoes Layers of the Atmosphere
... Students know water vapor in the air moves from one place to another and can form fog or clouds, which are tiny droplets of water or ice, and can fall to Earth as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. ...
... Students know water vapor in the air moves from one place to another and can form fog or clouds, which are tiny droplets of water or ice, and can fall to Earth as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. ...
Y7GeU2B Weather typesPP Wk4
... the maximum and the minimum and be able to find the daily range (the difference between the 2) or the diurnal range. ...
... the maximum and the minimum and be able to find the daily range (the difference between the 2) or the diurnal range. ...
The Earth and Its Atmosphere
... the atmosphere; caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth. Water is the only substance that can be found naturally in the atmosphere in its ...
... the atmosphere; caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth. Water is the only substance that can be found naturally in the atmosphere in its ...
OMM-Stefanski
... rainfall to maintain vegetative growth favour egg laying within three weeks of fledging. • If the conditions are dry, immature adults can survive upto six months. Hot and dry weather combined with sparse vegetation could lead to death of the adults. ...
... rainfall to maintain vegetative growth favour egg laying within three weeks of fledging. • If the conditions are dry, immature adults can survive upto six months. Hot and dry weather combined with sparse vegetation could lead to death of the adults. ...
MSC APPLIED METEOROLOGY AND CLIMATOLOGY
... The course consists of 120 credits of taught modules and 60 credits of research dissertation modules. Taught modules comprise lectures, practical classes and tutorials and are scheduled in the autumn and spring terms. The majority of the examinations take place in May and early June. The dissertatio ...
... The course consists of 120 credits of taught modules and 60 credits of research dissertation modules. Taught modules comprise lectures, practical classes and tutorials and are scheduled in the autumn and spring terms. The majority of the examinations take place in May and early June. The dissertatio ...
Weather and Climate Notes
... Weather also includes temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind, etc. We base our day to day activities on weather. Weather can change quickly but follows predictable patterns. Climate is the average conditions for an area over a period of time. This can be over a season or over a number of years. T ...
... Weather also includes temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind, etc. We base our day to day activities on weather. Weather can change quickly but follows predictable patterns. Climate is the average conditions for an area over a period of time. This can be over a season or over a number of years. T ...
Marine Systems
... representation. Our overall quality goal is to develop, produce and market products and services of such a quality that we aim to exceed our customers expectations. We see our activities and products as an expression of our quality. To reach a level of total quality it is necessary to establish an ...
... representation. Our overall quality goal is to develop, produce and market products and services of such a quality that we aim to exceed our customers expectations. We see our activities and products as an expression of our quality. To reach a level of total quality it is necessary to establish an ...
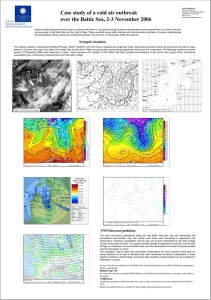
Case study of a cold air outbreak over the Baltic Sea, 2-3
... precipitation accumulation near the Latvian west coast were forecasted in agreement with observations. However, precipitation amount was not so good forecasted for the Gulf of Riga and the central part of Latvia. Convective activities along the trajectories of cold air over the Gulf of Riga in compa ...
... precipitation accumulation near the Latvian west coast were forecasted in agreement with observations. However, precipitation amount was not so good forecasted for the Gulf of Riga and the central part of Latvia. Convective activities along the trajectories of cold air over the Gulf of Riga in compa ...
Climate and Weather
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
... – Know your vessel – tolerances and procedures – Bad weather – factor in fatigue / seas sickness ...
... – Know your vessel – tolerances and procedures – Bad weather – factor in fatigue / seas sickness ...
Weather
... We have talked about broad scale climate patterns and introduced some of the factors driving them, now we move to localised weather patterns where broad scale synoptic systems are influenced by local topographic features and human developments. We are also interested in day to day variation as well ...
... We have talked about broad scale climate patterns and introduced some of the factors driving them, now we move to localised weather patterns where broad scale synoptic systems are influenced by local topographic features and human developments. We are also interested in day to day variation as well ...
4th Grade Weather Read and answer each question carefully. 1
... A) The air pressure is less on Mt. Lemmon than in Tucson. B) There is no measurable air pressure on Mt. Lemmon. C) There is no difference in air pressure between Mt. Lemmon and Tucson. D) The air pressure is greater on Mt. Lemmon than in Tucson. ...
... A) The air pressure is less on Mt. Lemmon than in Tucson. B) There is no measurable air pressure on Mt. Lemmon. C) There is no difference in air pressure between Mt. Lemmon and Tucson. D) The air pressure is greater on Mt. Lemmon than in Tucson. ...
Marine weather forecasting

Marine weather forecasting is the process by which mariners and meteorological organizations have attempted to forecast future weather conditions over the Earth's oceans. Mariners have had rules of thumb regarding the navigation around tropical cyclones for many years, dividing a storm into halves and sailing through the normally weaker and more navigable half of their circulation. Marine weather forecasts by various weather organizations can be traced back to the sinking of the Royal Charter in 1859 and the RMS Titanic in 1912.The wind is the driving force of weather at sea, as wind generates local wind waves, long ocean swells, and its flow around the subtropical ridge helps maintain warm water currents such as the Gulf Stream. The importance of weather over the ocean during World War II led to delayed or secret weather reports, in order to maintain a competitive advantage. Weather ships were established by various nations during World War II for forecasting purposes, and were maintained through 1985 to help with transoceanic plane navigation.Voluntary observations from ships, weather buoys, weather satellites, and numerical weather prediction have been used to diagnose and help forecast weather over the Earth's ocean areas. Since the 1960s, numerical weather prediction's role over the Earth's seas has taken a greater role in the forecast process. Weather elements such as sea state, surface winds, tide levels, and sea surface temperature are tackled by organizations tasked with forecasting weather over open oceans and seas. Currently, the Japan Meteorological Agency, the United States National Weather Service, and the United Kingdom Met Office create marine weather forecasts for the Northern Hemisphere.