4.1 Classical Thermodynamics: The First Law
... James Joule carried out some ingenious experiments into the nature of work and heat transfer in materials in the 1840s. In his most famous experiment, Joule filled a container with a fluid and used a rotating paddle wheel, driven by falling weights, to stir the water. The container was thermally ins ...
... James Joule carried out some ingenious experiments into the nature of work and heat transfer in materials in the 1840s. In his most famous experiment, Joule filled a container with a fluid and used a rotating paddle wheel, driven by falling weights, to stir the water. The container was thermally ins ...
Potential Energy
... The second form of potential energy that we will discuss is elastic potential energy. Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in elastic materials as the result of their stretching or compressing. Elastic potential energy can be stored in rubber bands, bungee cords, trampolines, springs, an ar ...
... The second form of potential energy that we will discuss is elastic potential energy. Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in elastic materials as the result of their stretching or compressing. Elastic potential energy can be stored in rubber bands, bungee cords, trampolines, springs, an ar ...
Unit 9: Energy, Work, and Power
... described as ____. A. Thermal B. Chemical C. Nuclear D. Kinetic ...
... described as ____. A. Thermal B. Chemical C. Nuclear D. Kinetic ...
Forces Motion and Energy
... Electrical generators convert chemical energy in fossil fuels to electrical energy. Fuels are burned to create thermal energy. The thermal energy is converted to kinetic energy when steam pushes against turbine blades. The turbine spins a generator which converts kinetic energy into electrical energ ...
... Electrical generators convert chemical energy in fossil fuels to electrical energy. Fuels are burned to create thermal energy. The thermal energy is converted to kinetic energy when steam pushes against turbine blades. The turbine spins a generator which converts kinetic energy into electrical energ ...
Document
... amount of energy is the same before and after any process. All energy is accounted for. Conserving Energy When you hear or read about conserving energy, don’t get confused with the law of conservation of energy. Conserving energy means saving energy, or not wasting it! ...
... amount of energy is the same before and after any process. All energy is accounted for. Conserving Energy When you hear or read about conserving energy, don’t get confused with the law of conservation of energy. Conserving energy means saving energy, or not wasting it! ...
File
... Spontaneity is independent of time it takes for the process to occur (that is kinetics) ...
... Spontaneity is independent of time it takes for the process to occur (that is kinetics) ...
Chapter 9 Energy and Energy Resources
... What forms can energy take? • Kinetic energy and potential energy are two types of energy that can come in many different forms. • Some common forms of energy include mechanical, sound, electromagnetic, electrical, chemical, thermal, and nuclear energy. • Energy is expressed in joules (J). ...
... What forms can energy take? • Kinetic energy and potential energy are two types of energy that can come in many different forms. • Some common forms of energy include mechanical, sound, electromagnetic, electrical, chemical, thermal, and nuclear energy. • Energy is expressed in joules (J). ...
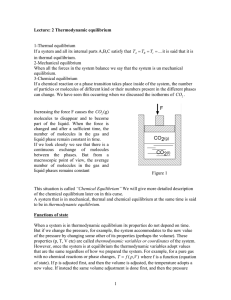
1 Lecture: 2 Thermodynamic equilibrium 1
... conclusions that we arrive at. Extensive use of this is done in the field of thermochemistry which we shall use as an example of application of thermodynamics next class. Some thermodynamic functions do not satisfy these properties, (i.e. they are not analytical, or they are not state functions). Th ...
... conclusions that we arrive at. Extensive use of this is done in the field of thermochemistry which we shall use as an example of application of thermodynamics next class. Some thermodynamic functions do not satisfy these properties, (i.e. they are not analytical, or they are not state functions). Th ...
PHYS 196 Class Problem 1
... 3. Consider three points A,B,C on the x-y plane, where a uniform electric field E 100( N / C )iˆ exists. The coordinates in meters for these points are: A=(4,0), B=(-1,0) and C=(-2,2). Find the potential difference VB VA and VC VA . 4. At the points A and B, the potentials are 1000V and 1500V ...
... 3. Consider three points A,B,C on the x-y plane, where a uniform electric field E 100( N / C )iˆ exists. The coordinates in meters for these points are: A=(4,0), B=(-1,0) and C=(-2,2). Find the potential difference VB VA and VC VA . 4. At the points A and B, the potentials are 1000V and 1500V ...
Energy Resources and Energy Transfer
... The fossil fuels are coal, oil and natural gas. They formed millions of years ago from the remains of living things. Coal was formed from plants, and oil and natural gas from sea creatures. When the living things died, they were gradually buried by layers of rock. The buried remains were put under p ...
... The fossil fuels are coal, oil and natural gas. They formed millions of years ago from the remains of living things. Coal was formed from plants, and oil and natural gas from sea creatures. When the living things died, they were gradually buried by layers of rock. The buried remains were put under p ...
Does the Third Law of Thermodynamics Hold
... First, we examine the calculation of Sv N , which was based on applying the von Neumann formula to the reduced density matrix. But as we pointed out in Ref. 5, for a system with a non-negligible interaction energy, “—the von Neumann formula can only be applied to the entire system and not to the red ...
... First, we examine the calculation of Sv N , which was based on applying the von Neumann formula to the reduced density matrix. But as we pointed out in Ref. 5, for a system with a non-negligible interaction energy, “—the von Neumann formula can only be applied to the entire system and not to the red ...
15-2 Thermodynamic Processes and the First Law
... The process above does not violate the first law of thermodynamics and the law of conservation of energy. Since this process does not occur in nature, the second law of thermodynamics was ...
... The process above does not violate the first law of thermodynamics and the law of conservation of energy. Since this process does not occur in nature, the second law of thermodynamics was ...
CHAPTER 2: Special Theory of Relativity
... 2) The events do not occur at the same space and time coordinates in the two inertial frames To transform time and space coordinates between inertial frames, one needs to use the Lorentz transformation (instead of the Galilean transformations) There is no physical difference between K and K’, proper ...
... 2) The events do not occur at the same space and time coordinates in the two inertial frames To transform time and space coordinates between inertial frames, one needs to use the Lorentz transformation (instead of the Galilean transformations) There is no physical difference between K and K’, proper ...
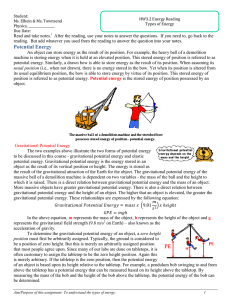
Lecture28_Potential
... Notice the amount of potential energy stored by any charge in a potential V is ...
... Notice the amount of potential energy stored by any charge in a potential V is ...
Overview - RI
... kinetic energy of the substance, where atoms are colliding. Students can recognize that energy is conserved in atomic collisions. In addition, kinetic energy is converted into an excited state in Excited States and Photons. Once atoms are excited, energy can be converted into light (as photons). Pha ...
... kinetic energy of the substance, where atoms are colliding. Students can recognize that energy is conserved in atomic collisions. In addition, kinetic energy is converted into an excited state in Excited States and Photons. Once atoms are excited, energy can be converted into light (as photons). Pha ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.